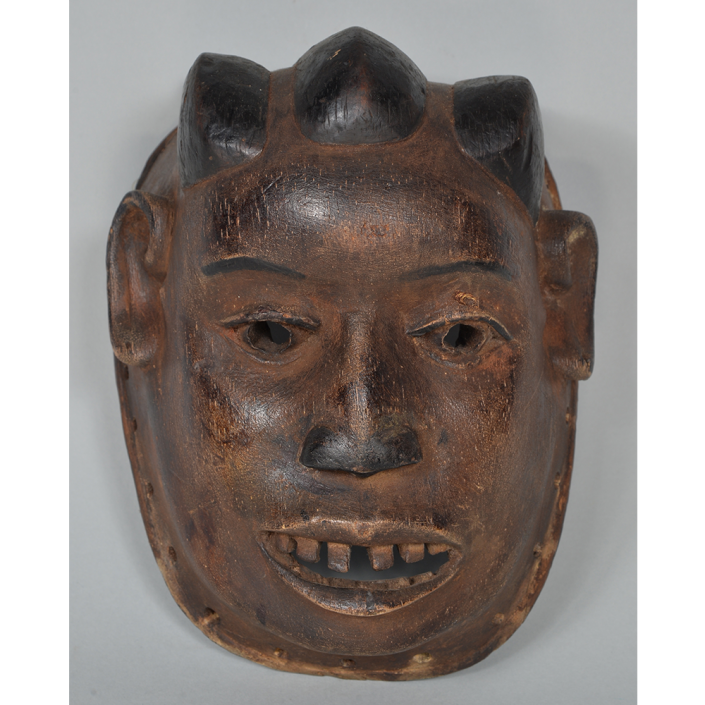
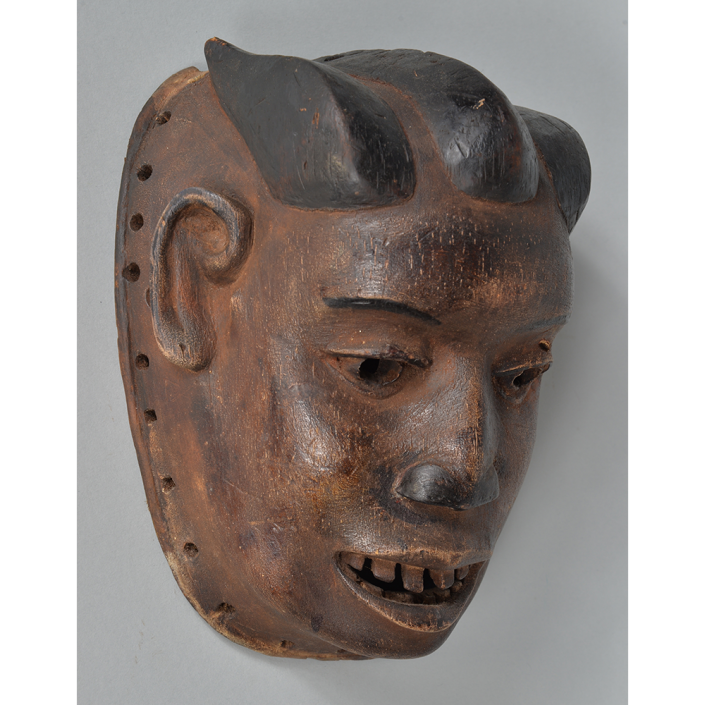
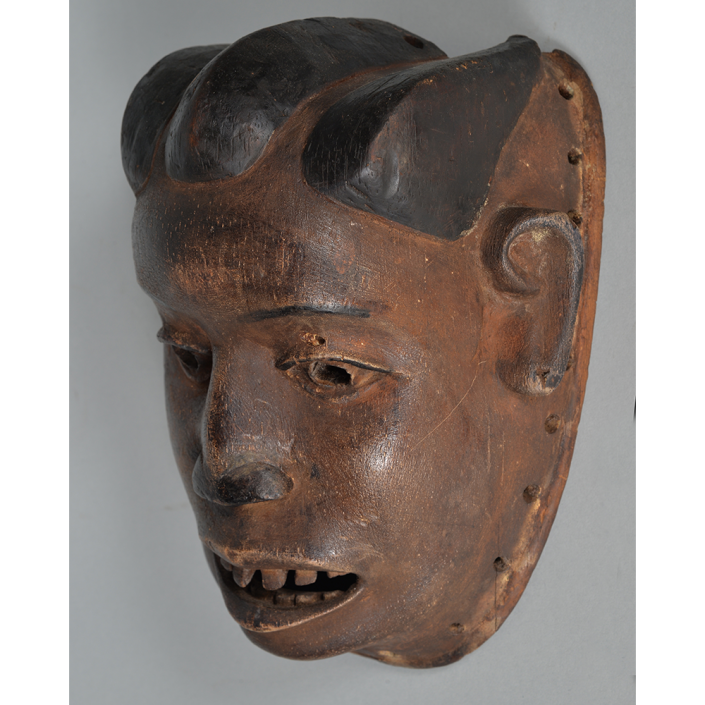
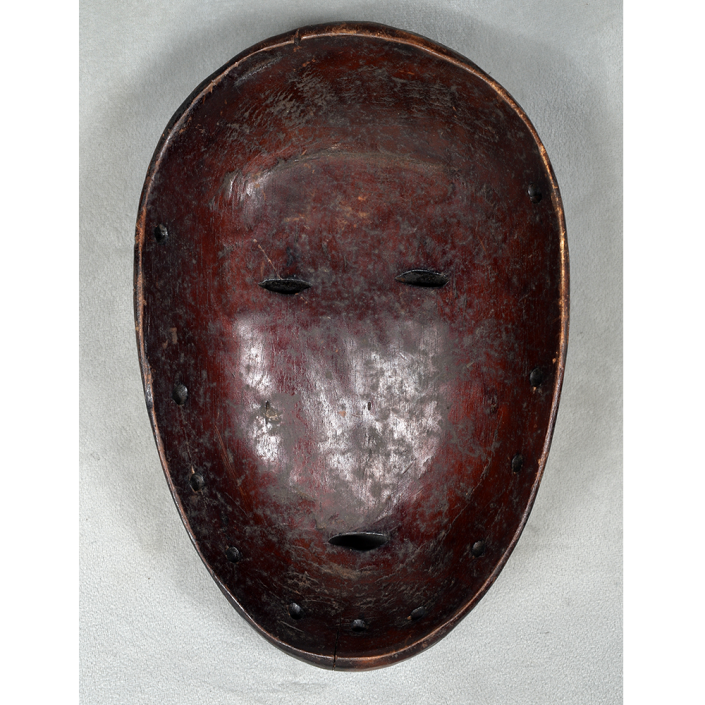
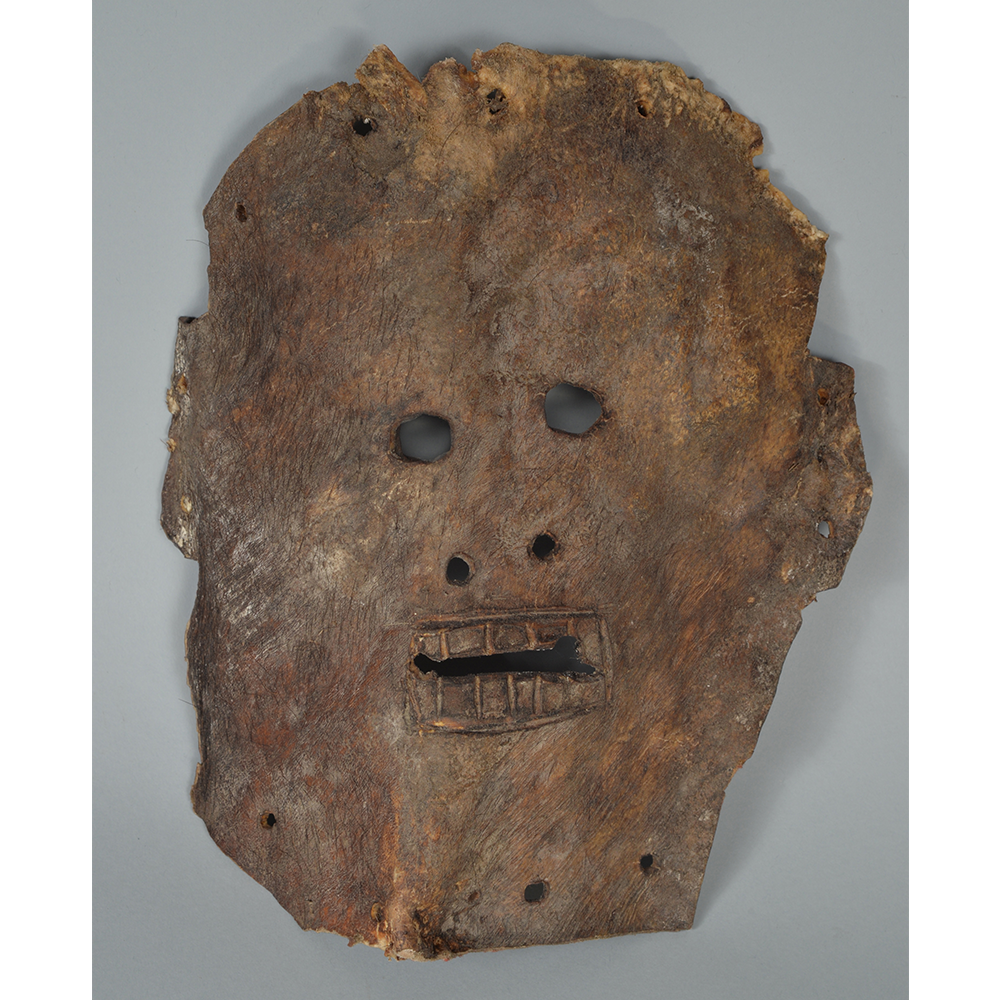
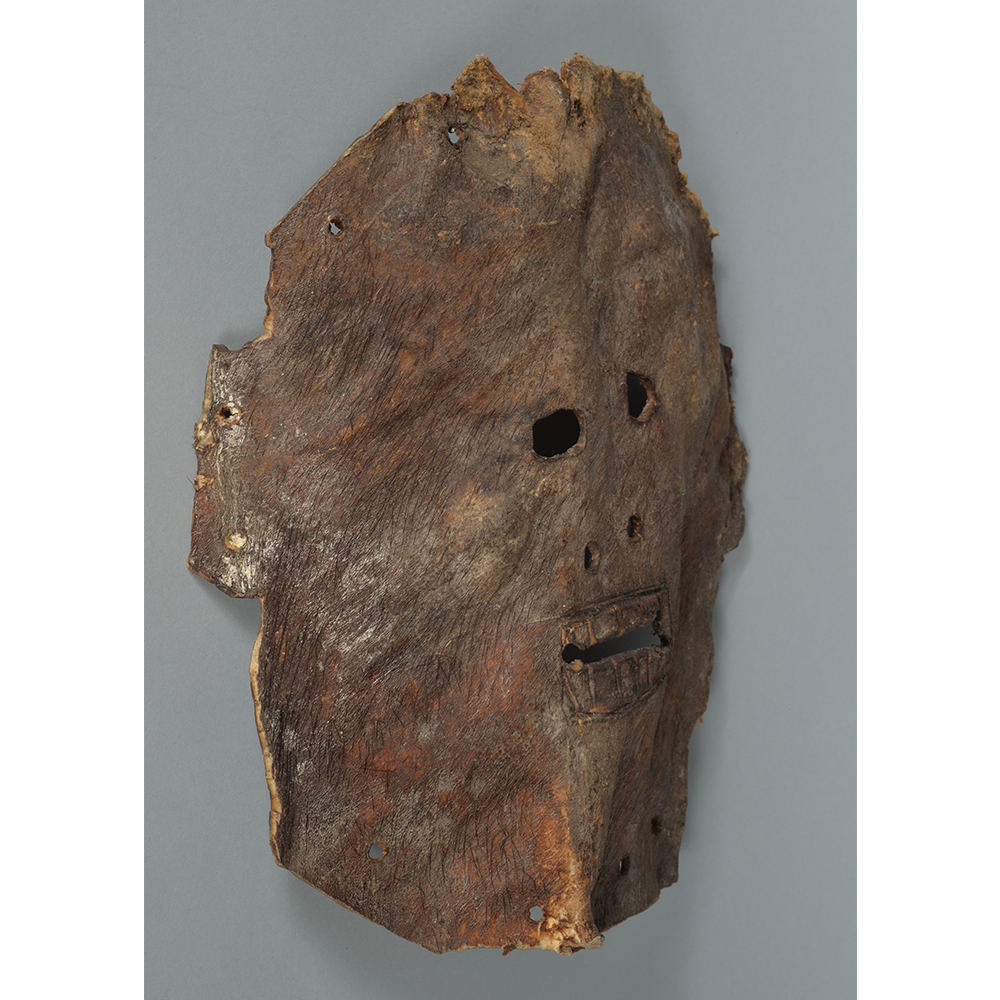
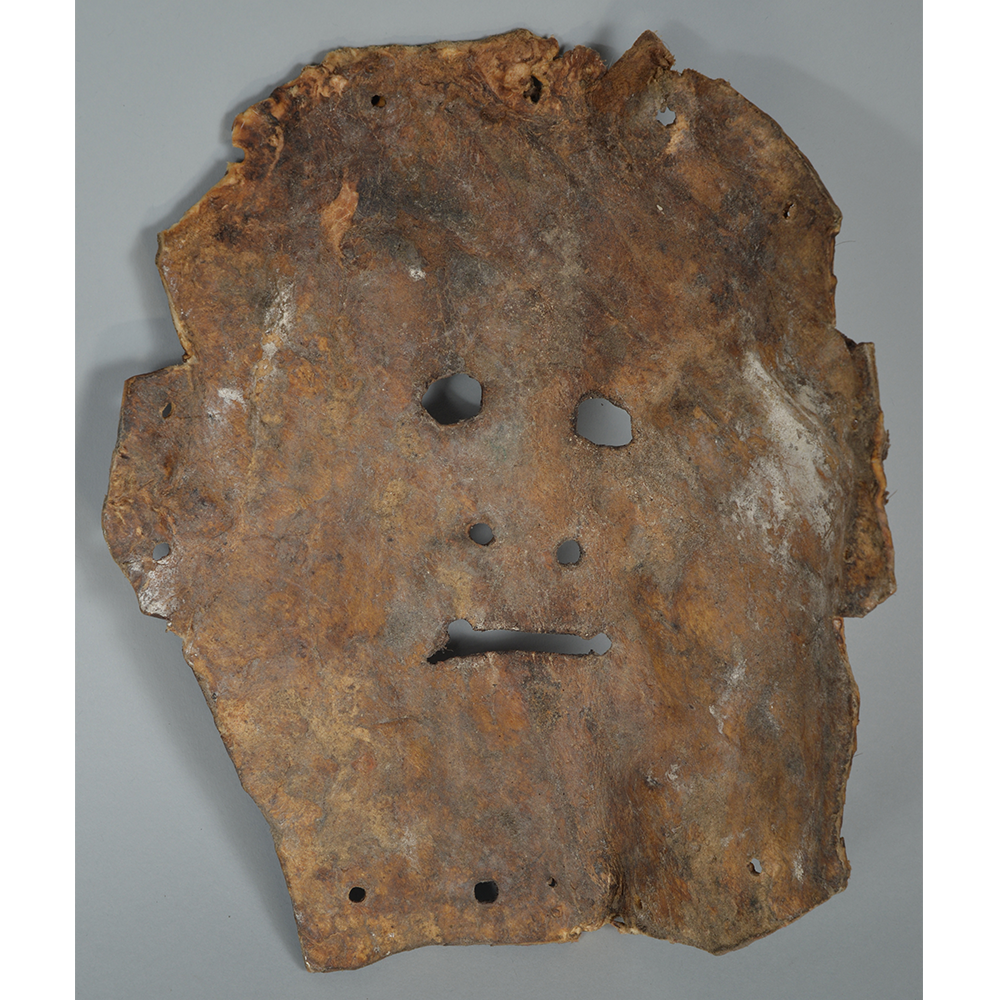
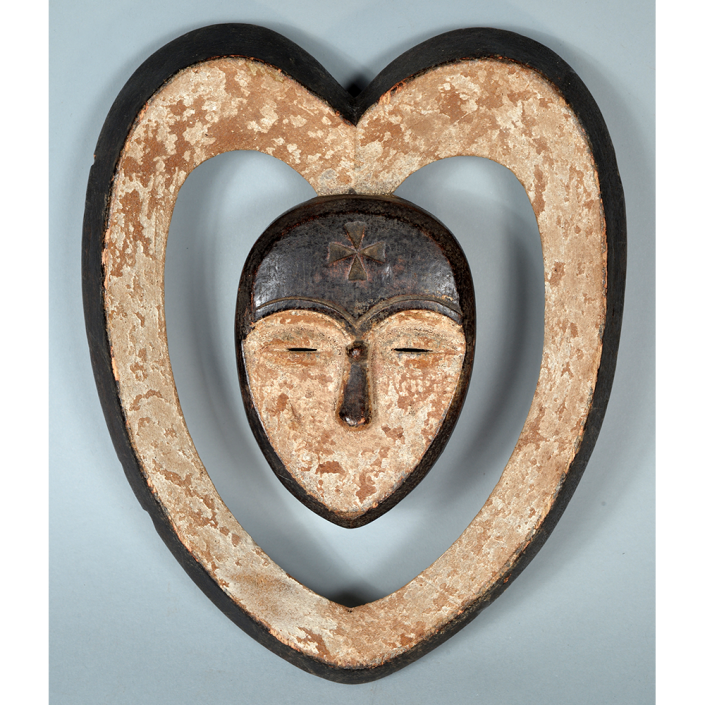
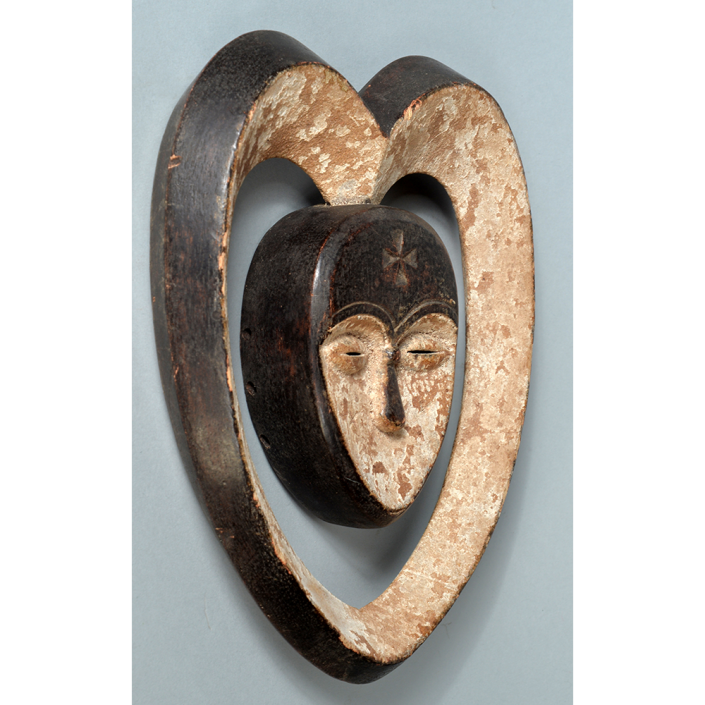
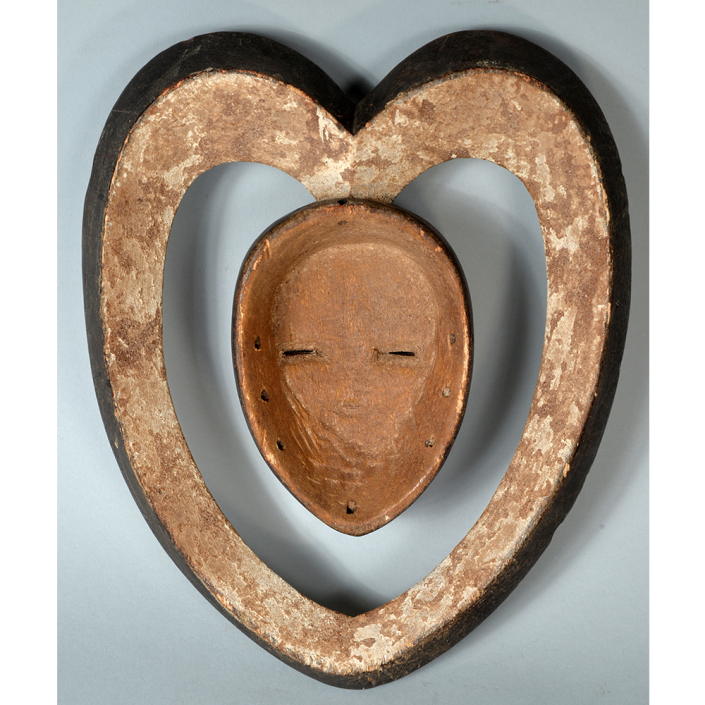
TITLE: Flums Carnival Mask
TYPE: face mask
GENERAL REGION: Europe
COUNTRY: Switzerland
SUBREGION: Flums
ETHNICITY: Swiss
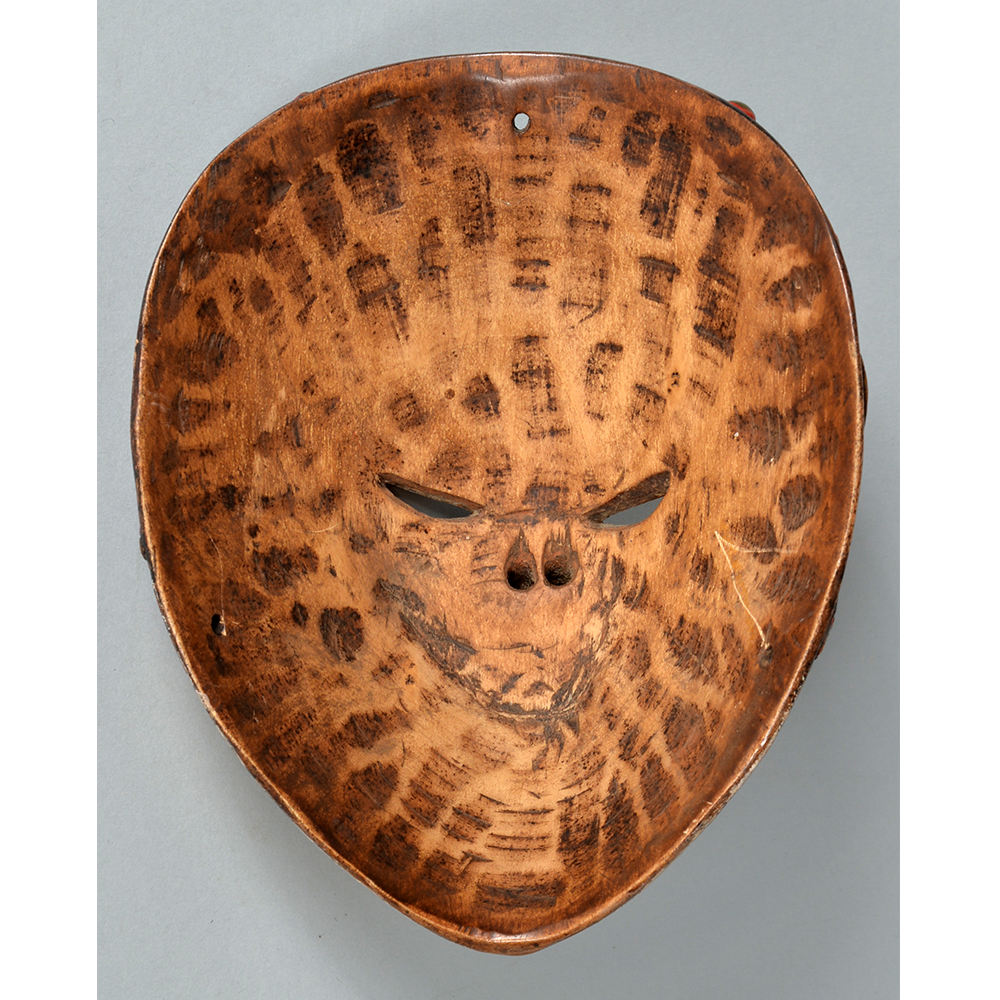
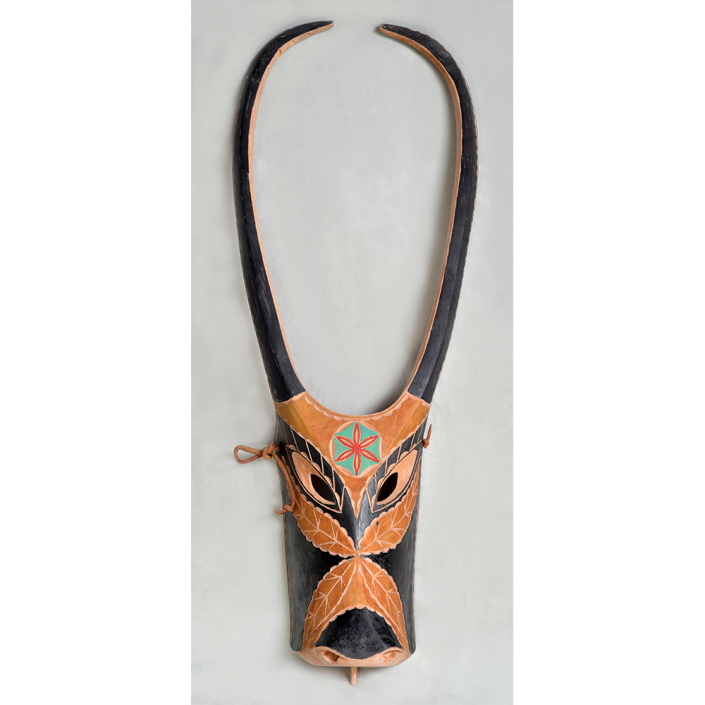
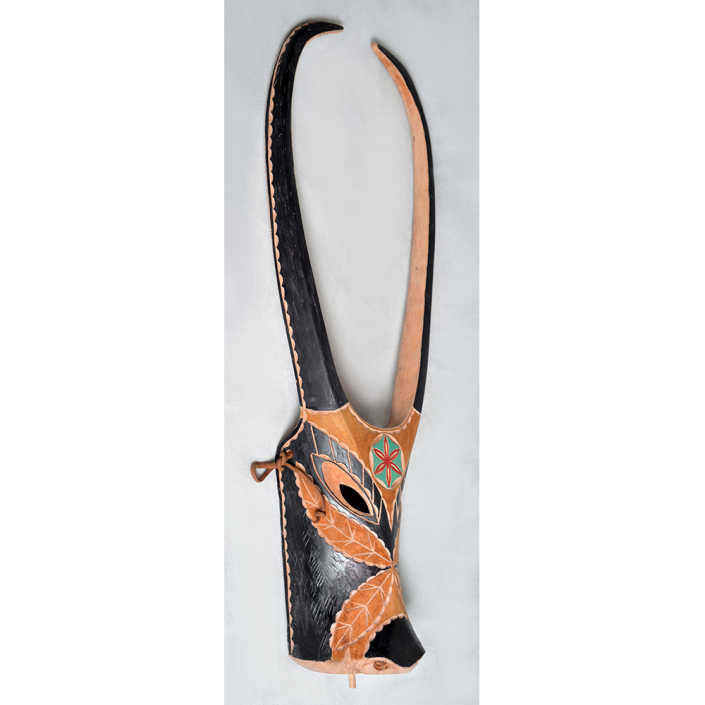
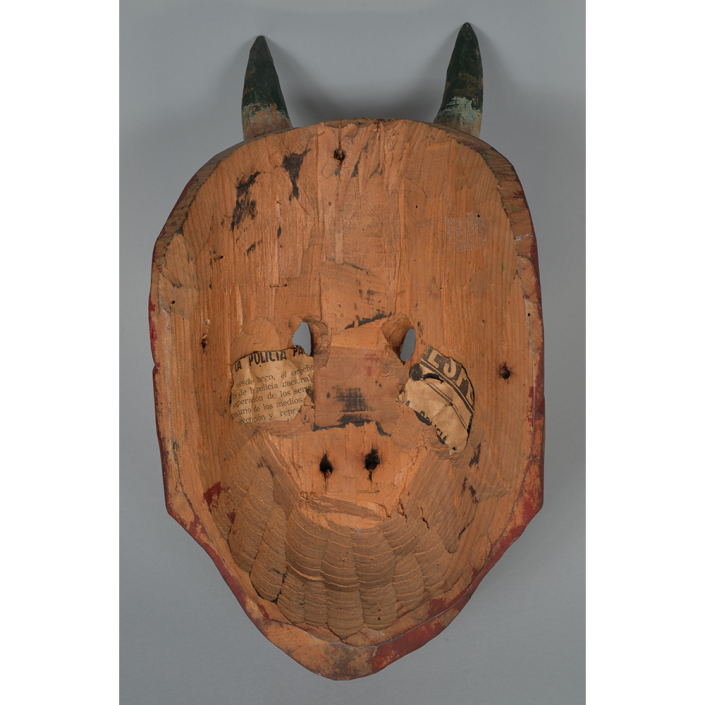
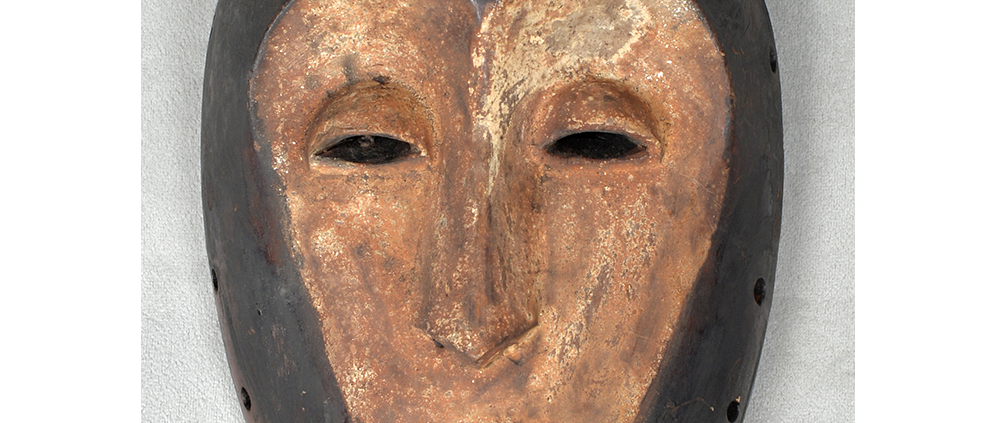
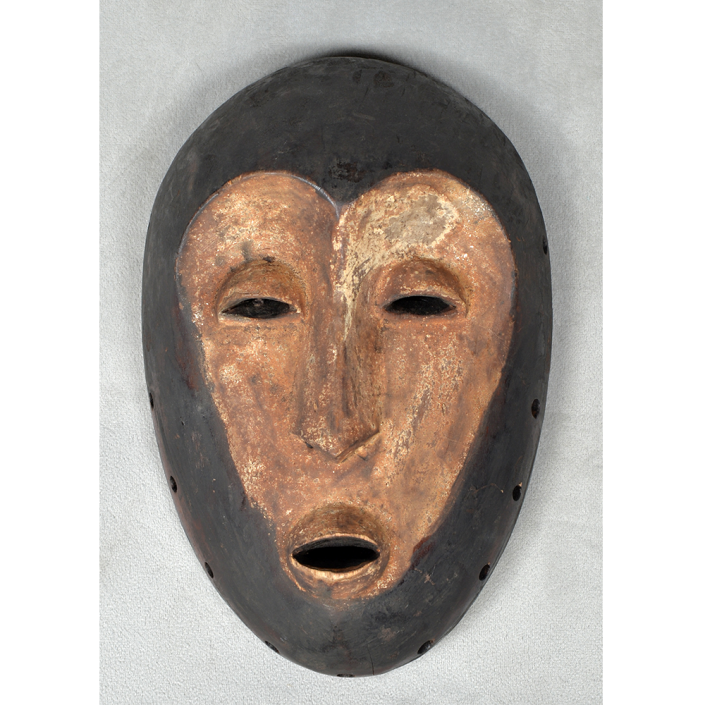
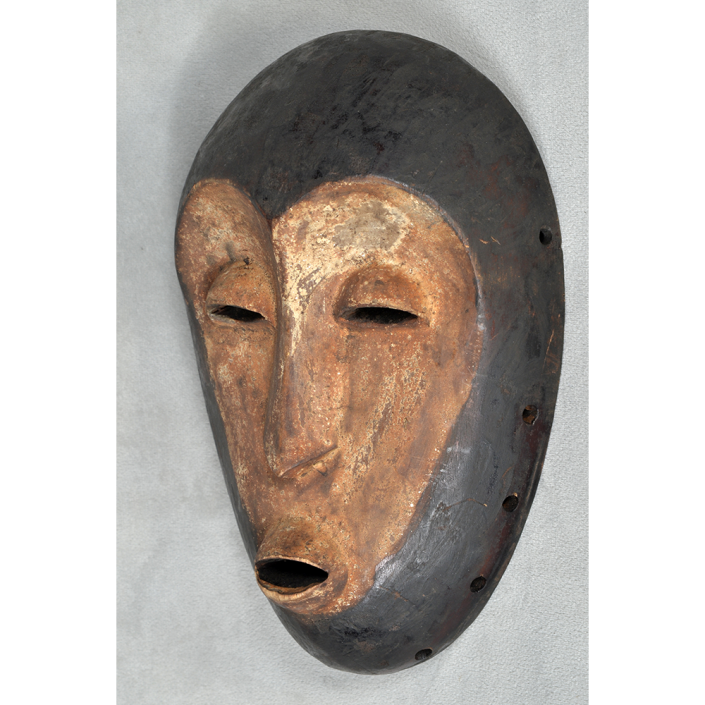
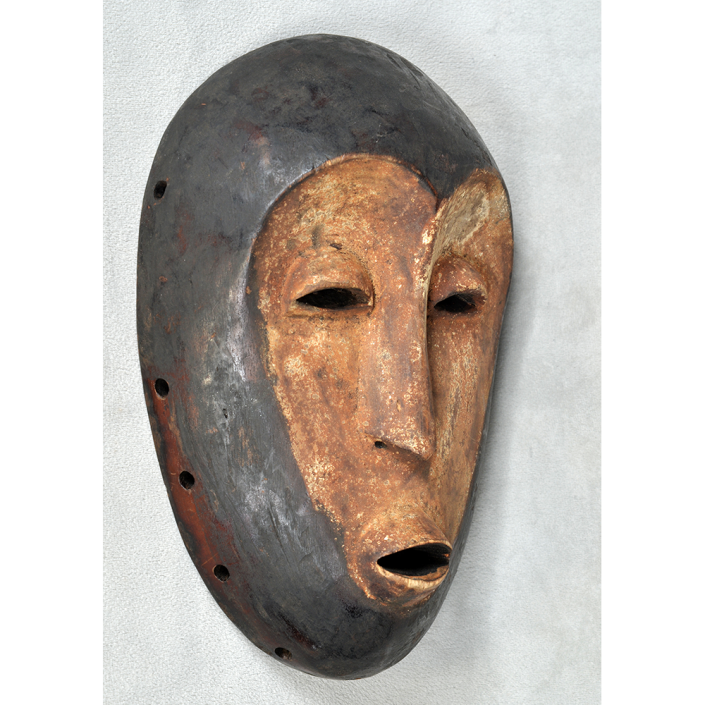
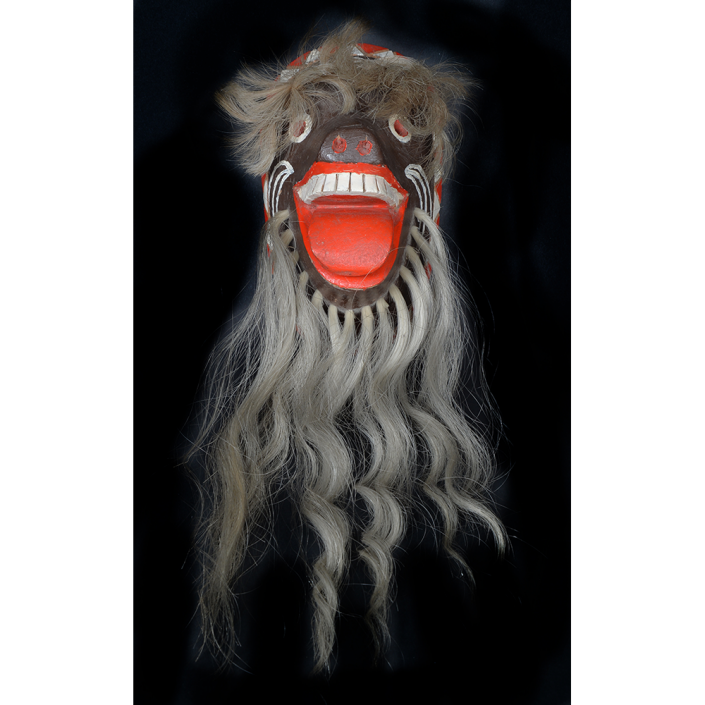
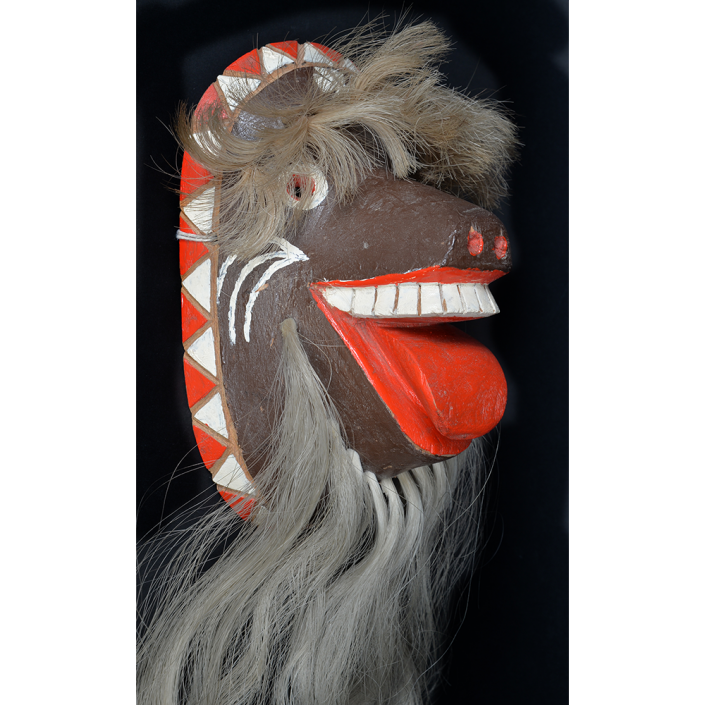
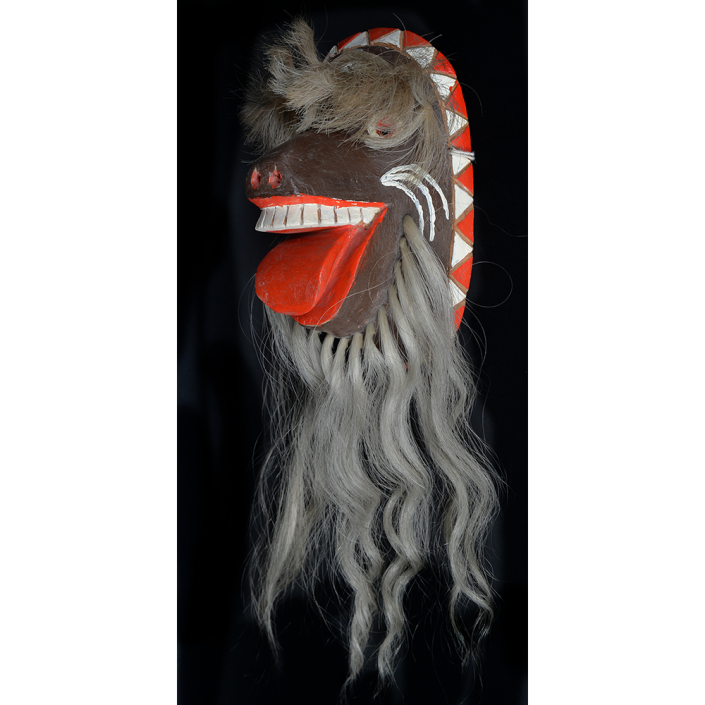
DESCRIPTION: Chrottni Mask
CATALOG ID: EUCH007
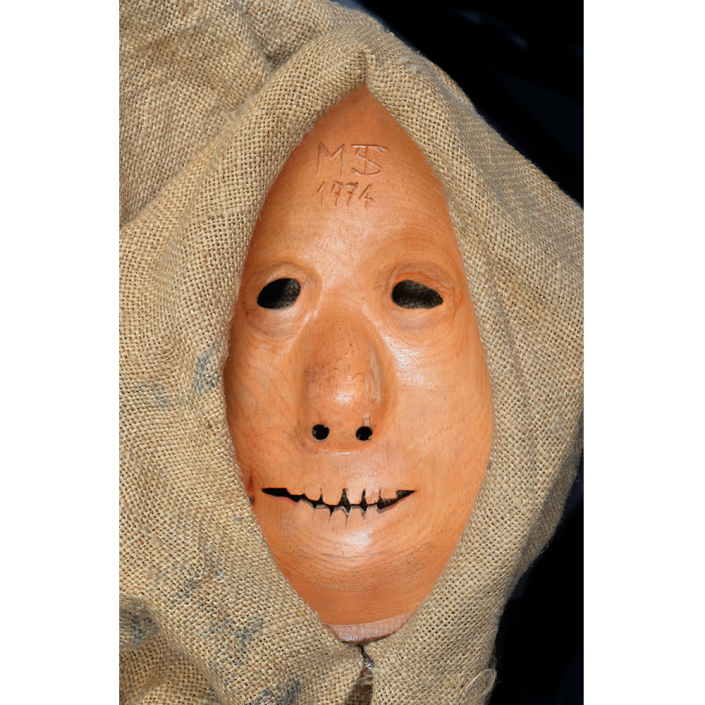
MAKER: Margrit Stoop (Flums, 1926-?)
CEREMONY: Fasnacht (carnival)
AGE: 1974
MAIN MATERIAL: wood
OTHER MATERIALS: paint; dyed burlap
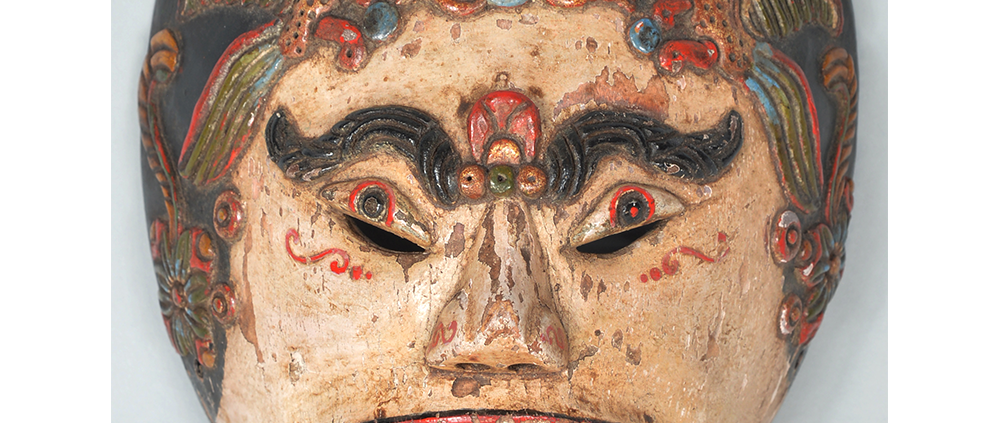
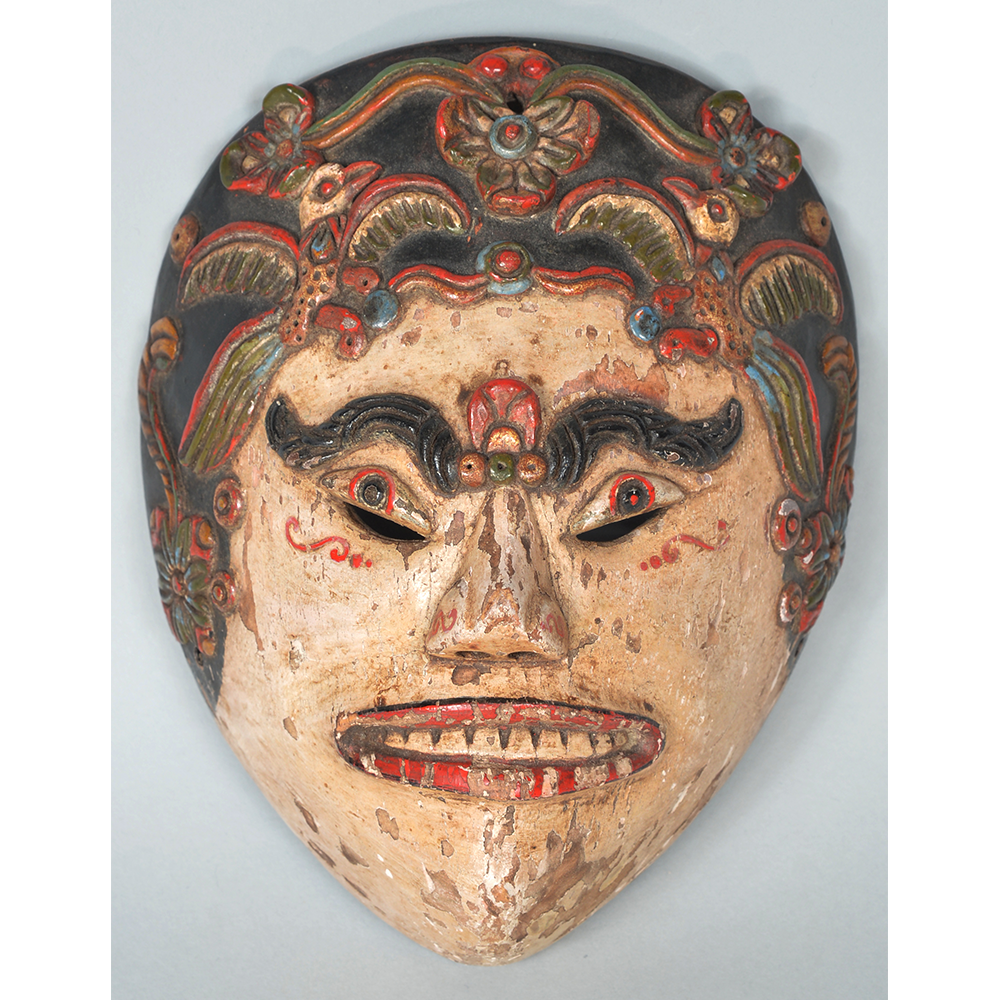
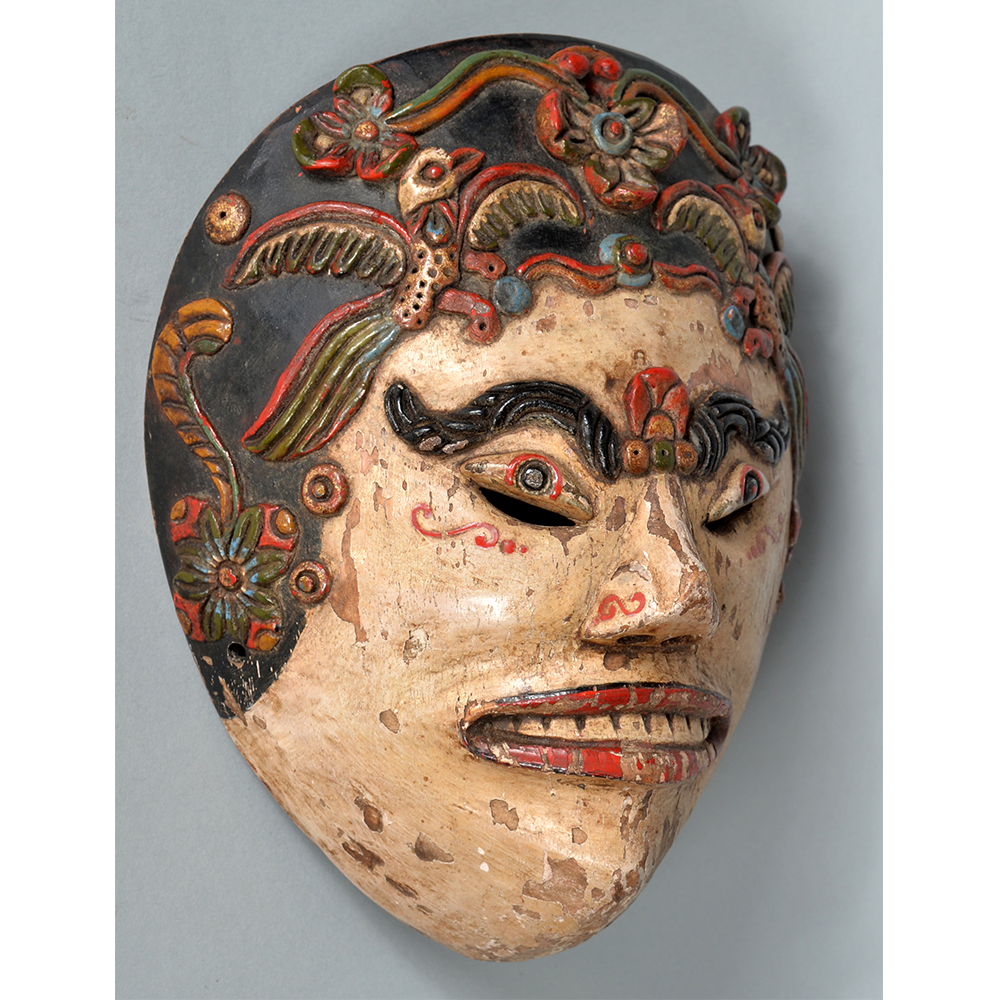
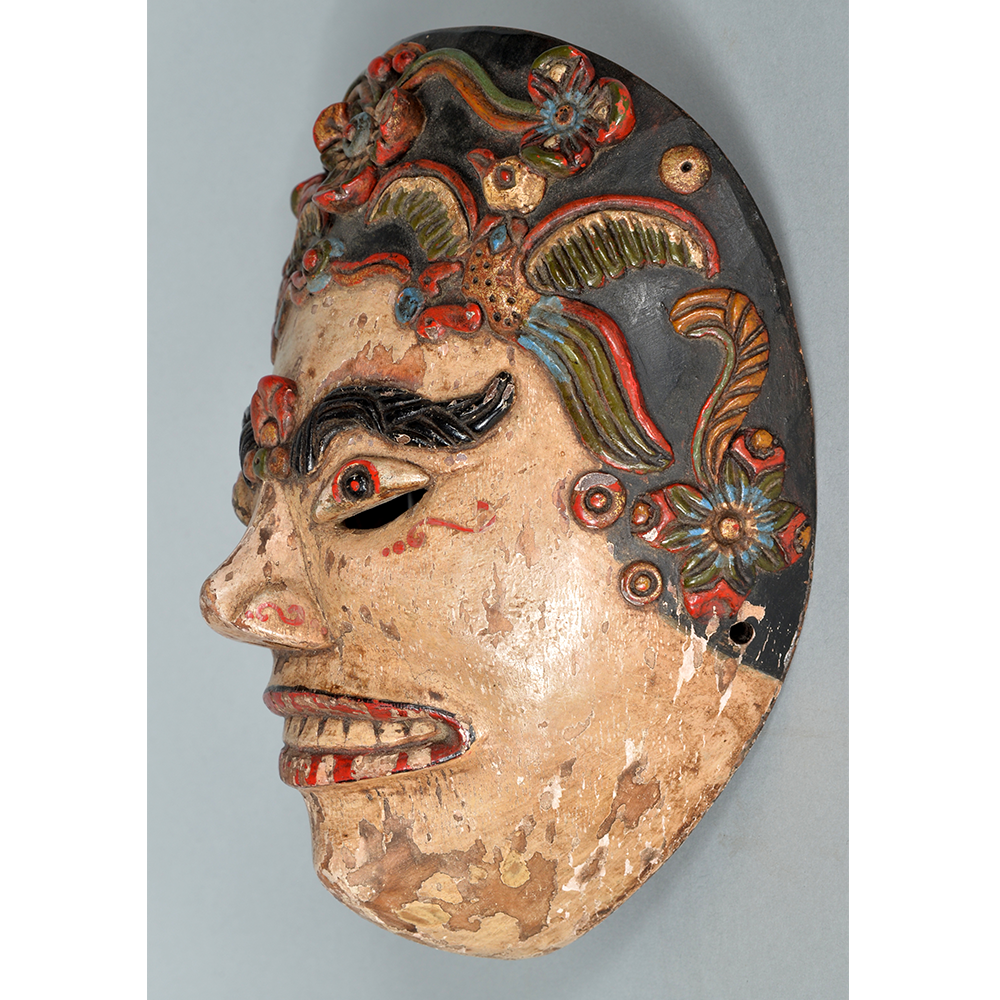
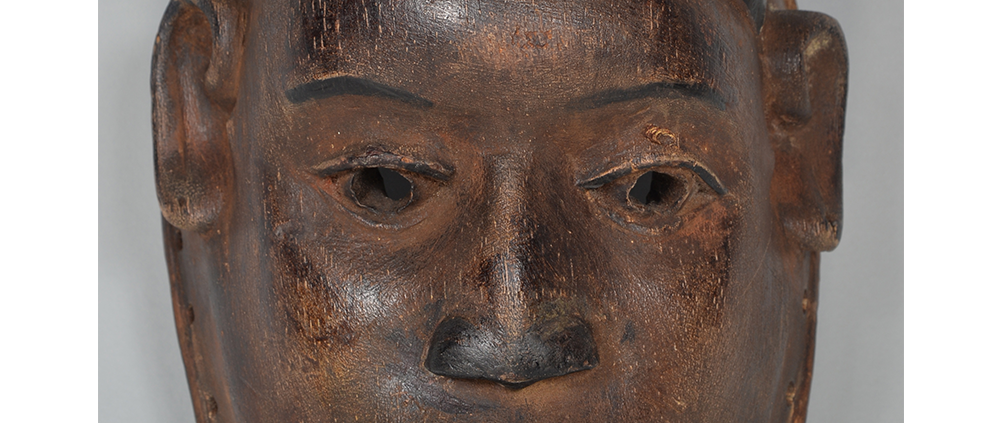
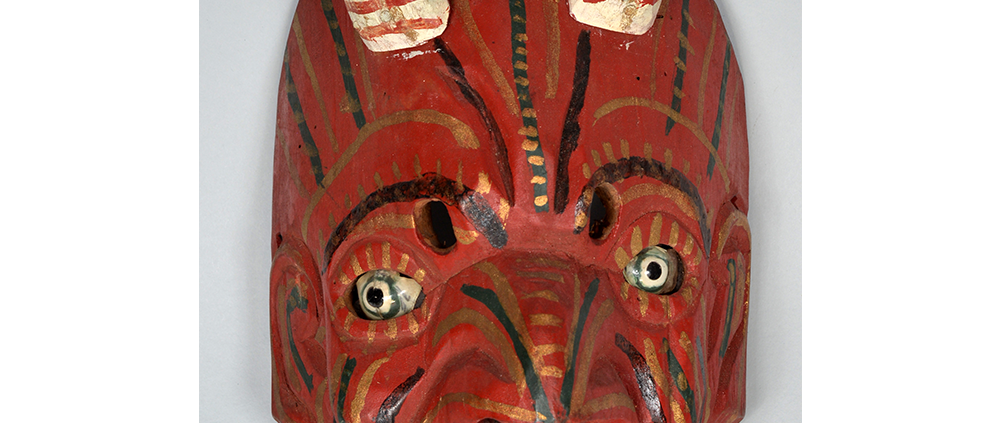
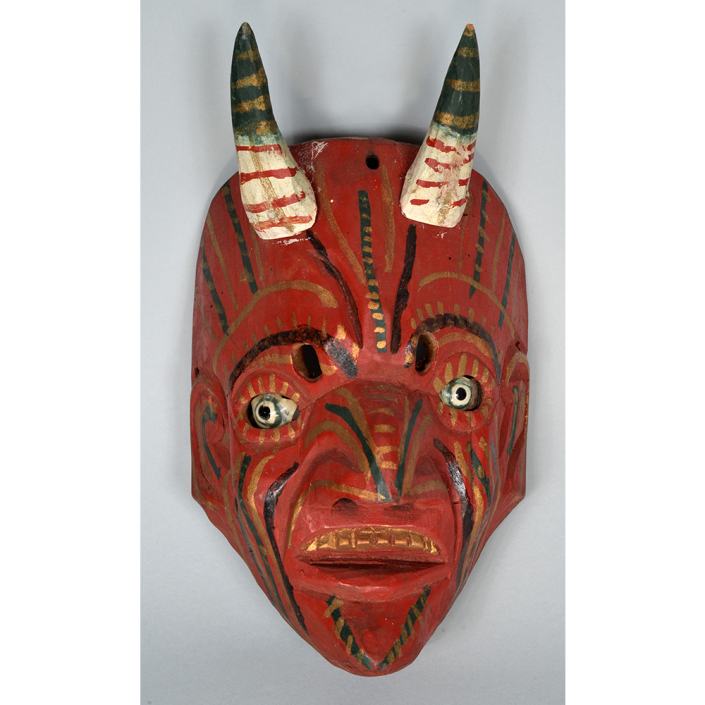
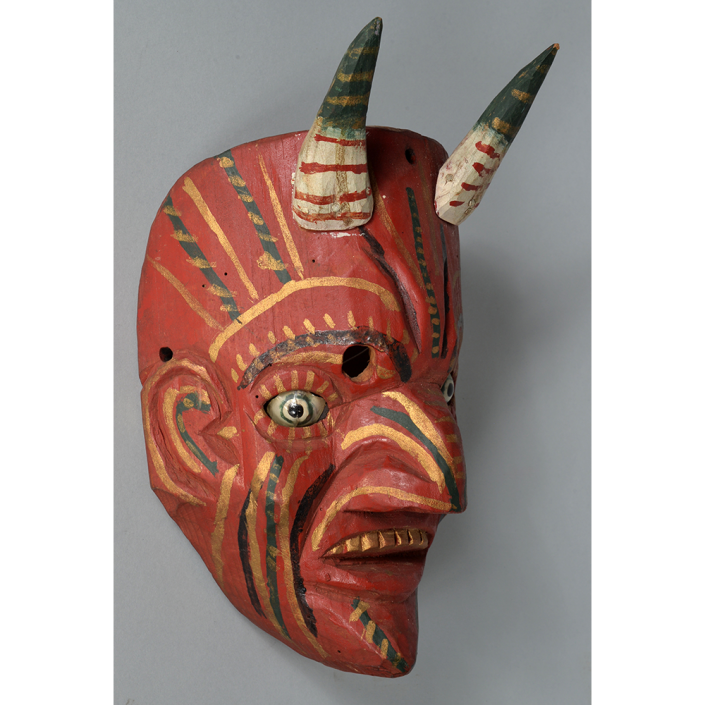
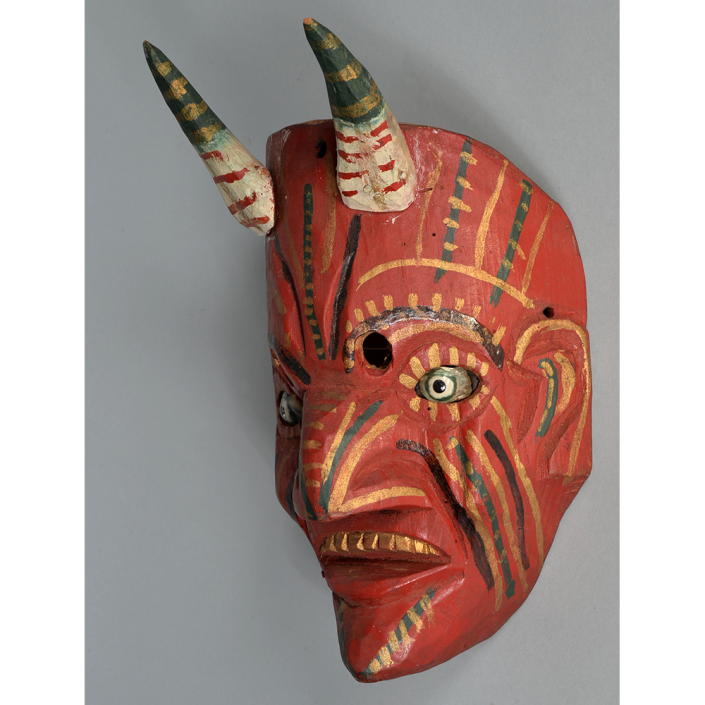
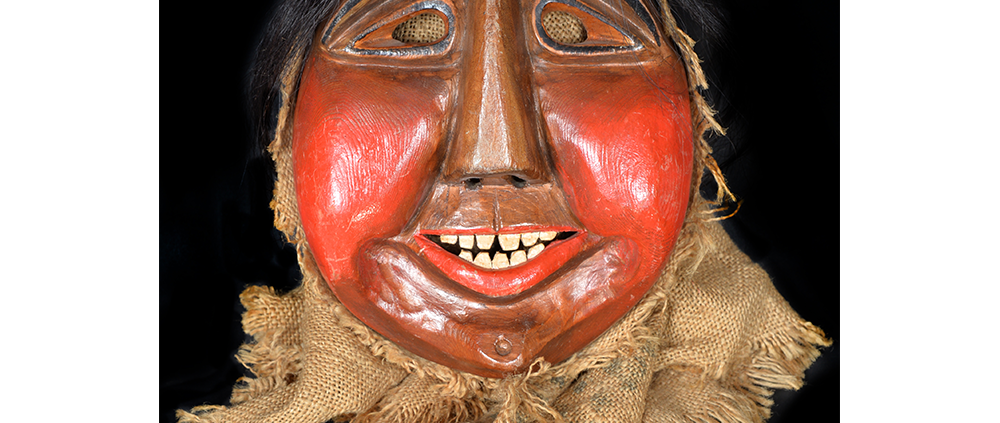
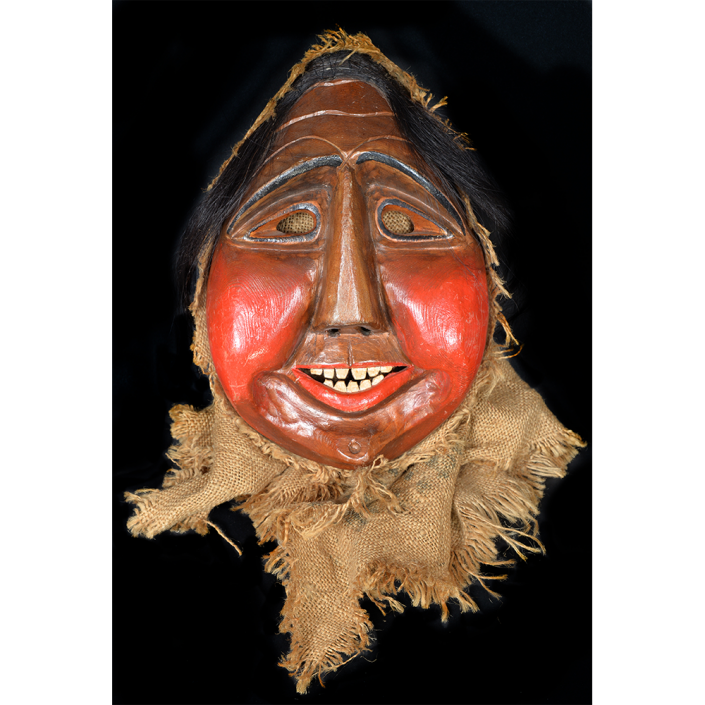
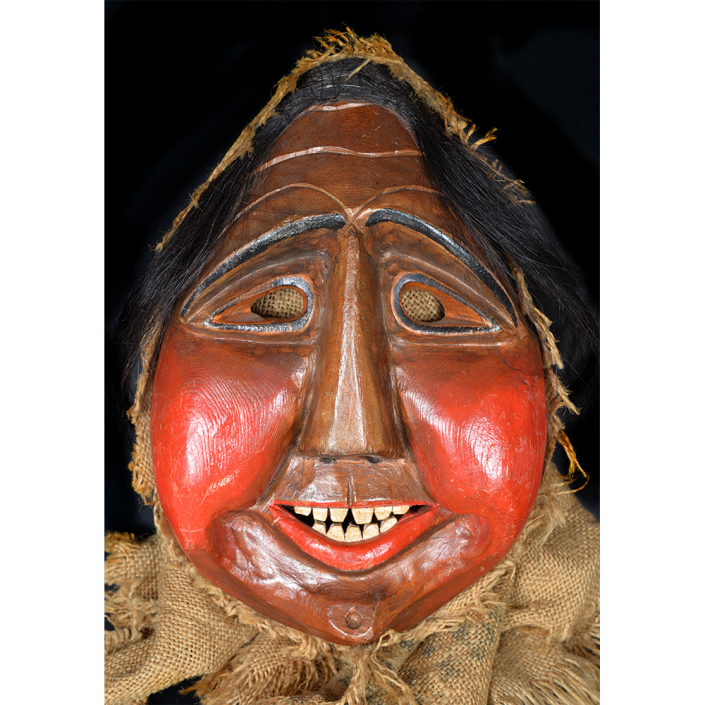
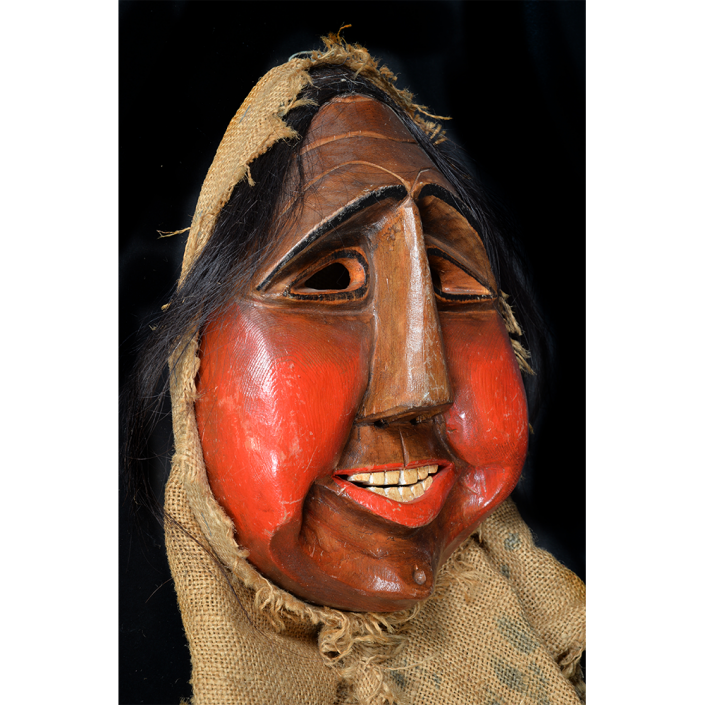
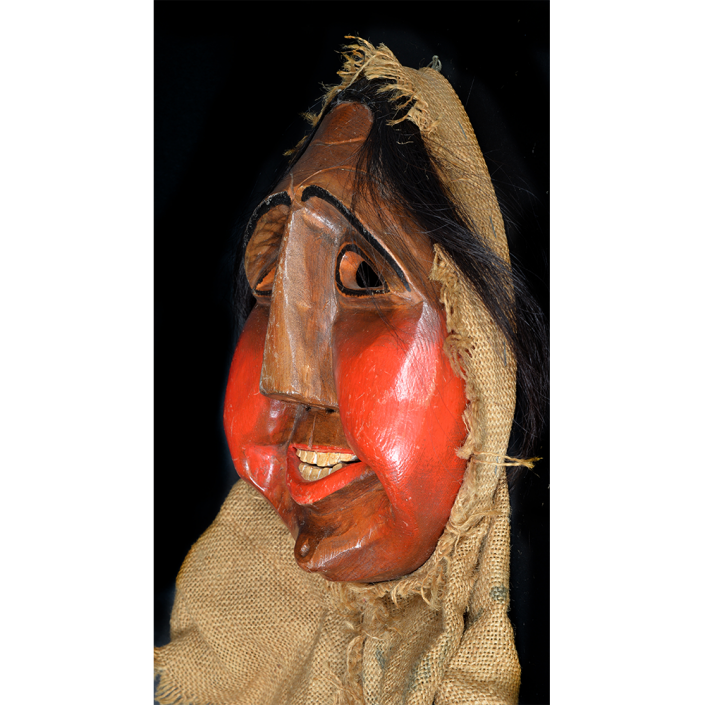
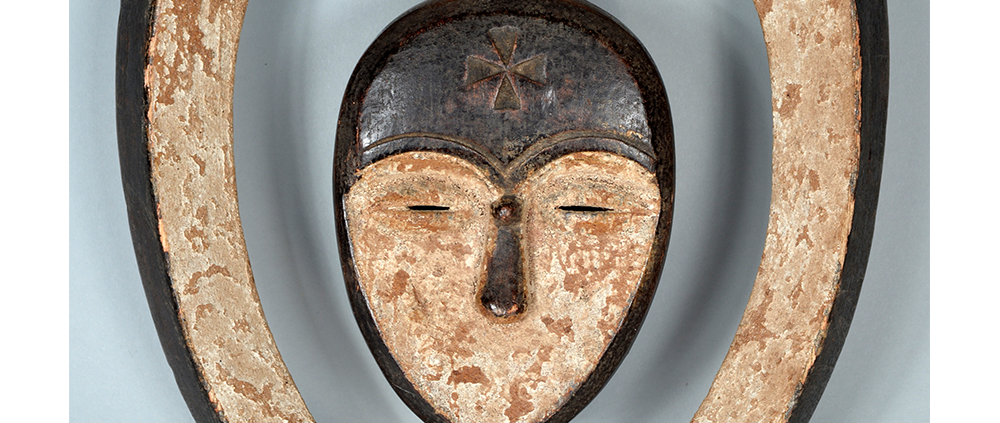
Fasnacht is what the Swiss call Carnival. In many towns in Austria, southern Germany, Switzerland, and northern Italy, local folk don elaborate masks and costumes to parade through the town. Different towns have variations on the parade, such as the Schemenlaufen of Imst, the Schellerlaufen of Nassereith, and the Muller and Matschgerer of Innsbruck, Austria. In Flums, carnival masks have a distinctive pear shape and tend to have a satirical purpose. The Flums style has been highly influential in neighboring villages.
This mask is a character known in the local dialect as Chrottni, a masculine looking woman who has been suggested to represent a hermaphrodite. The name probably derives from the word Kröte, a toad. Local legend has it that Chrottni lampoons a postman’s wife, who always knew everyone’s business before they themselves did, because she secretly opened the mail. The type was developed around 1840, and different carvers in Flums give it variants on its expression. Among the five most common expressions, this one is said to represent a Mona Lisa-type smile.
Unfortunately, the best book on Swiss masking traditions is available in German only: Albert Bärtsch, Holzmasken: Fasnachts- und Maskenbrauchtum in der Schweiz, in Süddeutschland und Österreich (AT Verlag 1993).