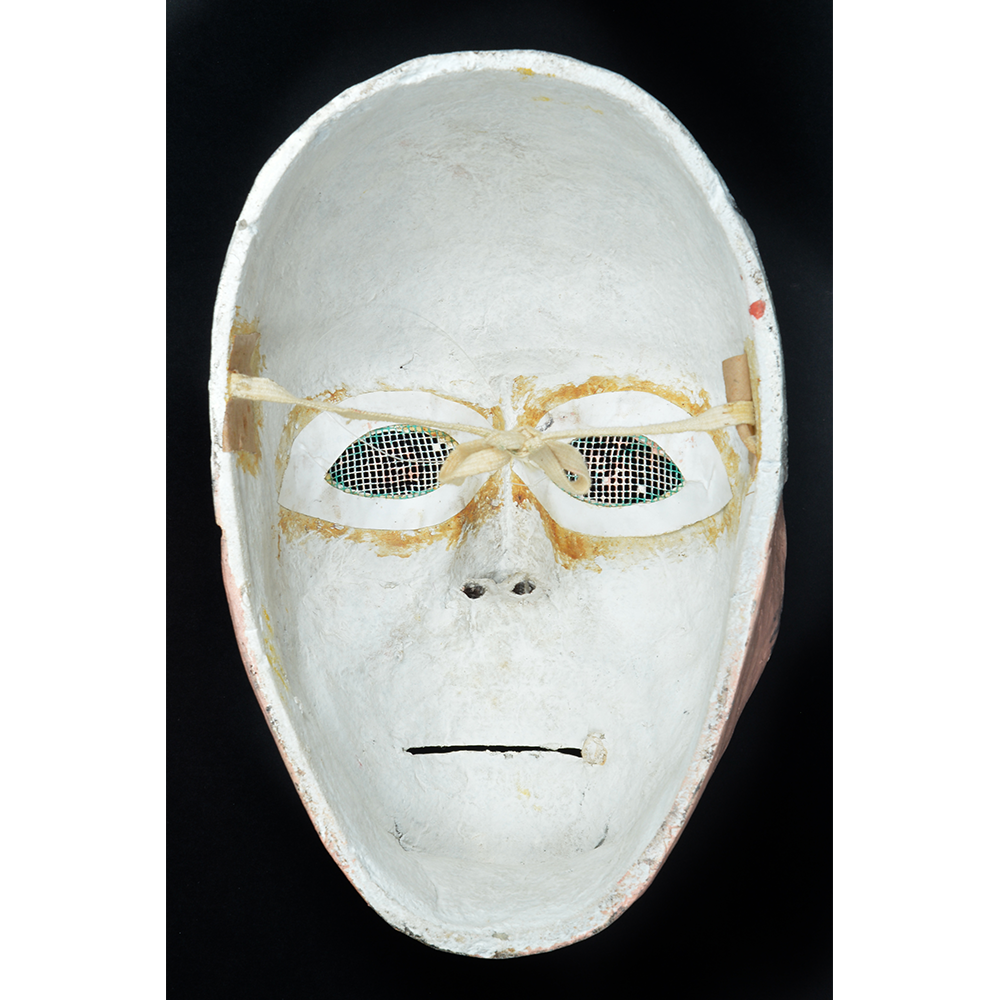
TITLE: Cajun Mardi Gras
TYPE: face mask
GENERAL REGION: North America
COUNTRY: United States of America
SUB-REGION: Acadiana, Louisiana
ETHNICITY: Cajun
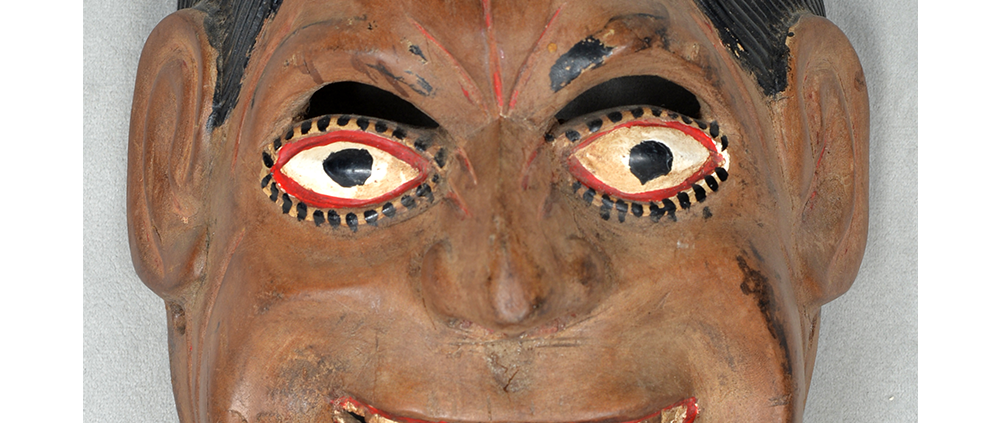
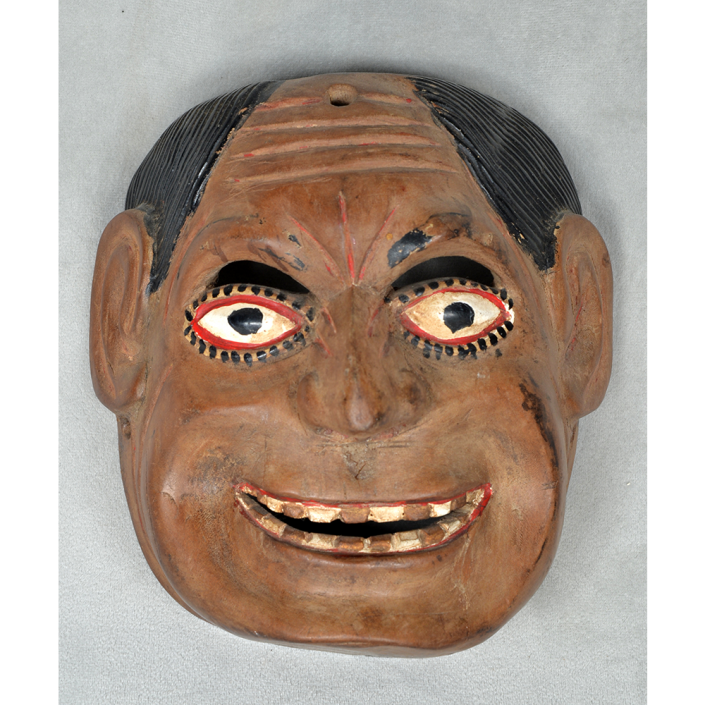
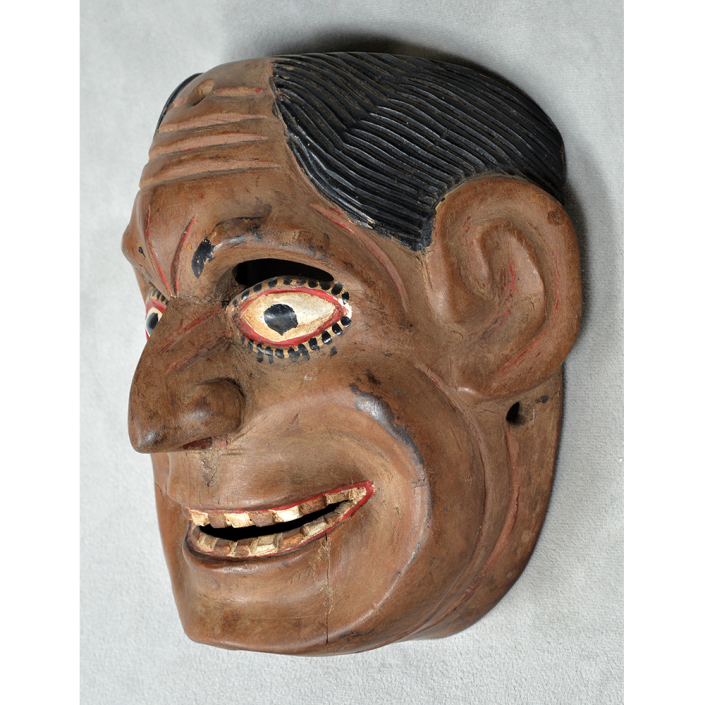
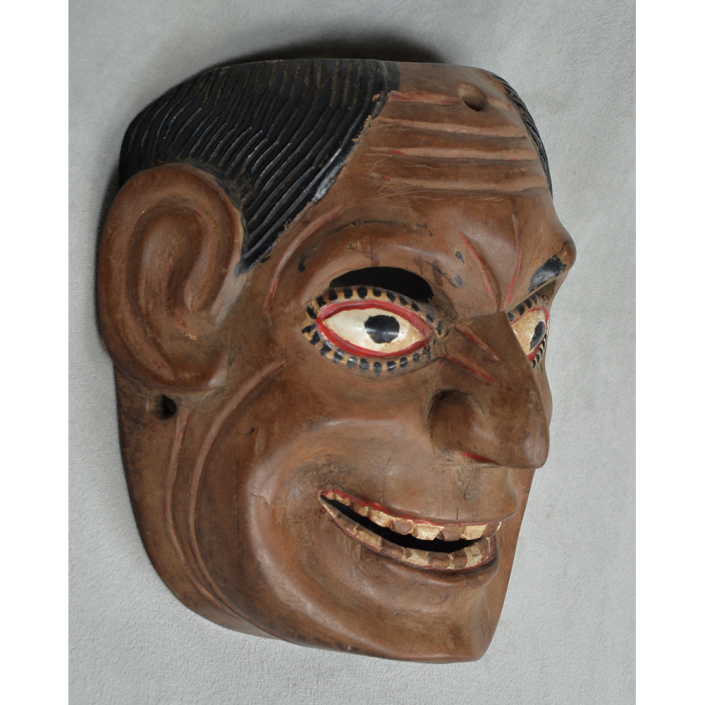
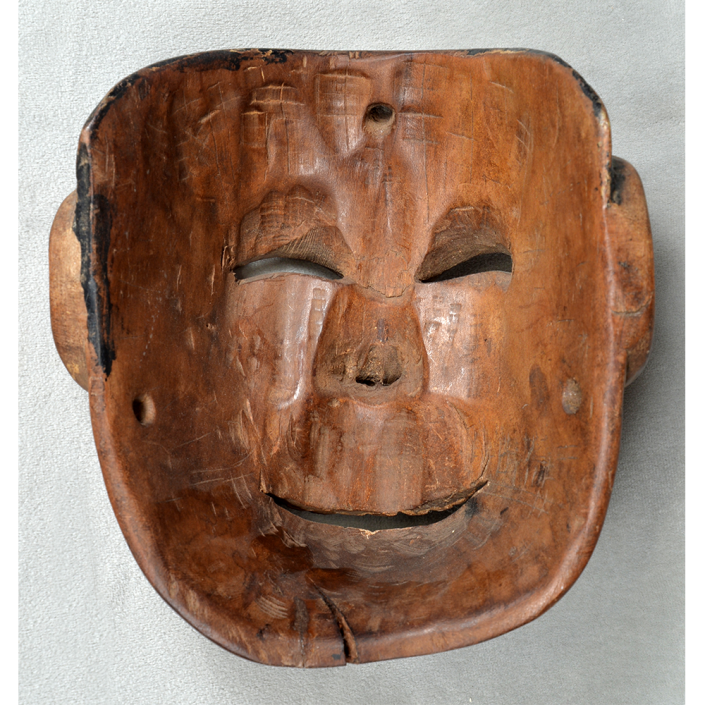
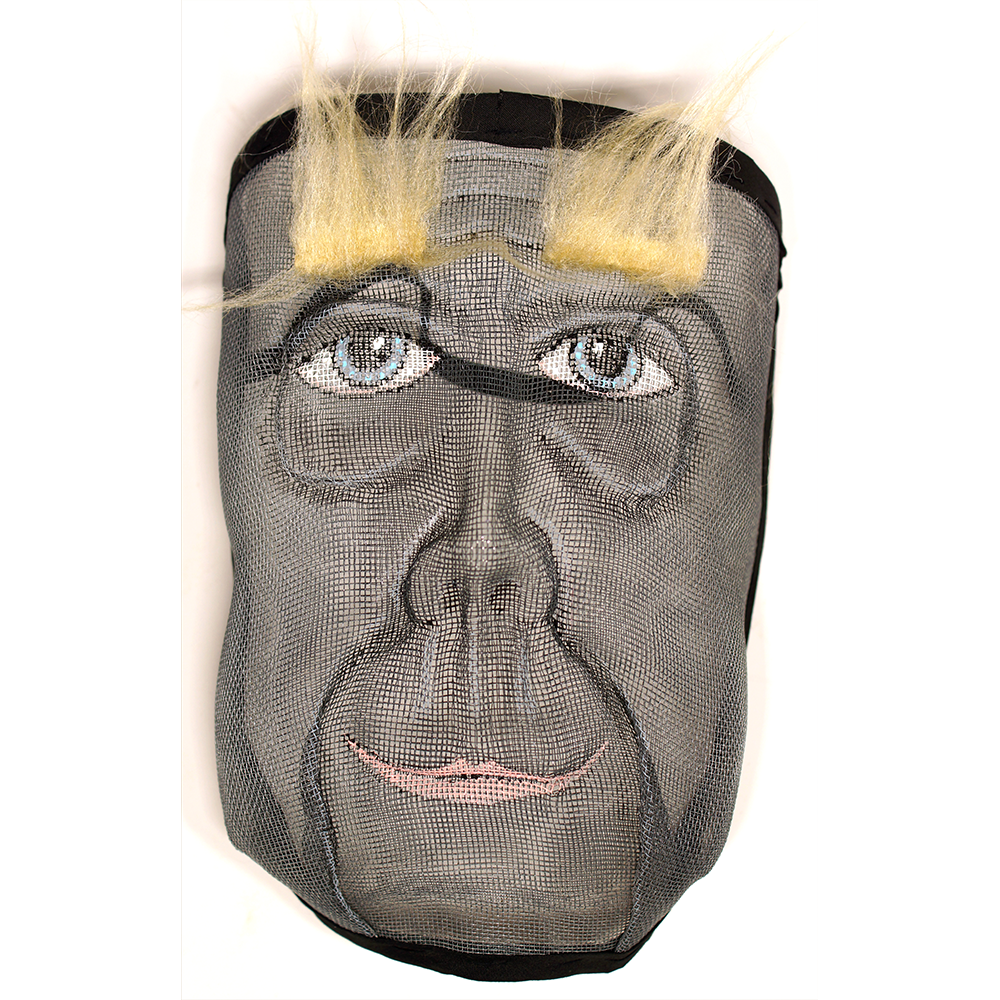
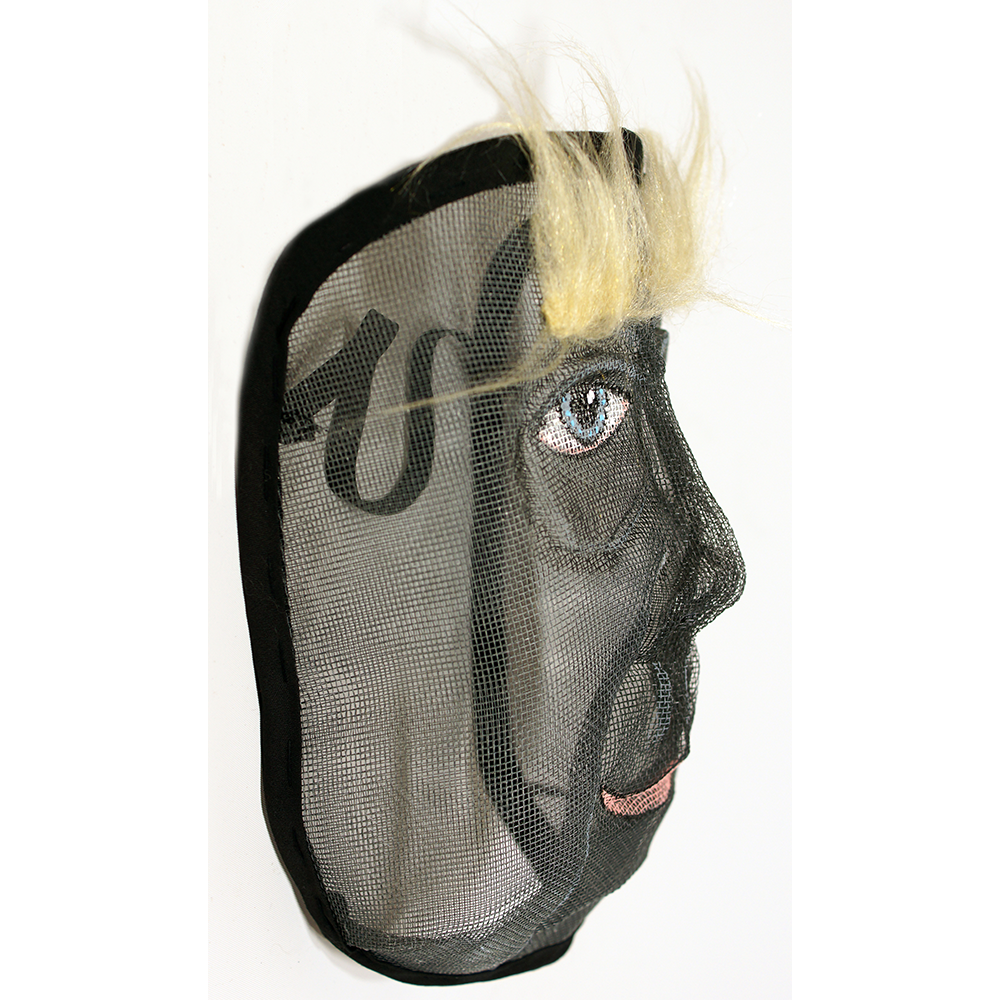
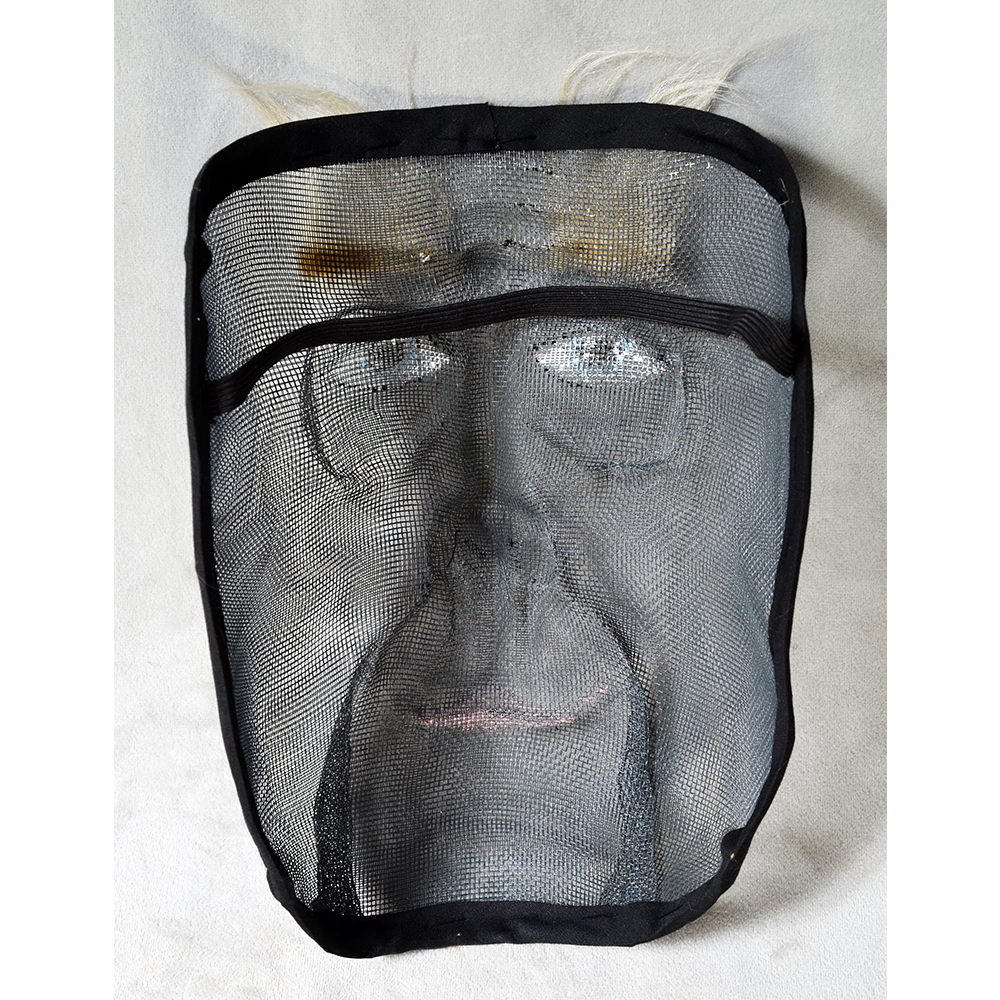
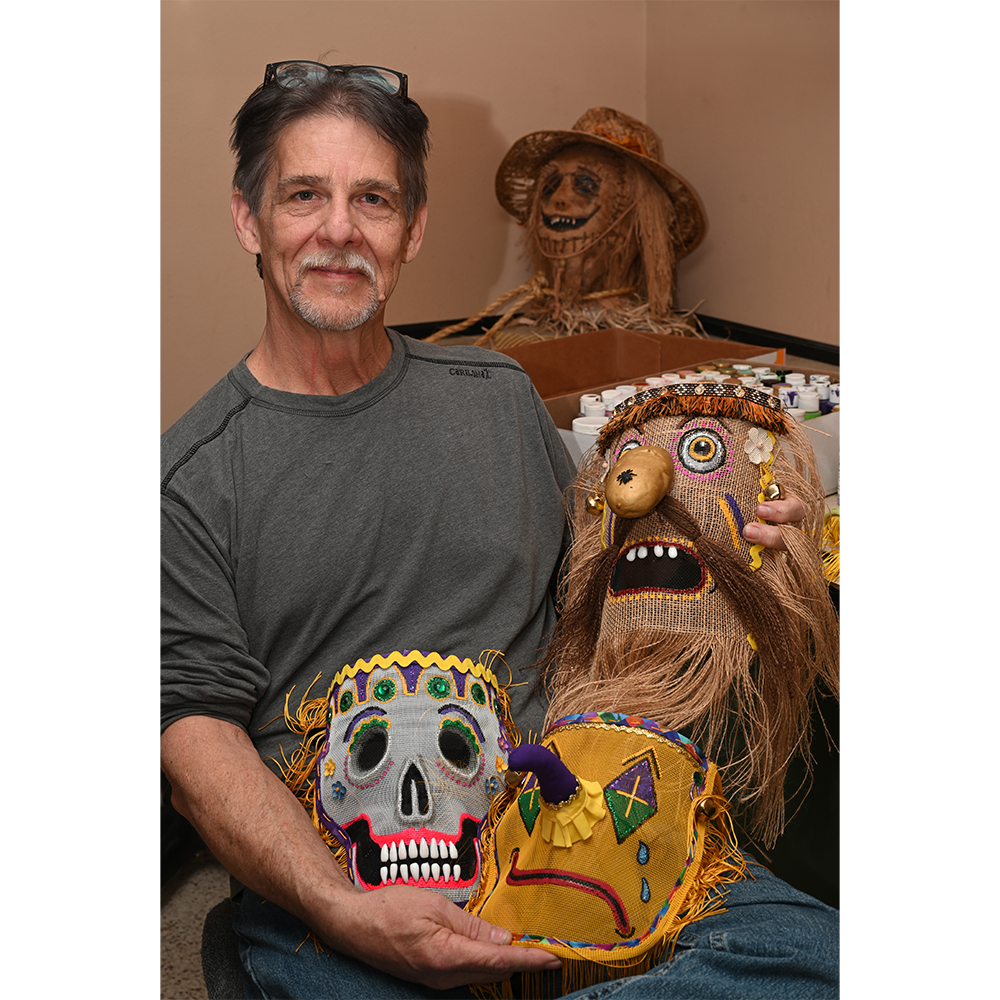
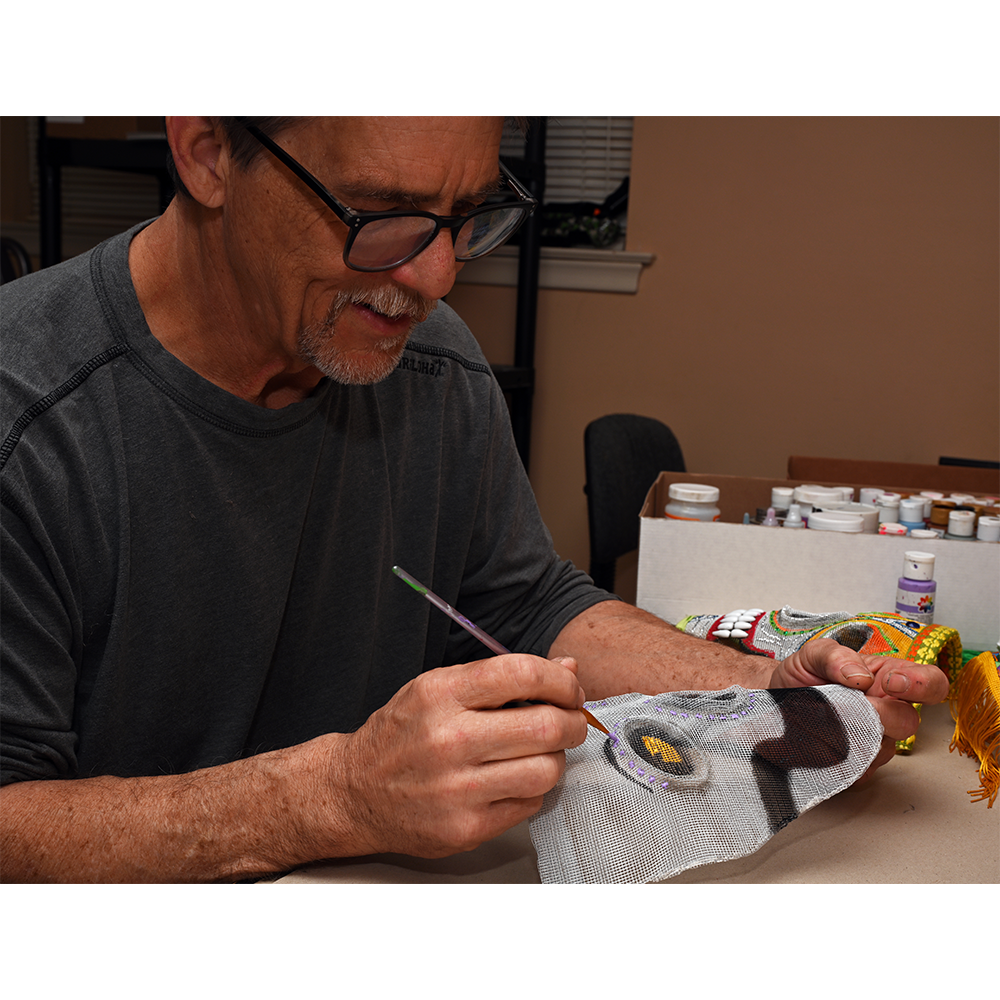
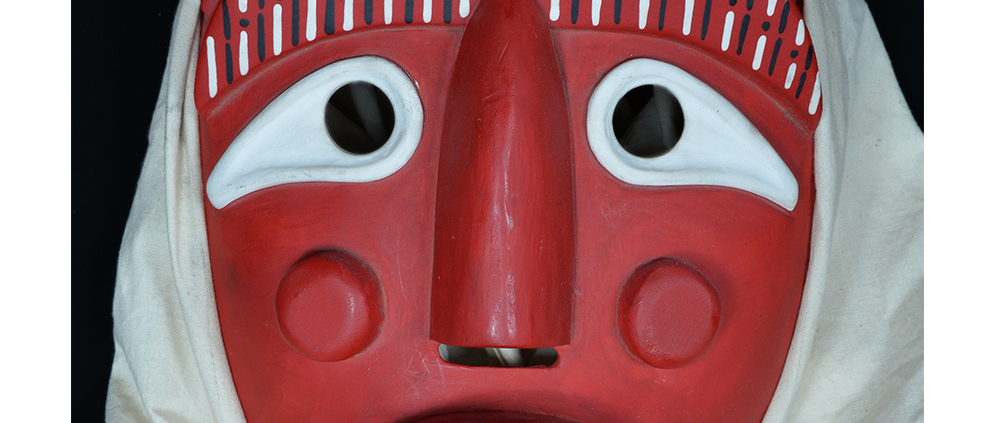
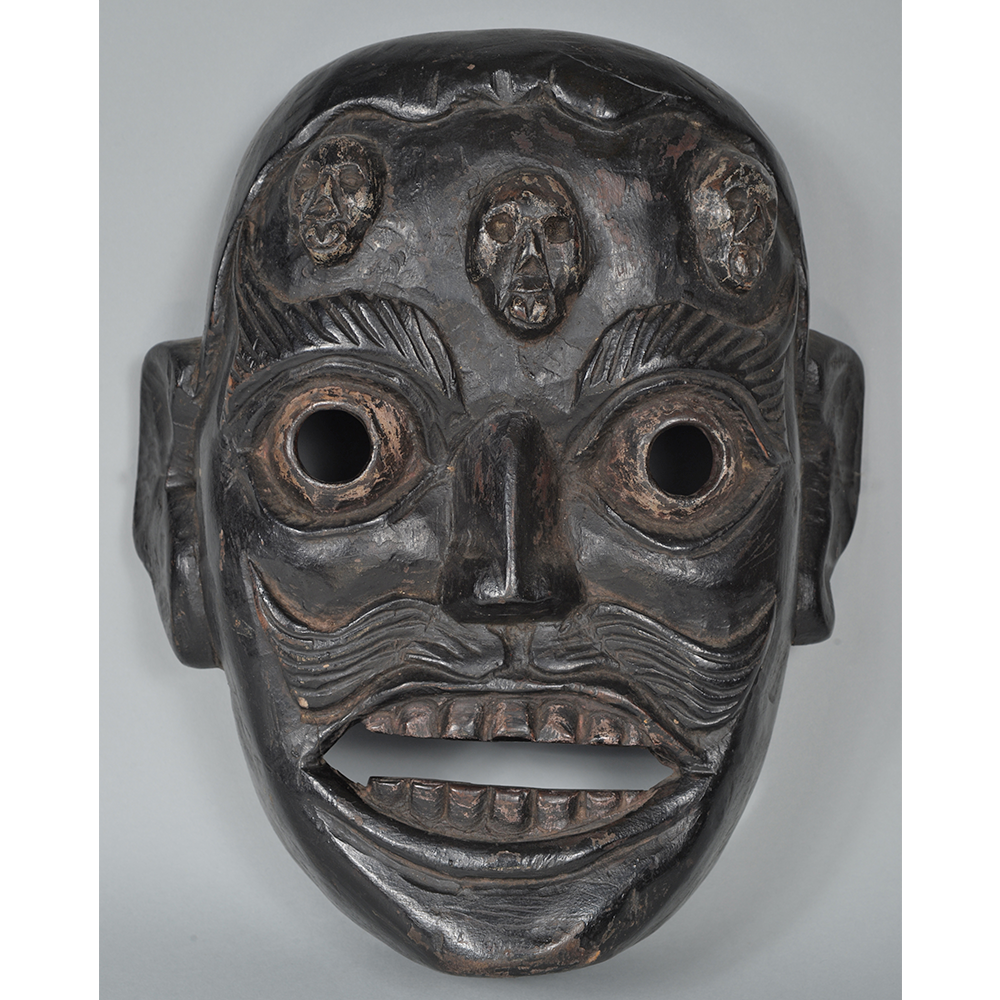
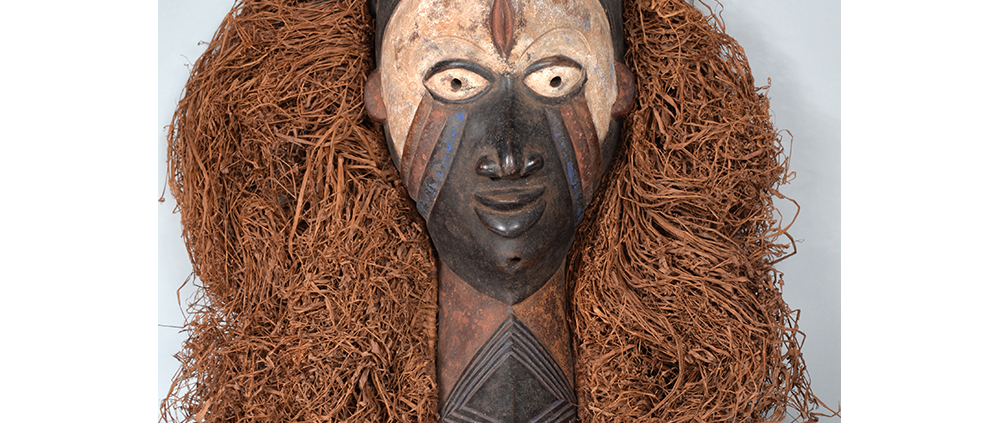
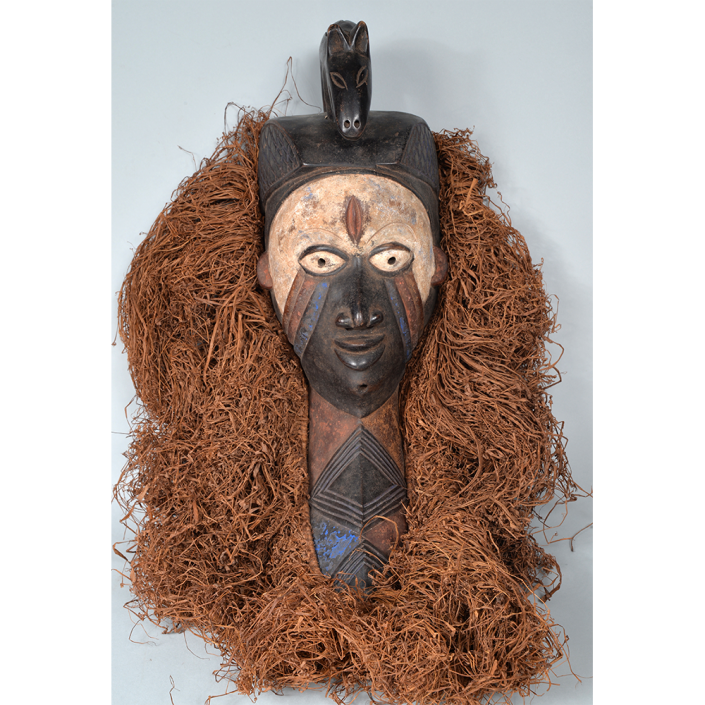
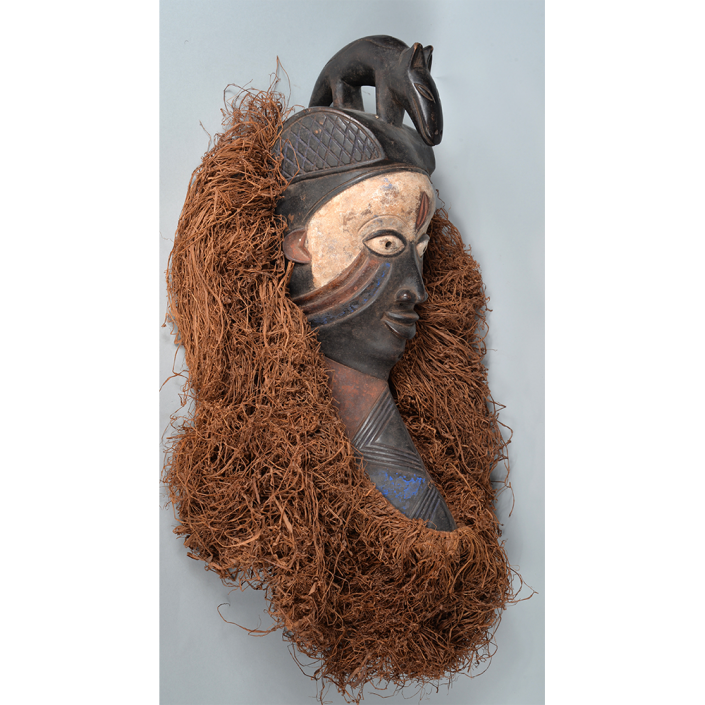
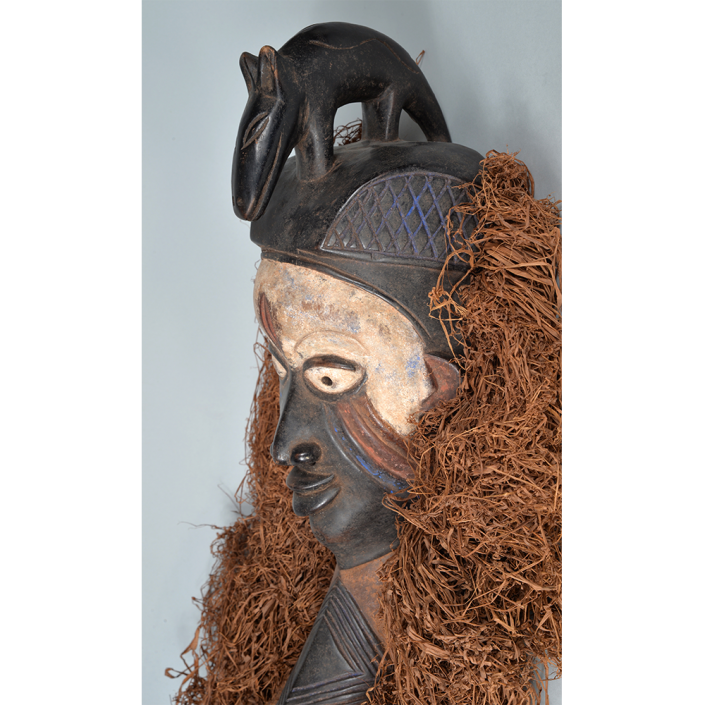
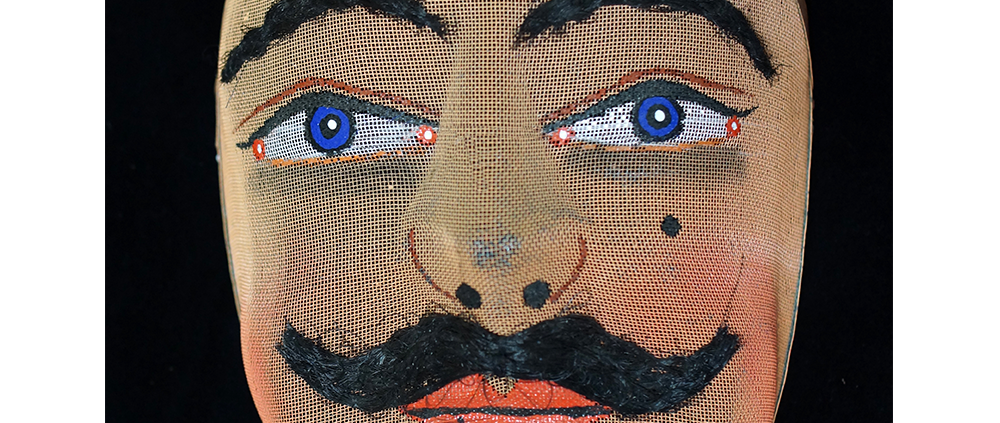
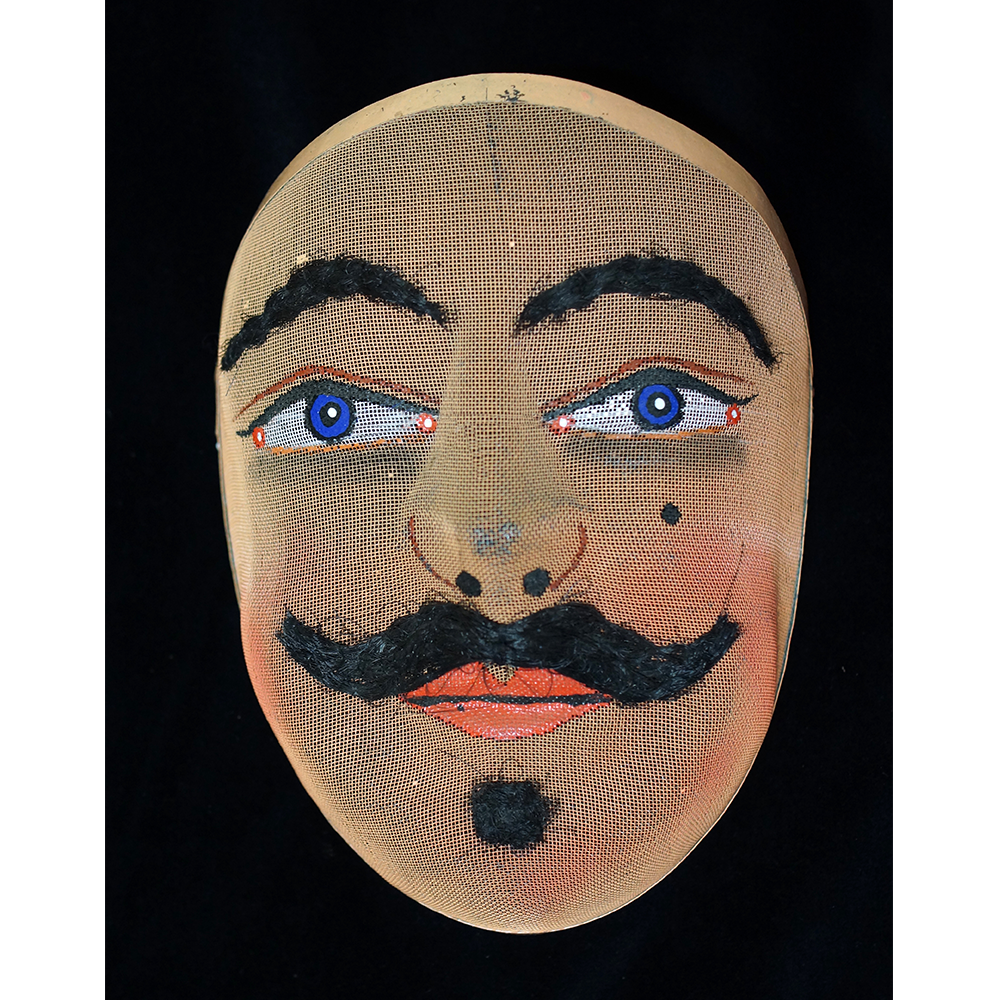
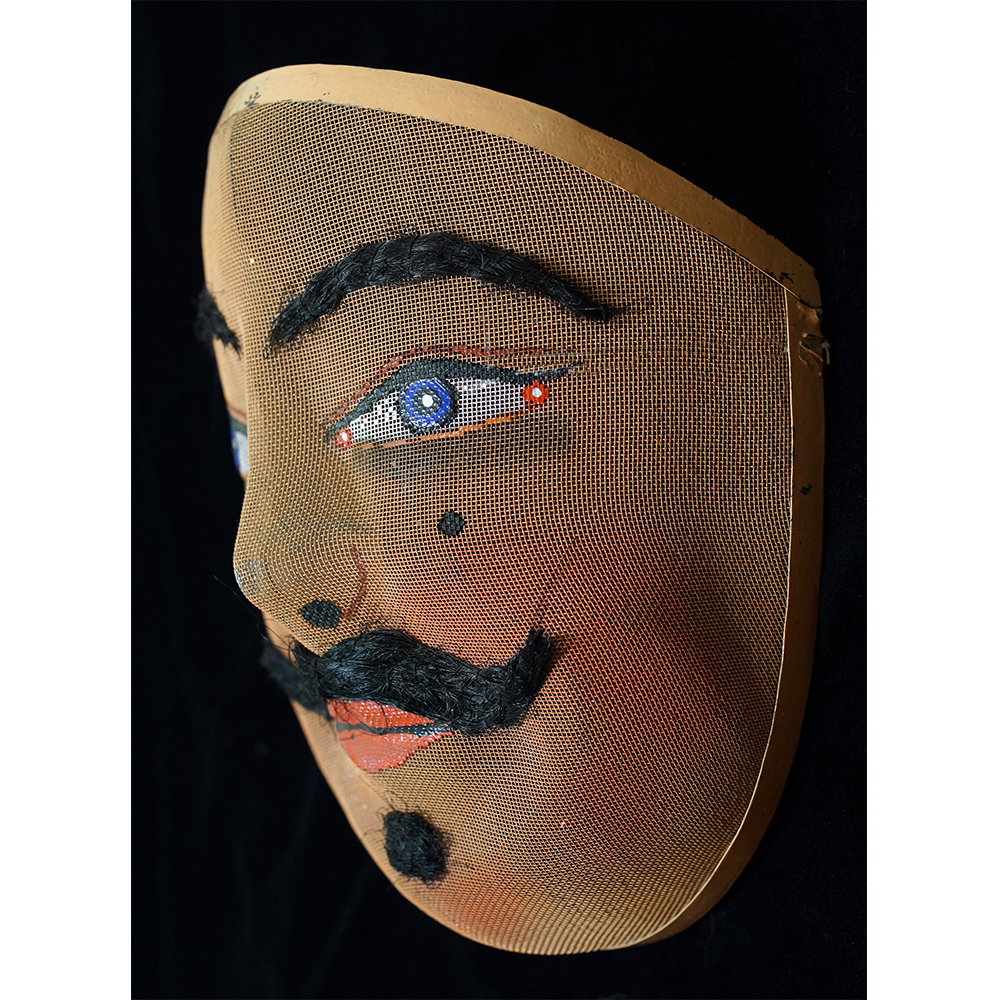
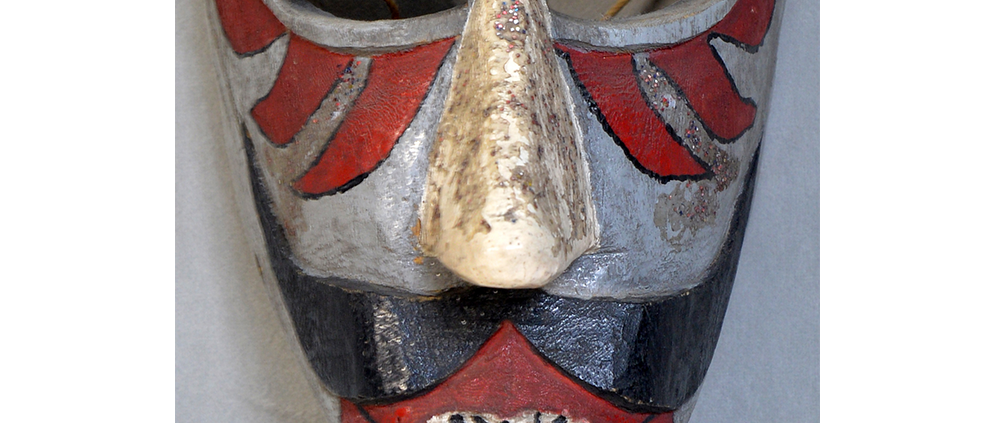
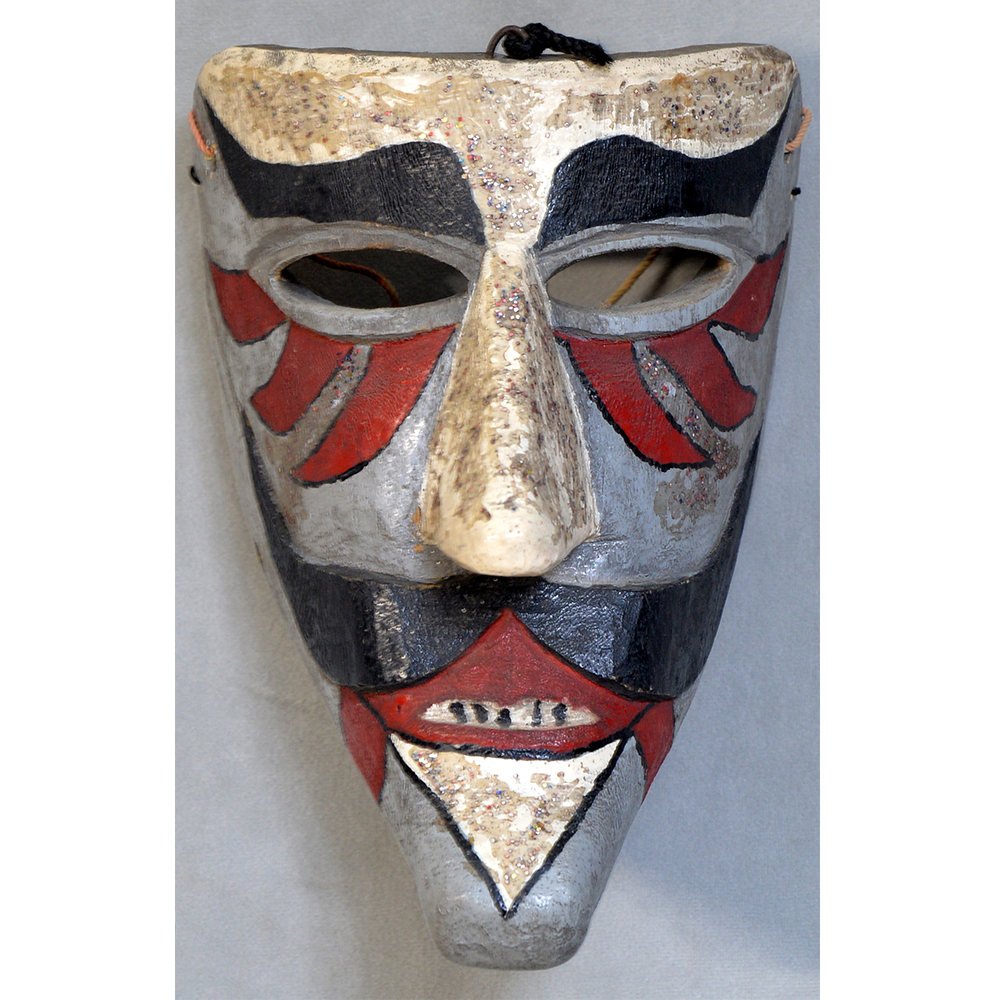
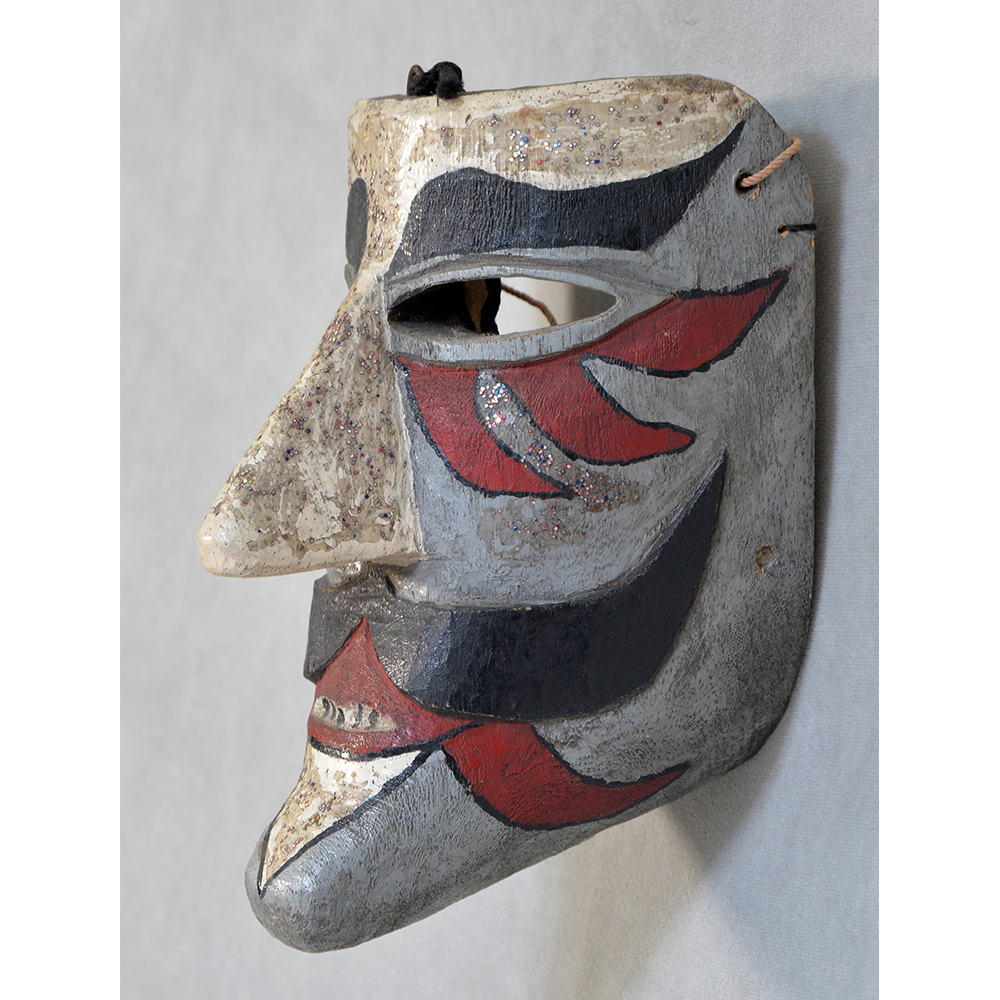
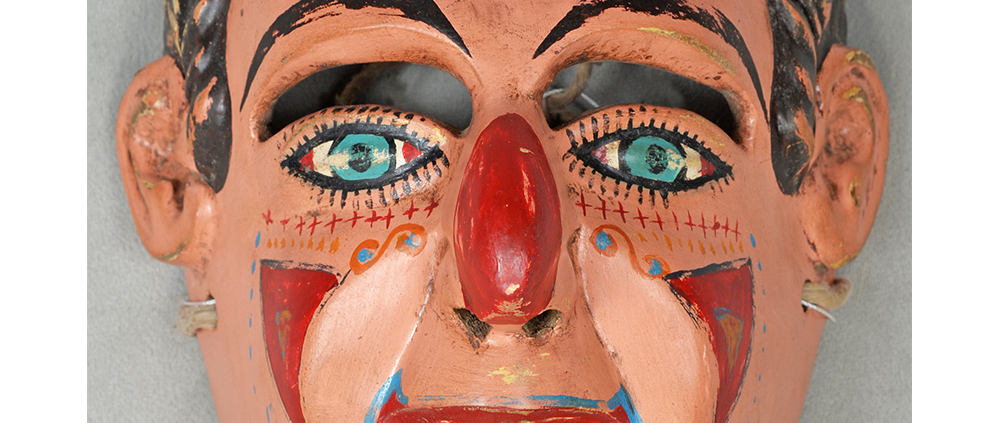
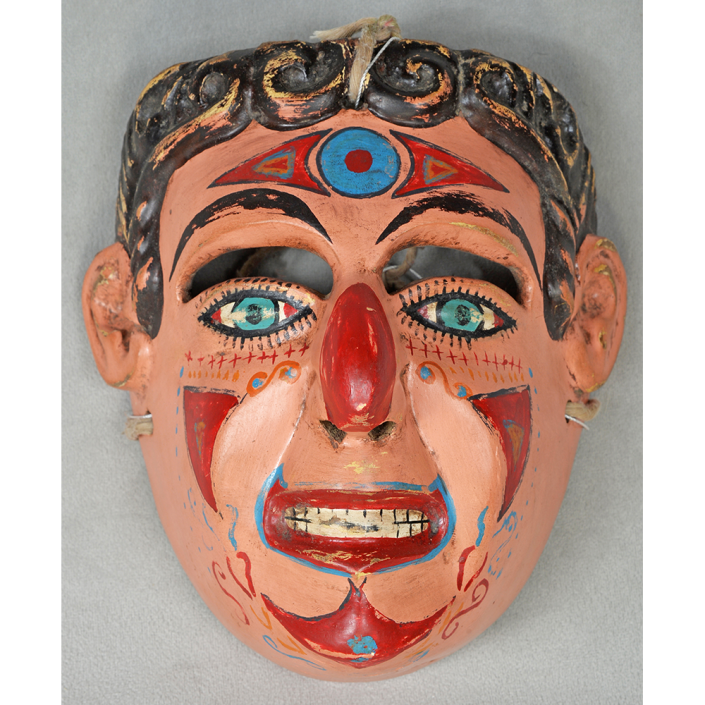
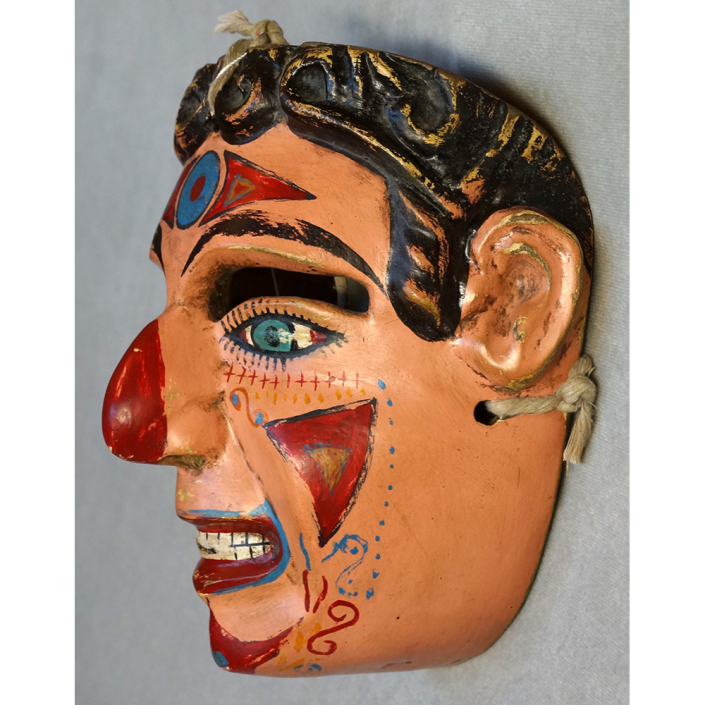
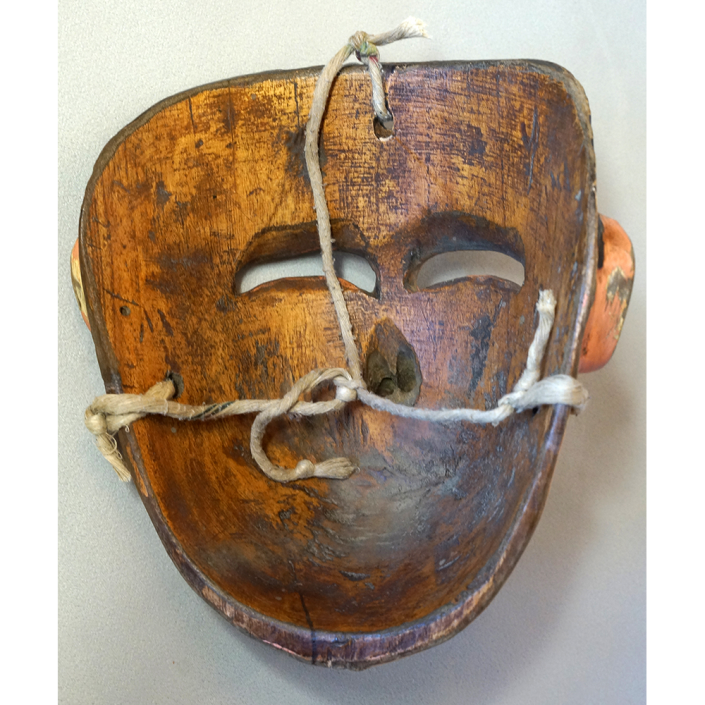
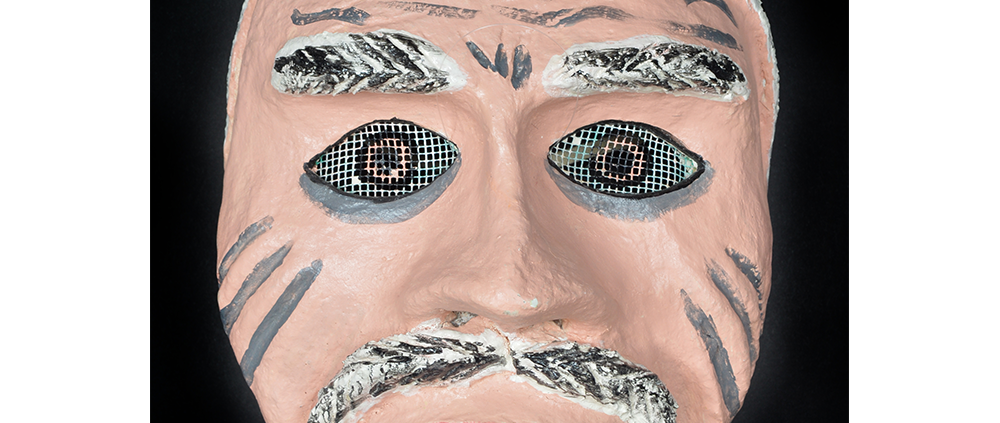
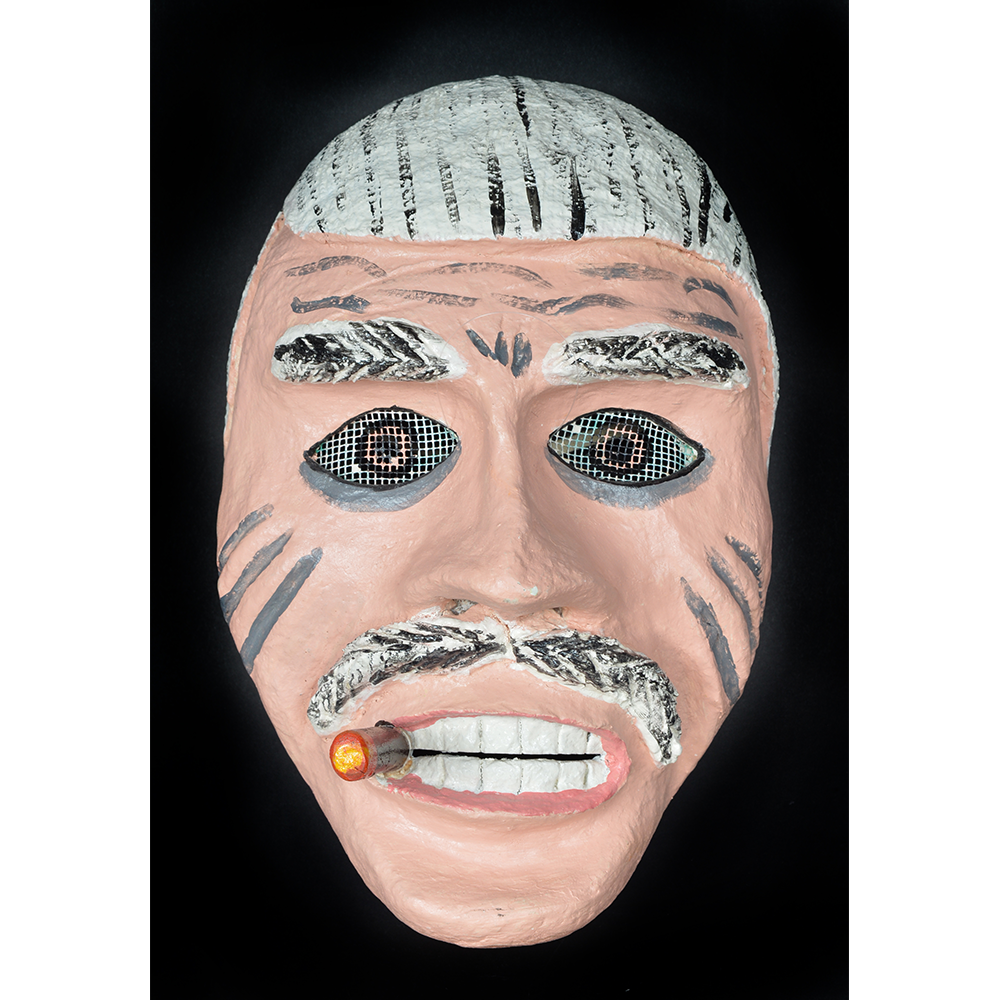
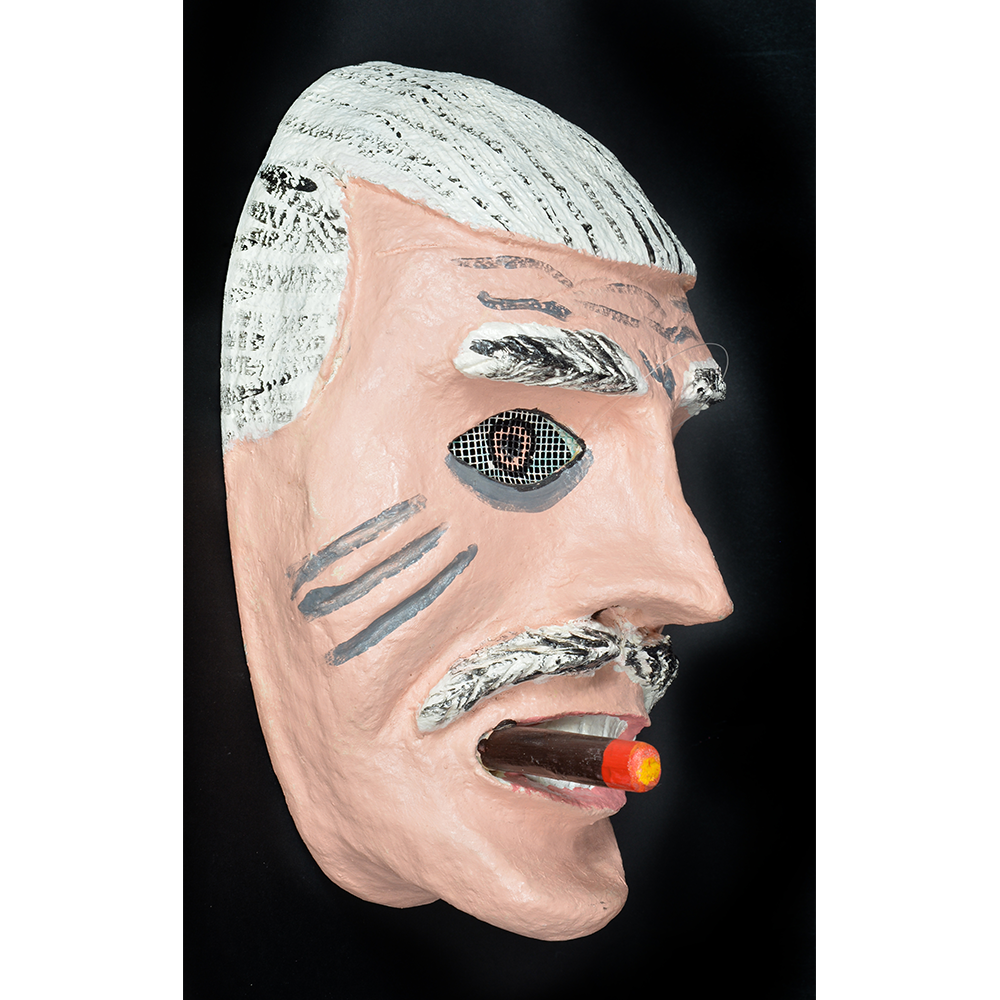
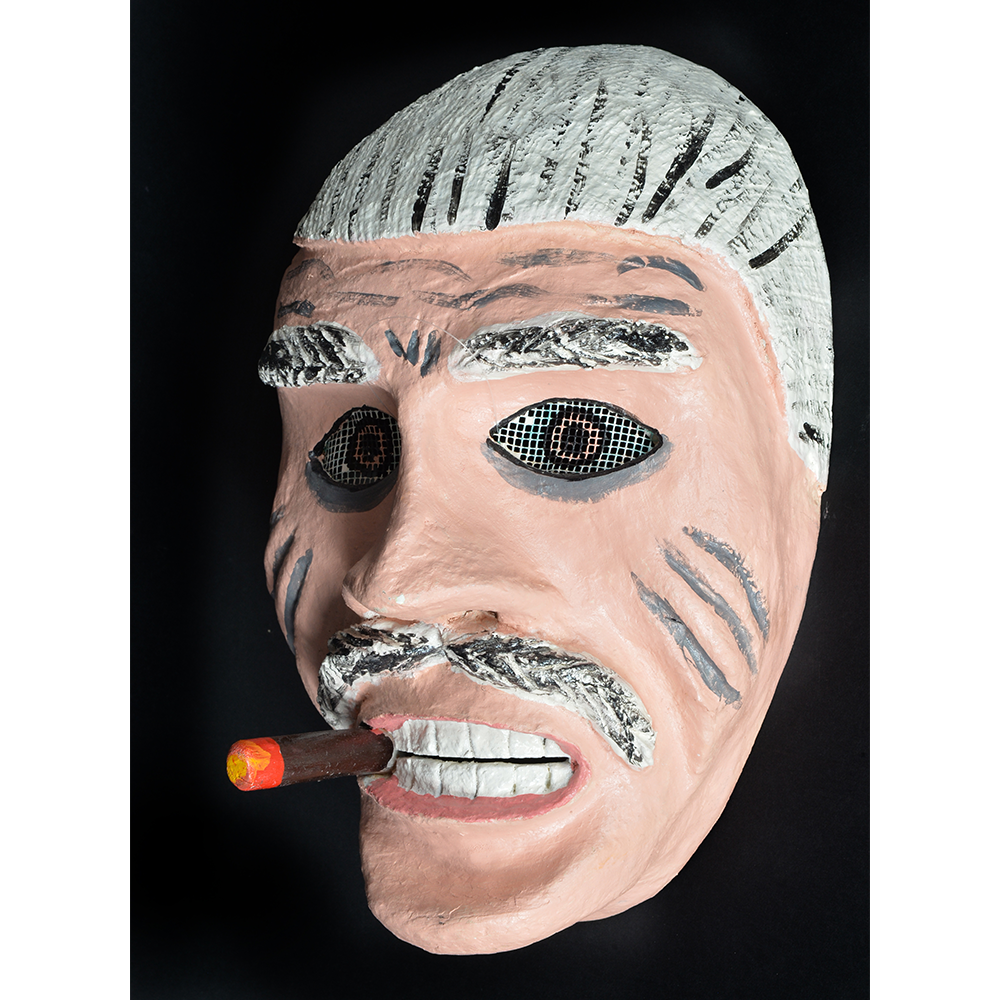
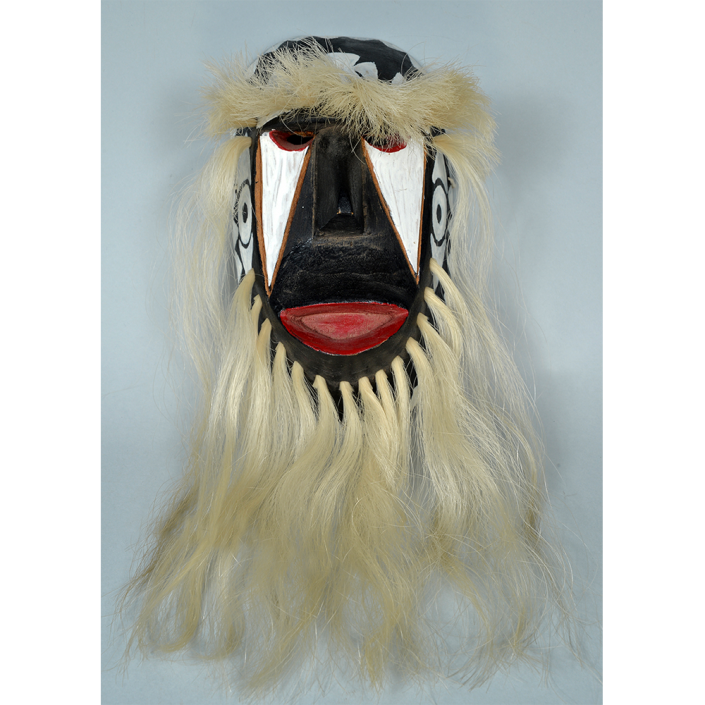
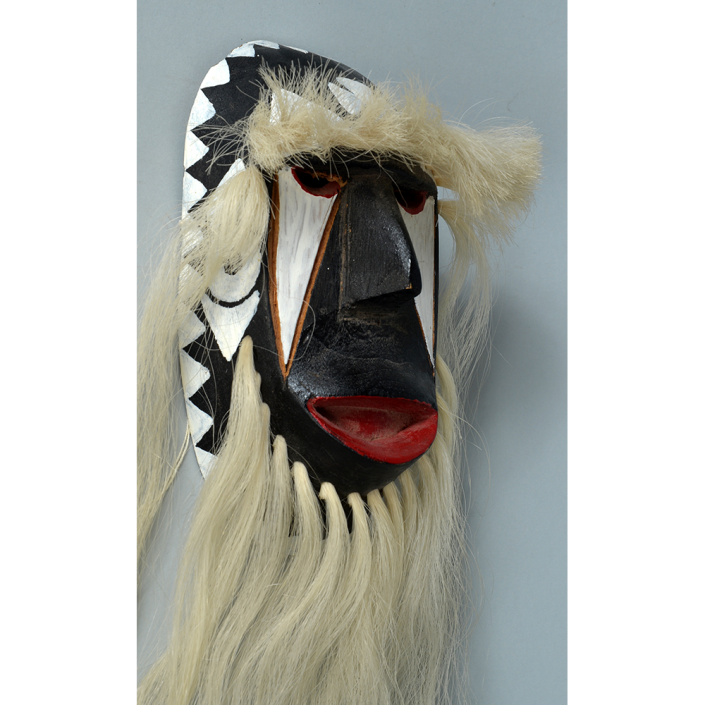
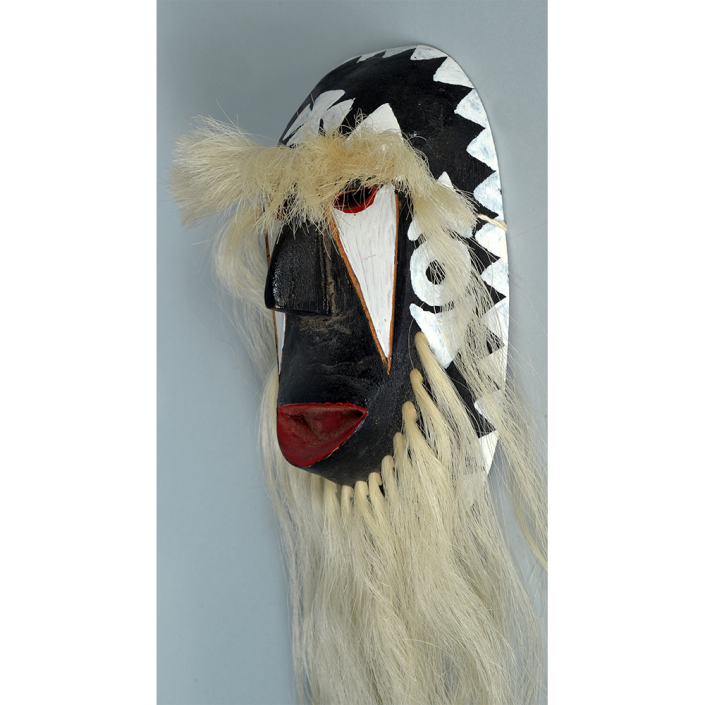
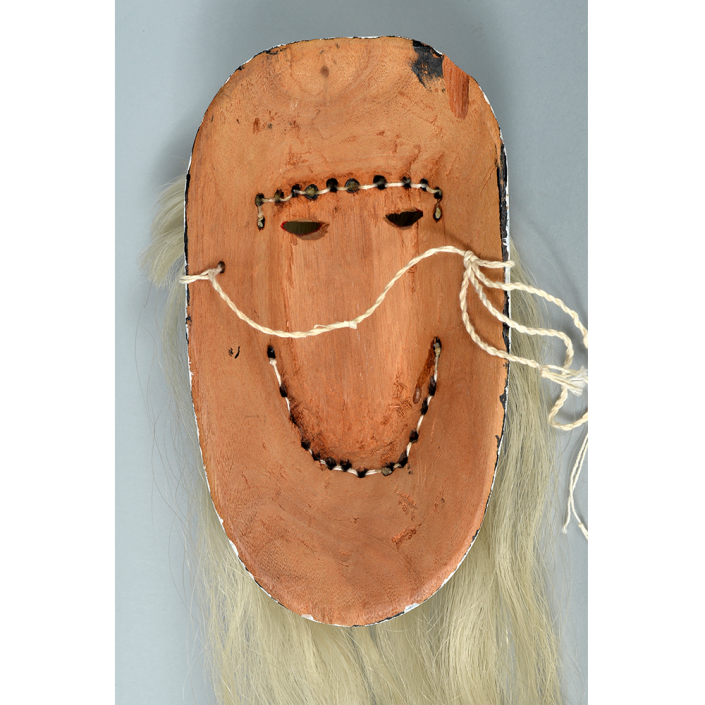
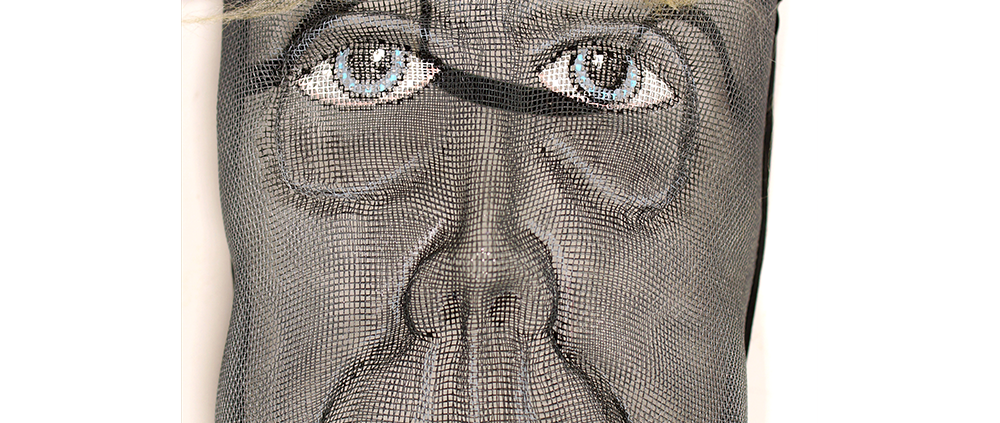
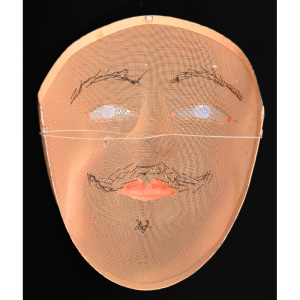
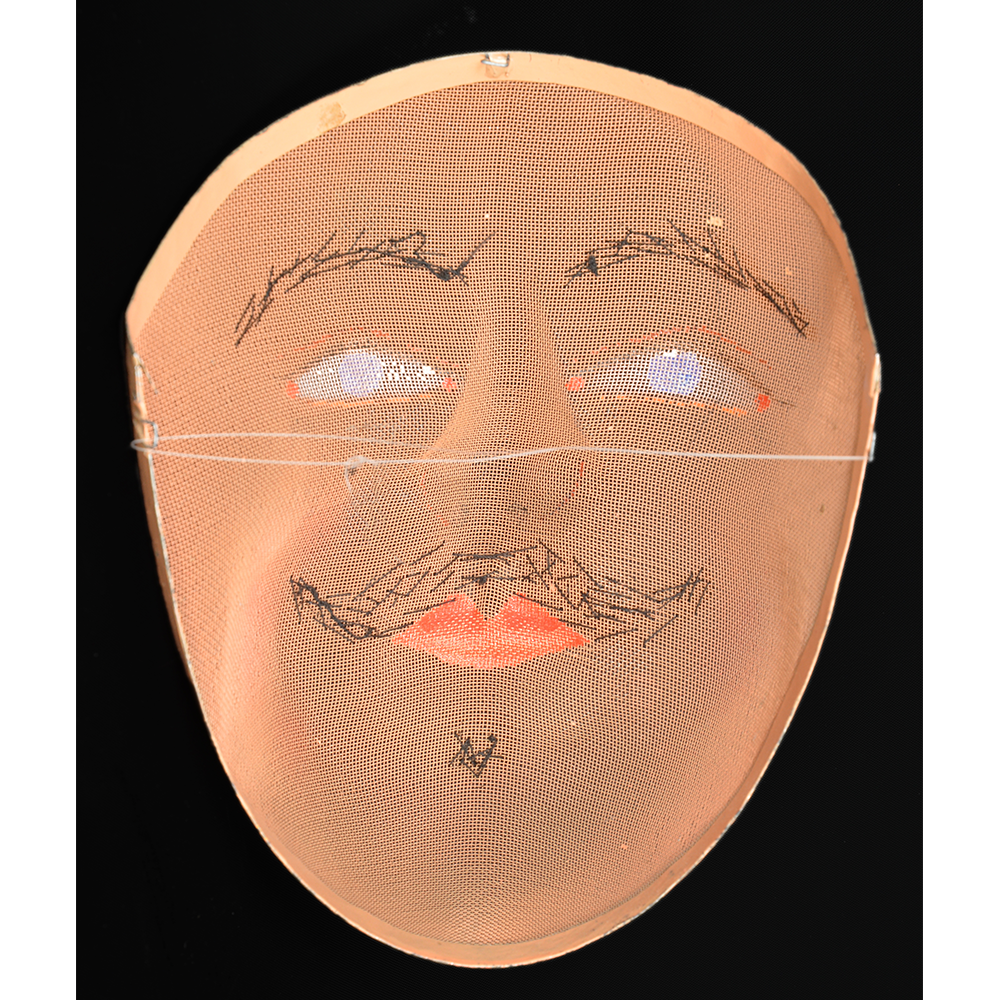
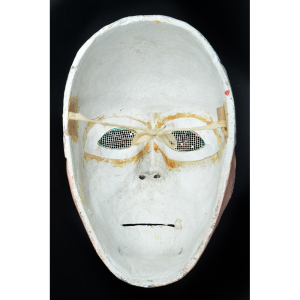
DESCRIPTION: Mesh Mardi Gras Mask
CATALOG ID: NAUS046
MAKER: Chris Raymond (Metairie, Louisiana, 1964- )
CEREMONY: Courir de Mardi Gras
AGE: 2014
MAIN MATERIAL: steel wire mesh
OTHER MATERIALS: dyed cotton cloth; synthetic fur; glue; paint; elastic band
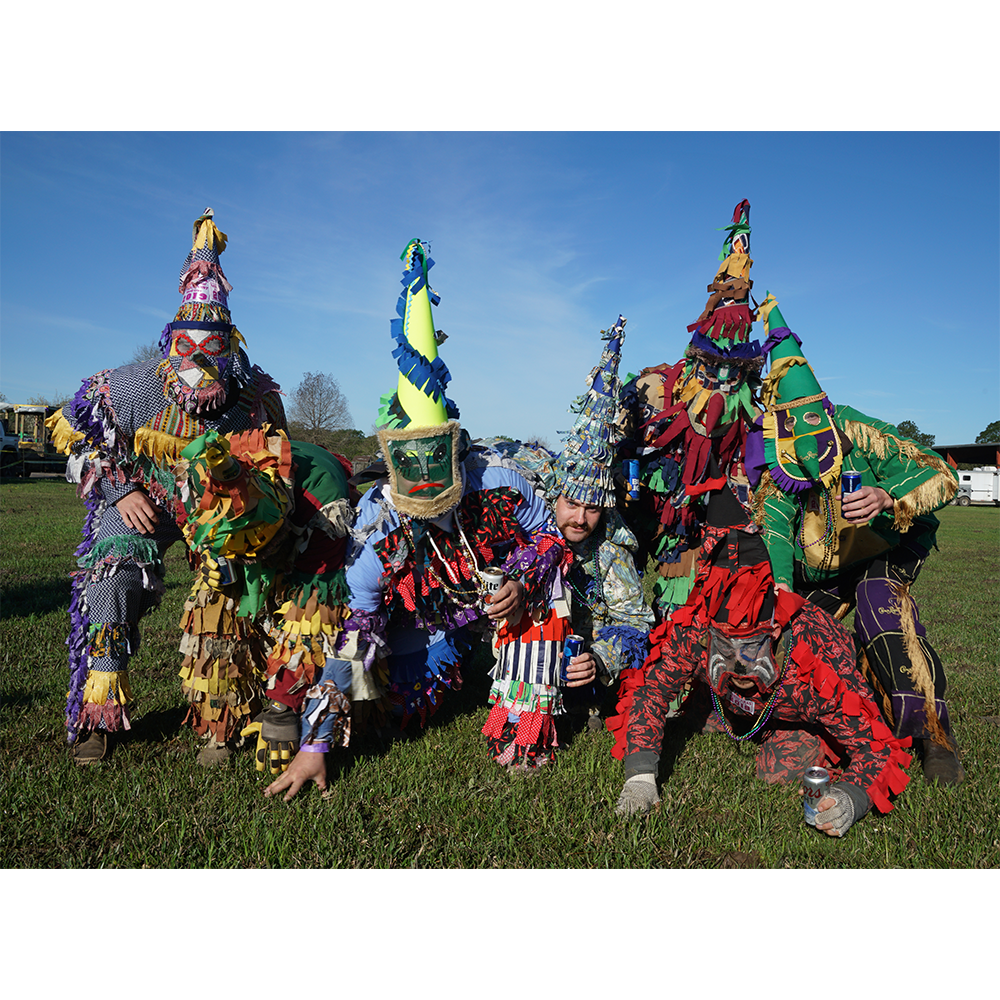
In Catholic practice, Mardi Gras (“Fat Tuesday”) is the last day of celebration of Carnival before the fasting period of Lent. In the Acadiana country of southern Louisiana, the descendants of French Canadian immigrants known as “Cajuns” (short for “Acadians”) celebrate Mardi Gras in a manner quite different from the better known Carnival of New Orleans. The Courir de Mardi Gras (Mardi Gras parade) occurs in most towns of Cajun country only on Mardi Gras itself.
Masqueraders wear full or partial wire mesh masks and quilted suits with tall, conical hats covered in colorful fabric. They either ride from farm to farm on horseback or drive as a group in trucks with an unmasked leader wearing the traditional Mardi Gras colors of green, purple, and gold. When they reach a farm, the captain, who carries a whip in one hand and a white flag in the other, approaches the farmer and asks: “Le Mardi Gras demande votre permission pour visiter ta maison” (“The Mardi Gras requests permission to visit your house”), or words to that effect. Upon assent, the revelers descend and run or crawl toward the house, singing a begging song, then exploding into pranks and comedic antics while the captain tries to subdue them with his whip. The only way to make them leave is to donate gifts or money, traditionally a chicken for the evening gumbo, in which the farmer is invited to partake.
For more on the Acadian Carnival celebration, see the excellent book by Carl Lindahl and Carolyn Ware, Cajun Mardi Gras Masks (University Press of Mississippi, 1997).