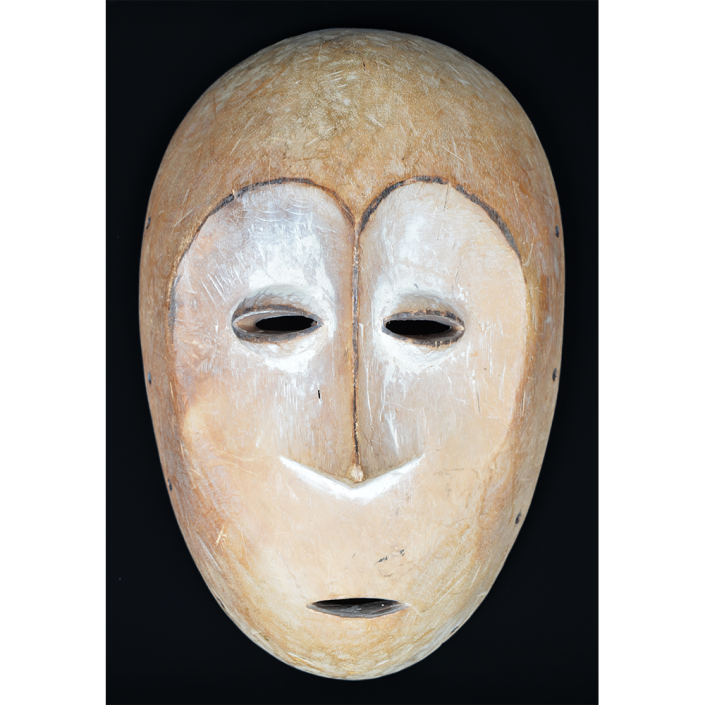
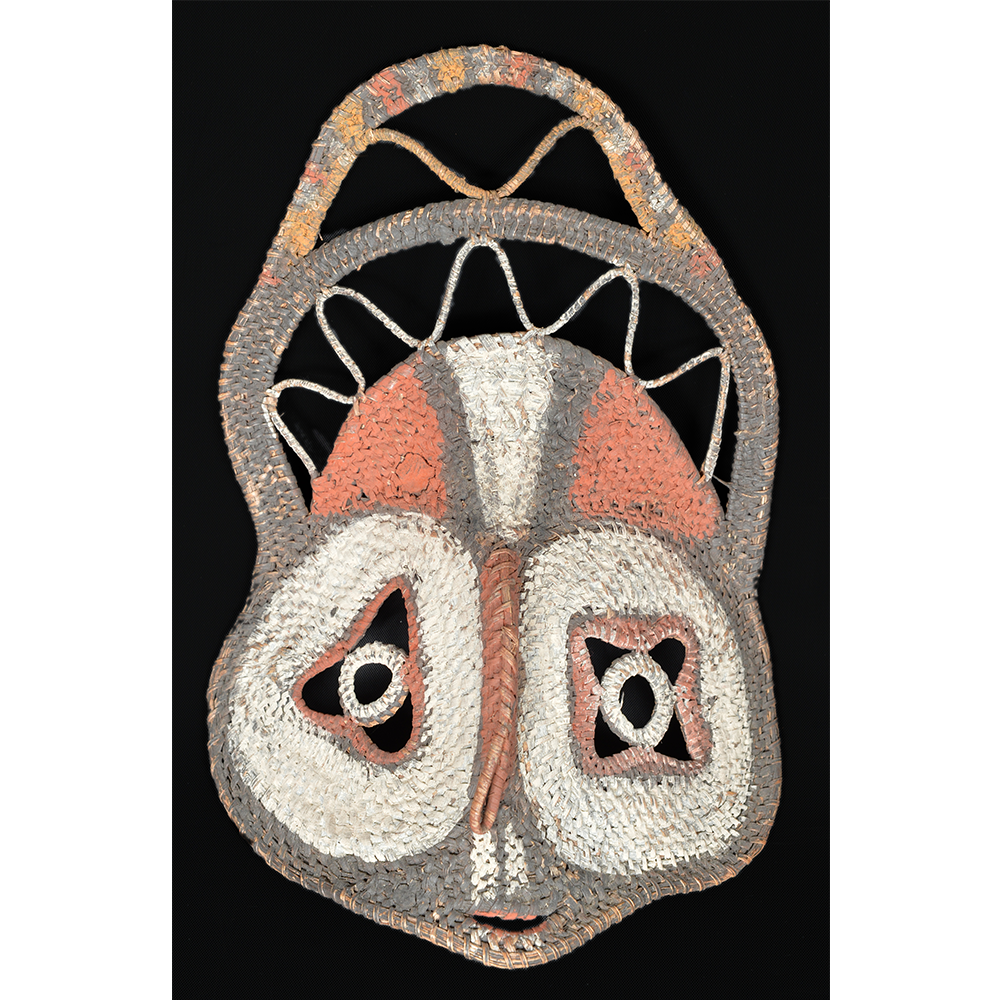
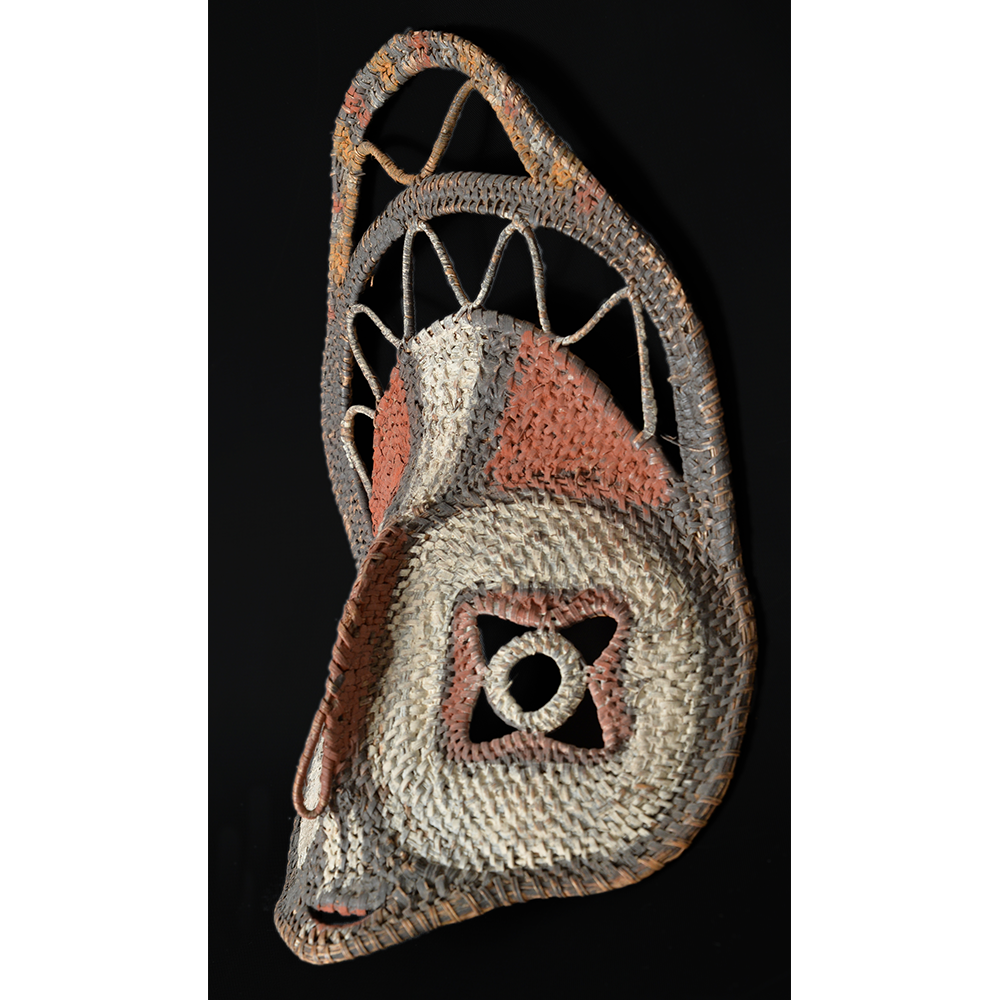
TITLE: Abelam Bapamimi Mask
TYPE: other mask
GENERAL REGION: Oceania
COUNTRY: Papua New Guinea
SUBREGION: East Sepik River
ETHNICITY: Melanesian (Abelam)
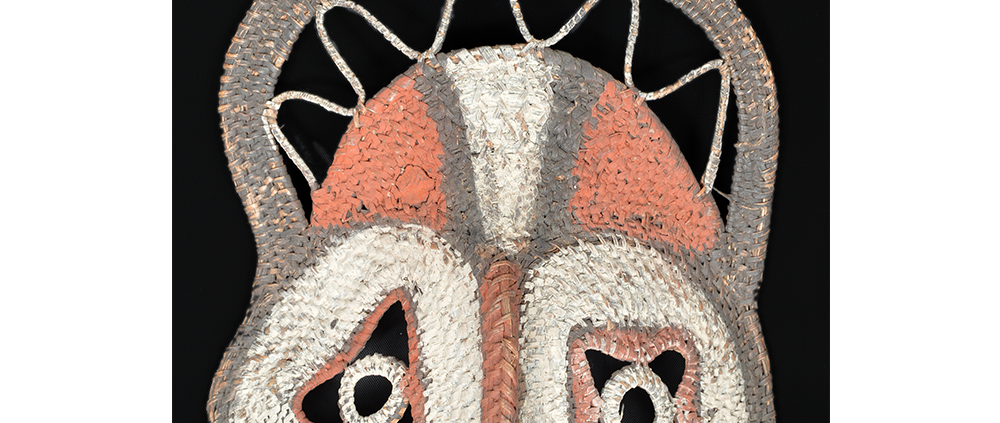
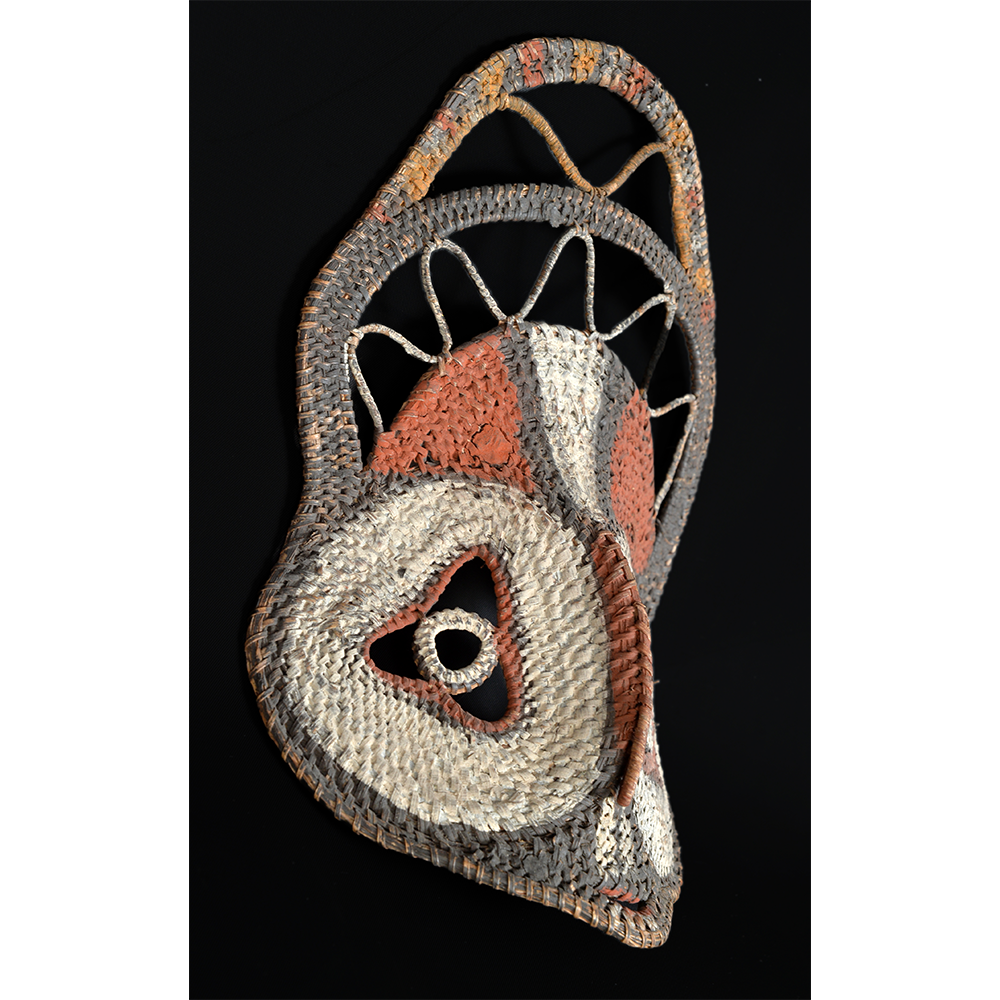
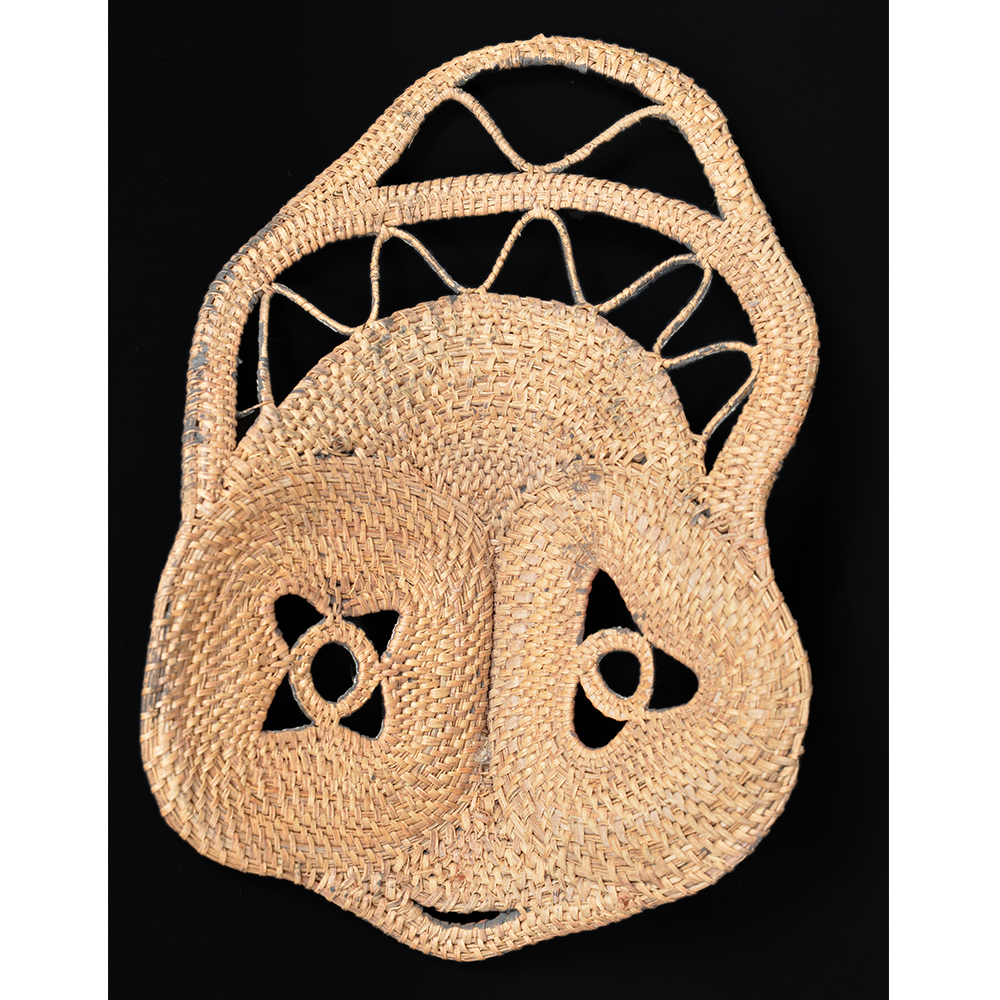
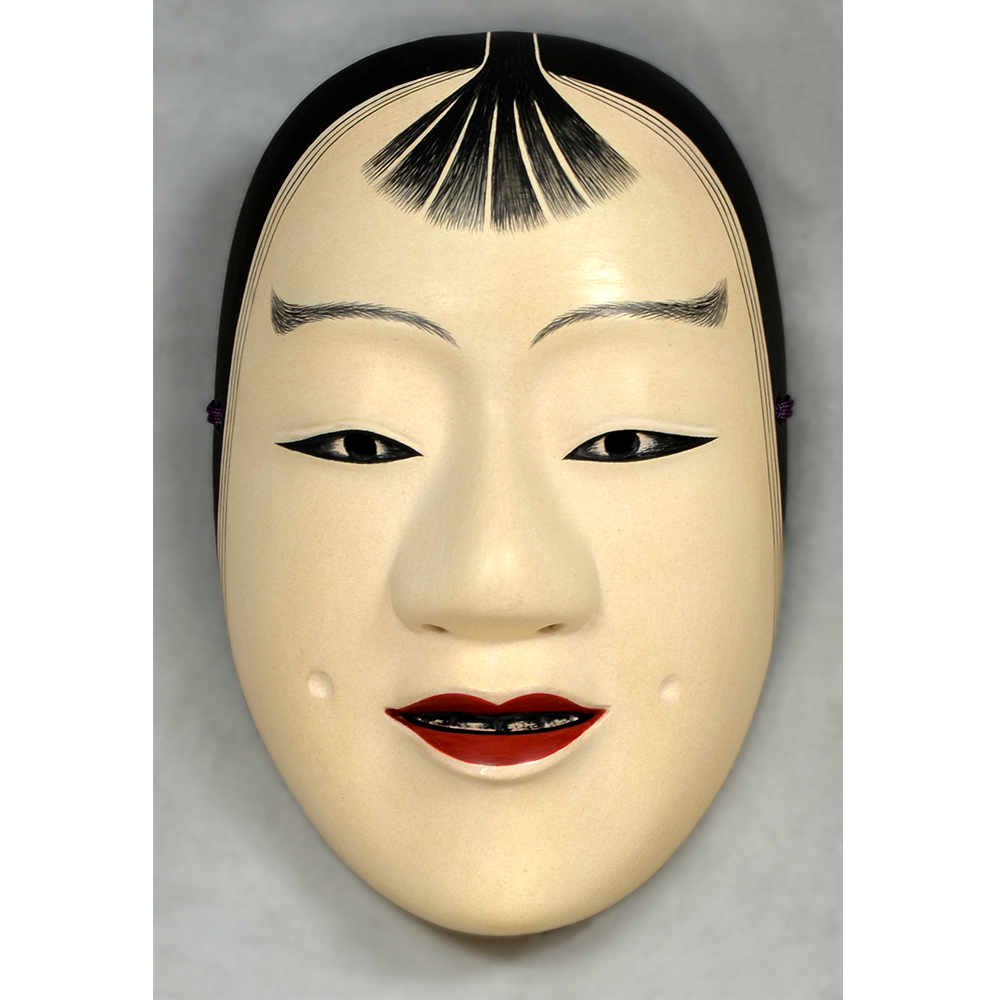
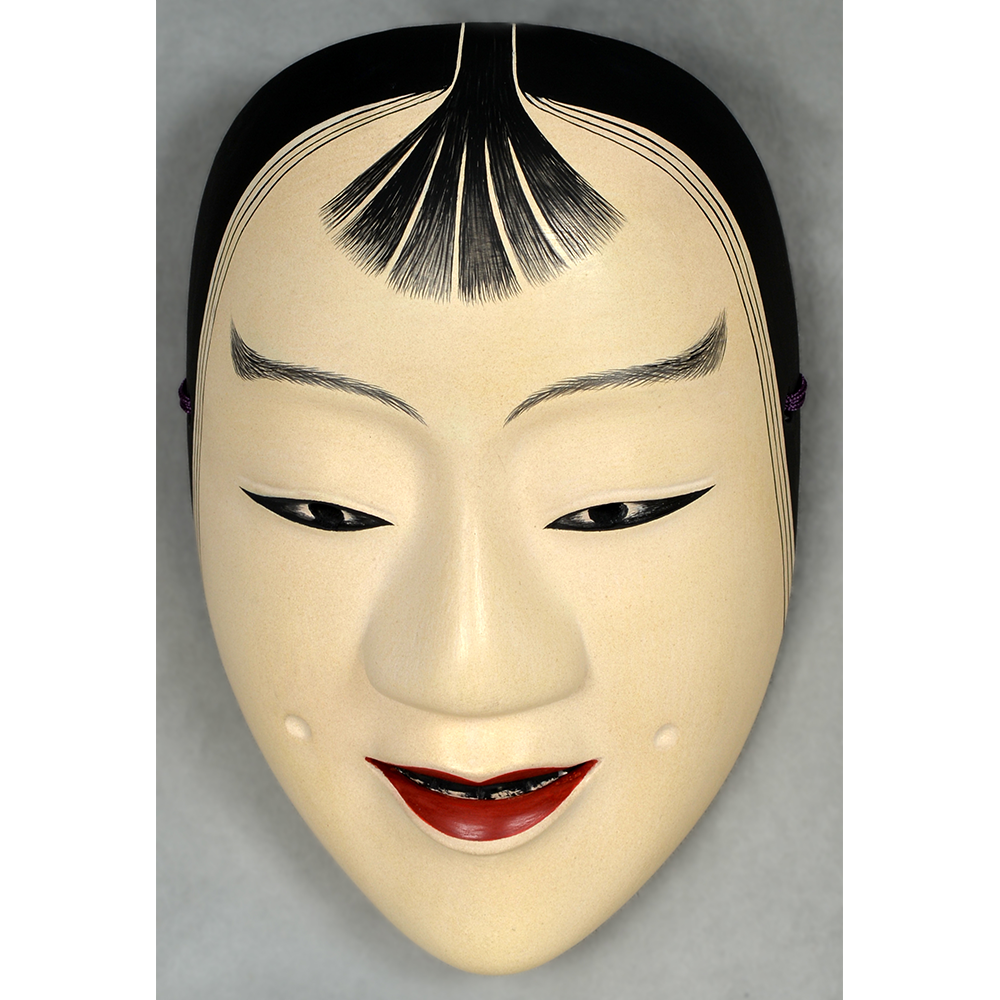
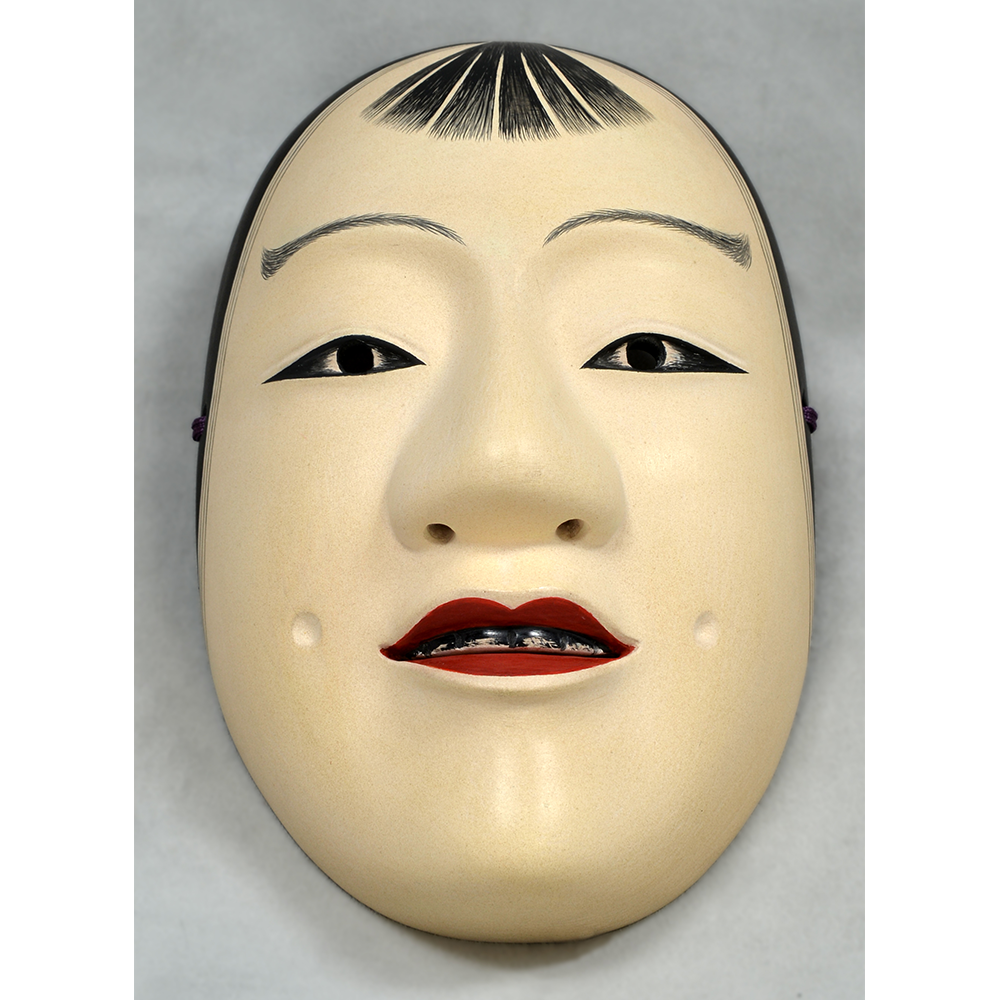
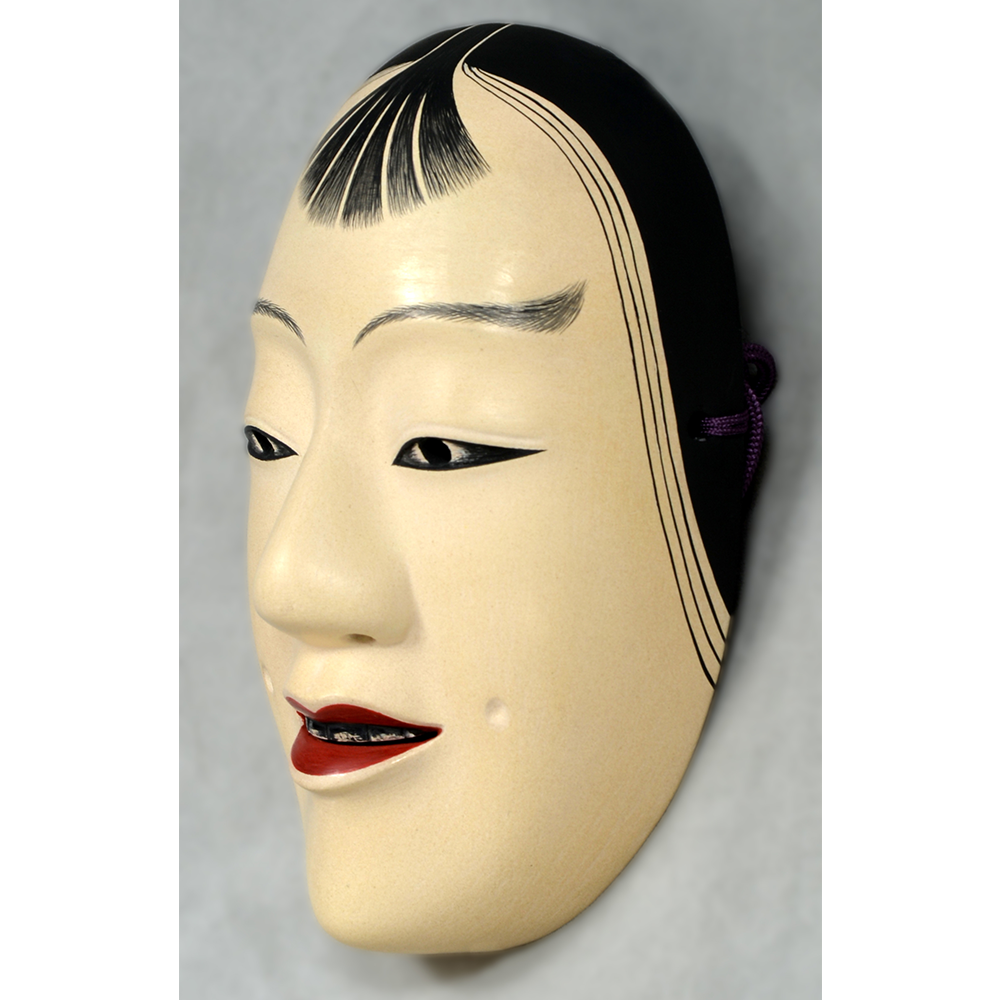
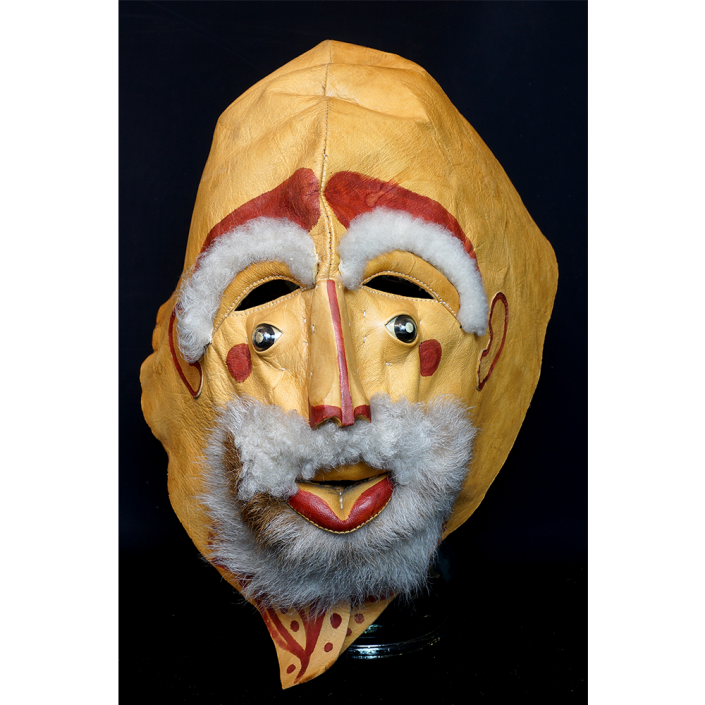
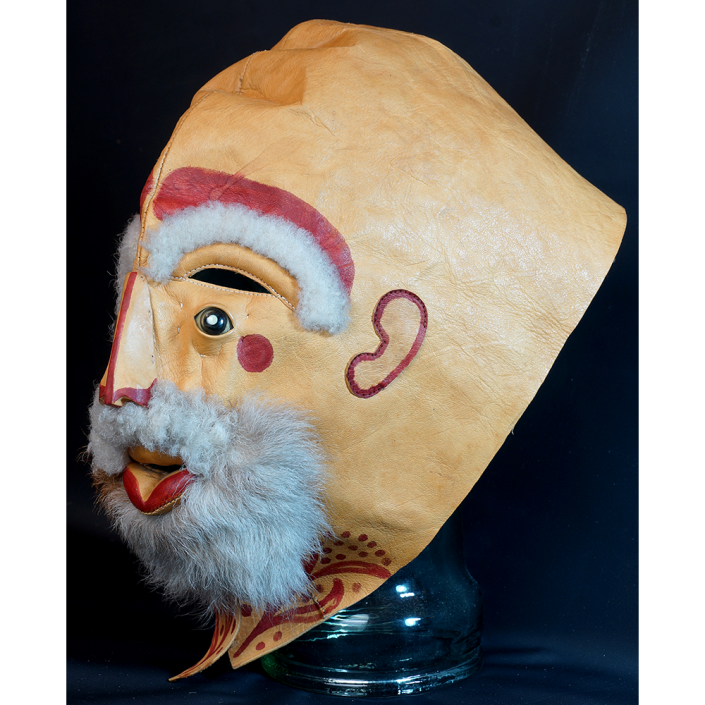
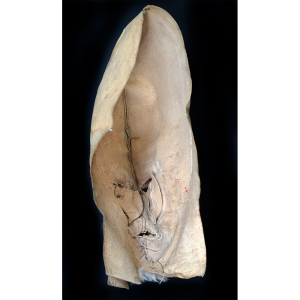
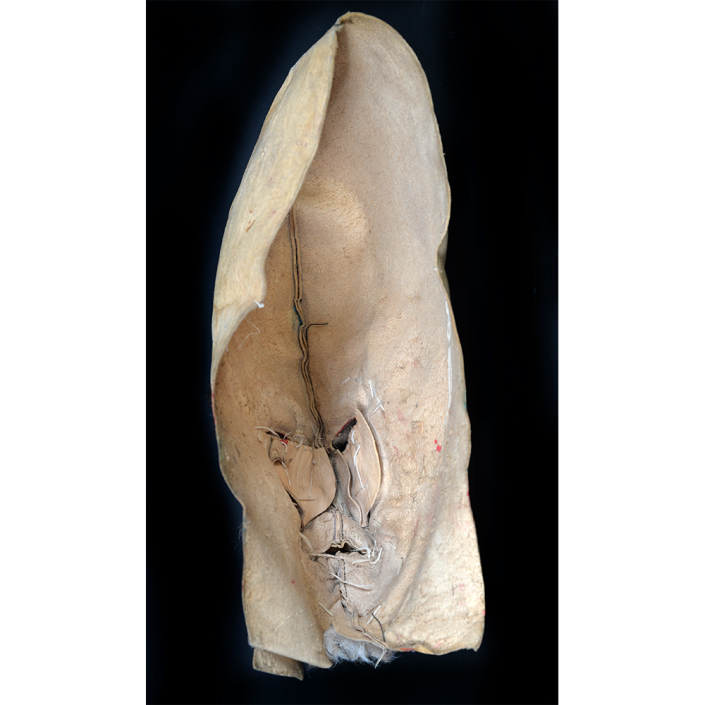
DESCRIPTION: Bapamimi (Yam) Mask
CATALOG ID: OCPG002
MAKER: Unknown
CEREMONY: Wapisaki
FUNCTION: Agriculture
AGE: ca. 1940s
MAIN MATERIAL: woven plant fiber
OTHER MATERIALS: natural pigments
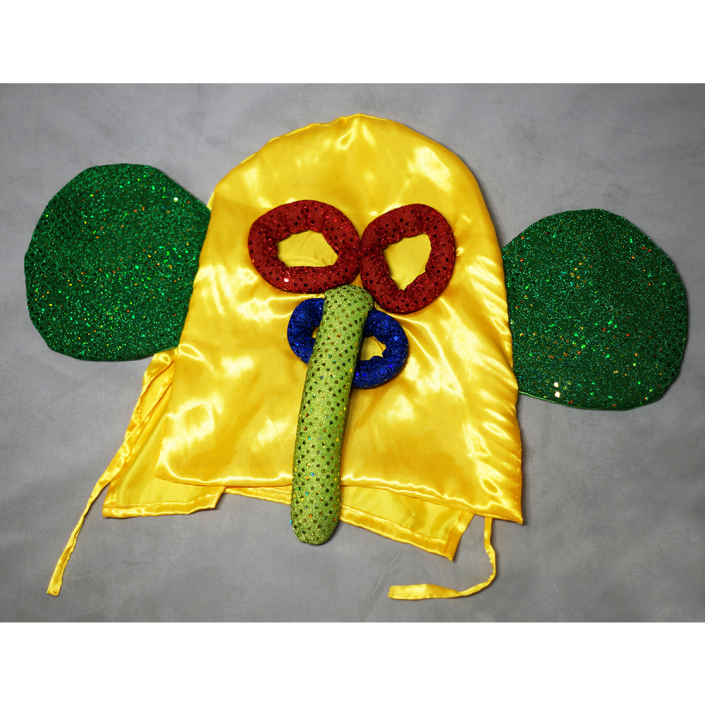
The Abelam people of the Sepik River area of Papua New Guinea use several types of masks, many of them intricately woven of plant fiber. The yam mask (bapamimi) is not worn by the tribe members, but instead is used to decorate giant yams after harvest during the yam festival (wapisaki). Abelam people assemble at a designated village and lines up the yams, which can reach up to three meters long and weigh over 50 kilograms. They decorate them with masks such as this one, flowers, and other regalia. Everyone then discusses the planting, harvesting, the shape and size, and other details of each yam, much in the same way that gardening aficionados in the Canada, Europe, and the United States compare their own vegetables and flowers at prize shows. The largest and best yams confer status on the grower.