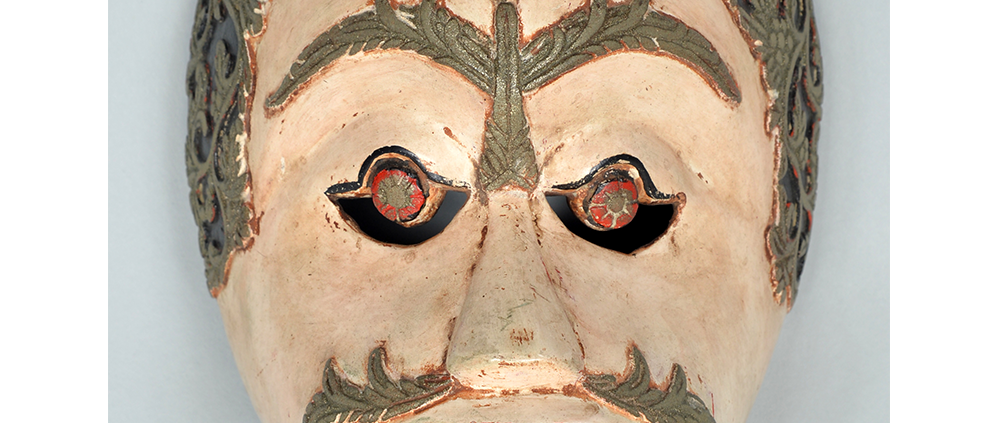
TITLE: Maximón Mask
TYPE: face mask
GENERAL REGION: Latin America
COUNTRY: Guatemala
SUBREGION: Solalá
ETHNICITY: Mayan
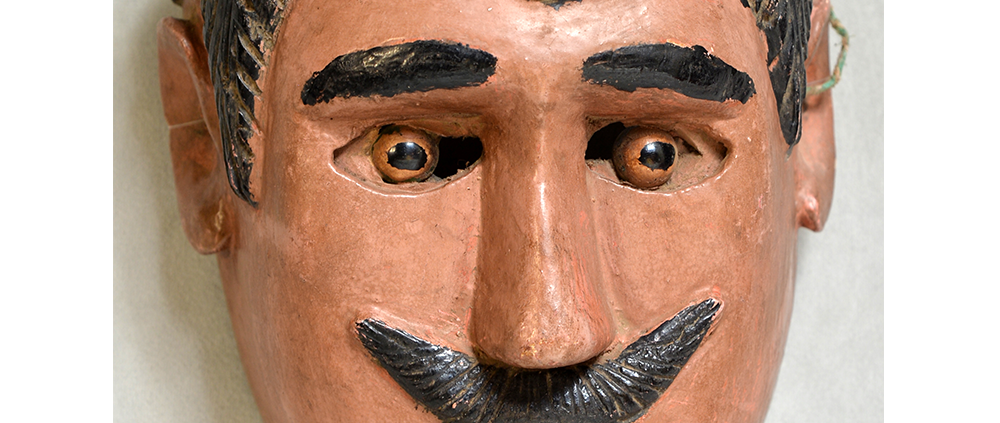
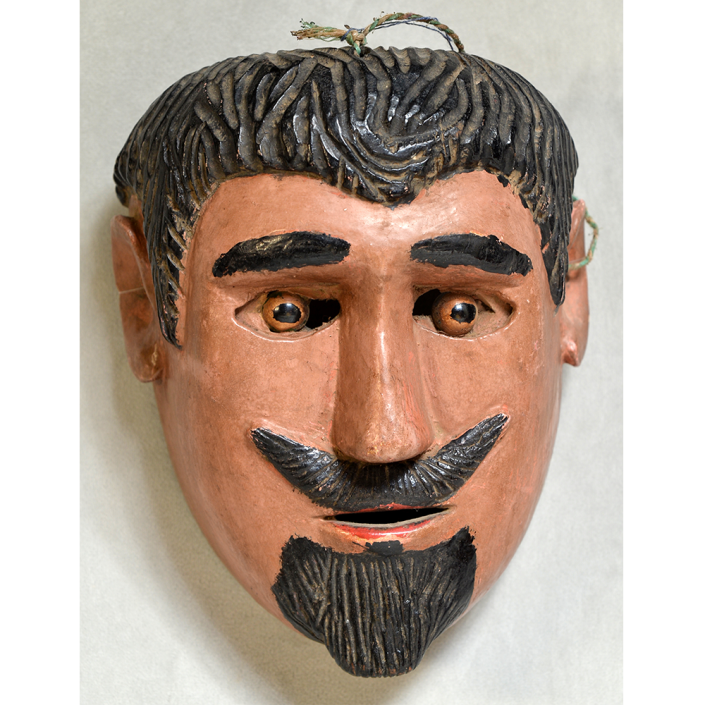
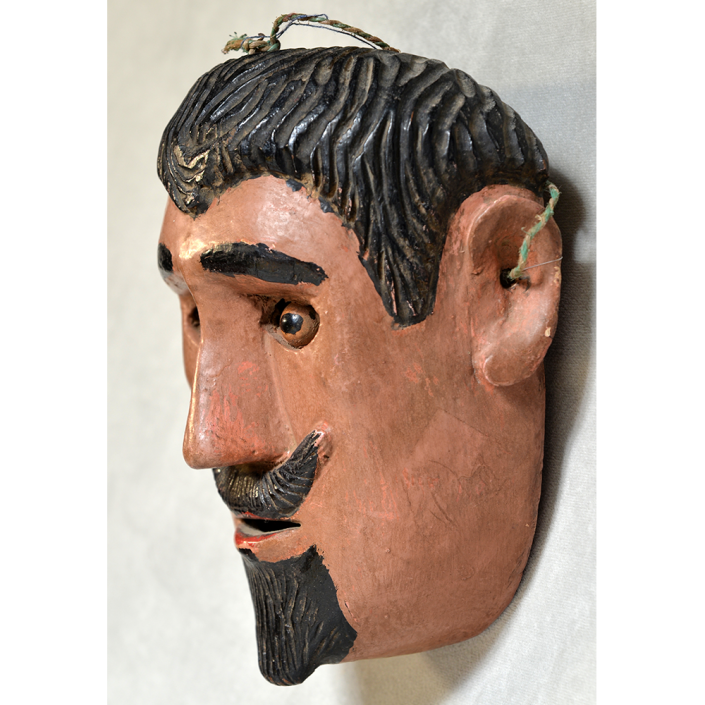
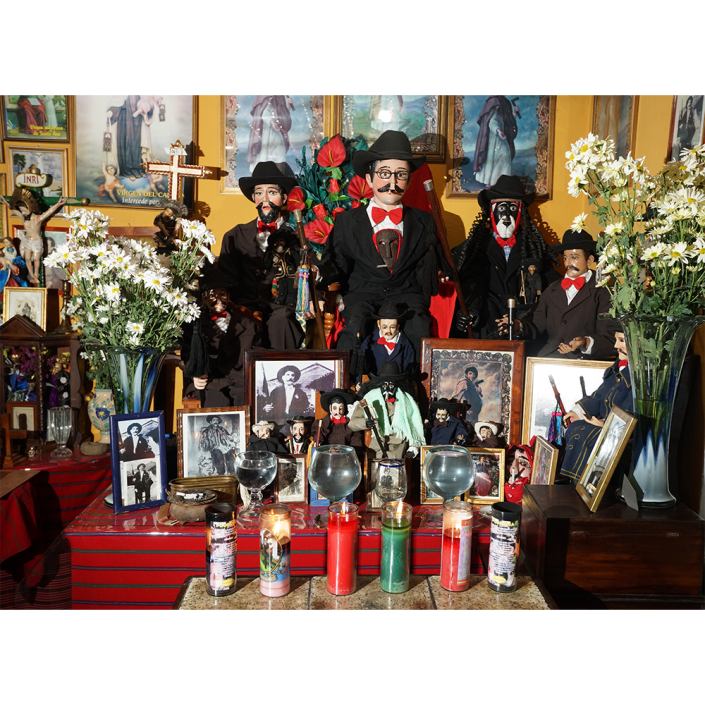
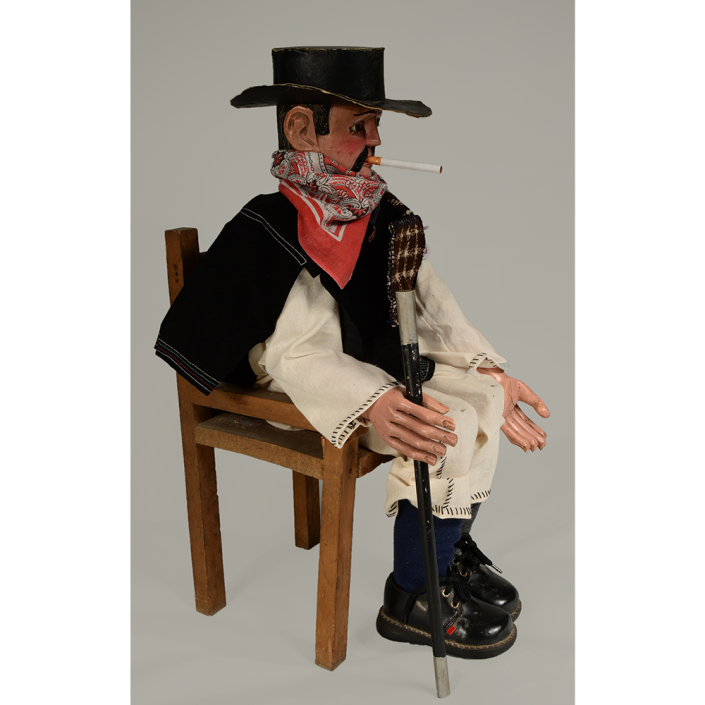
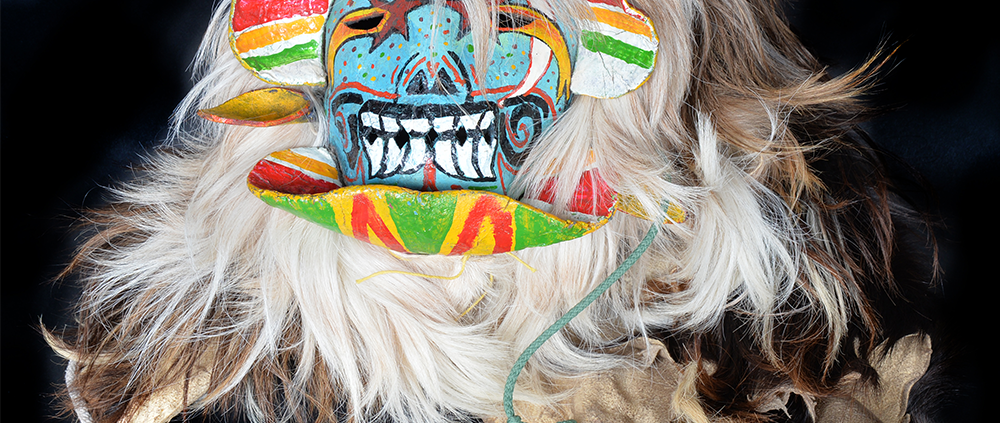
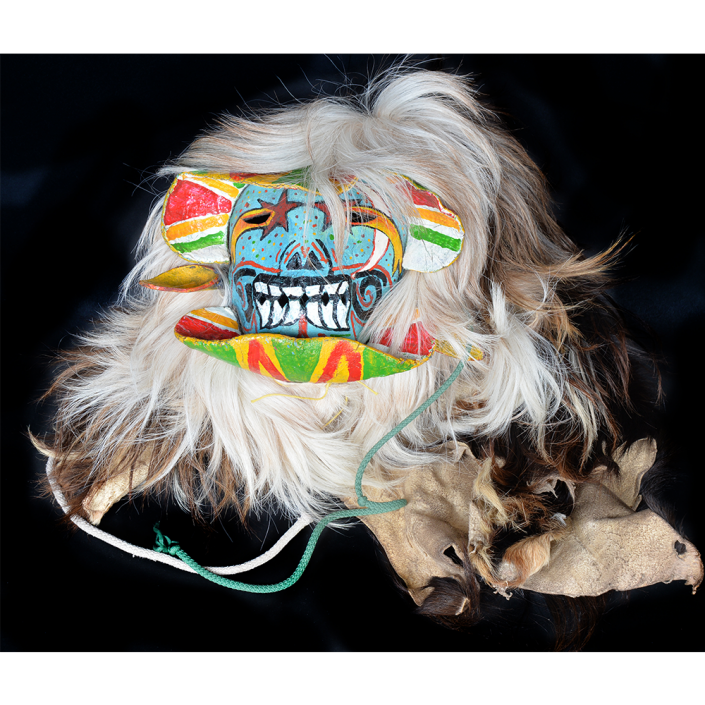
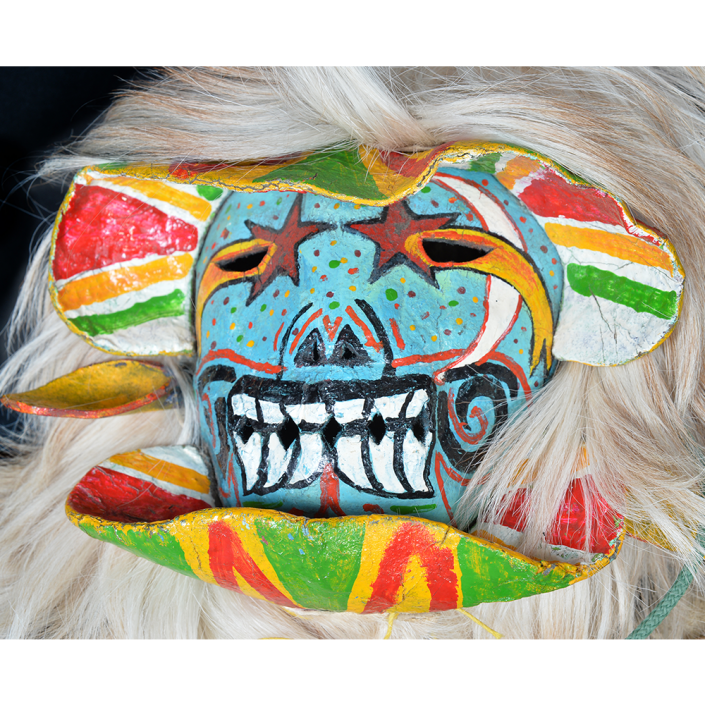
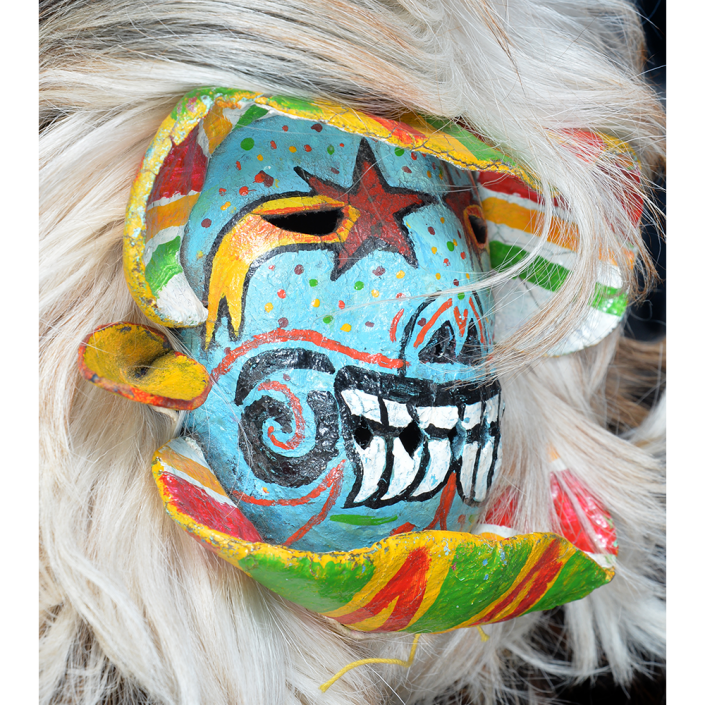
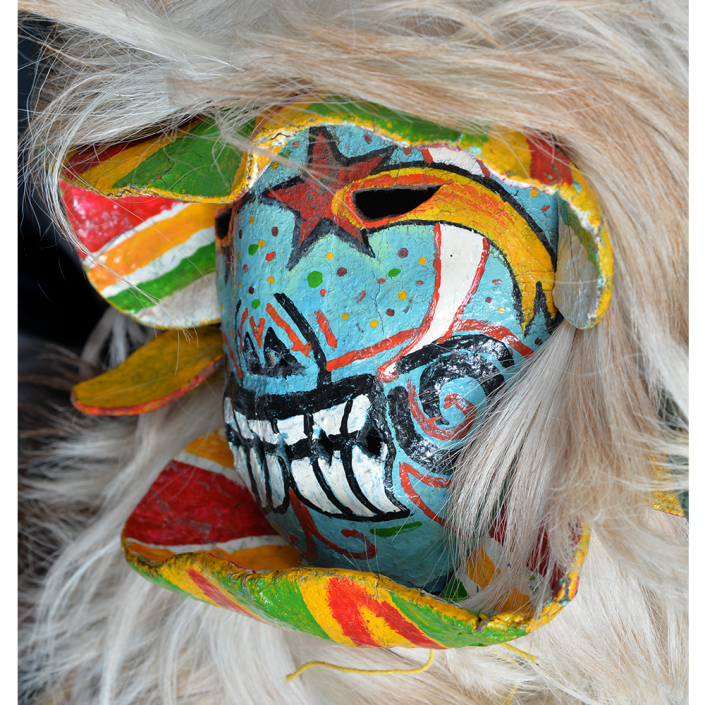
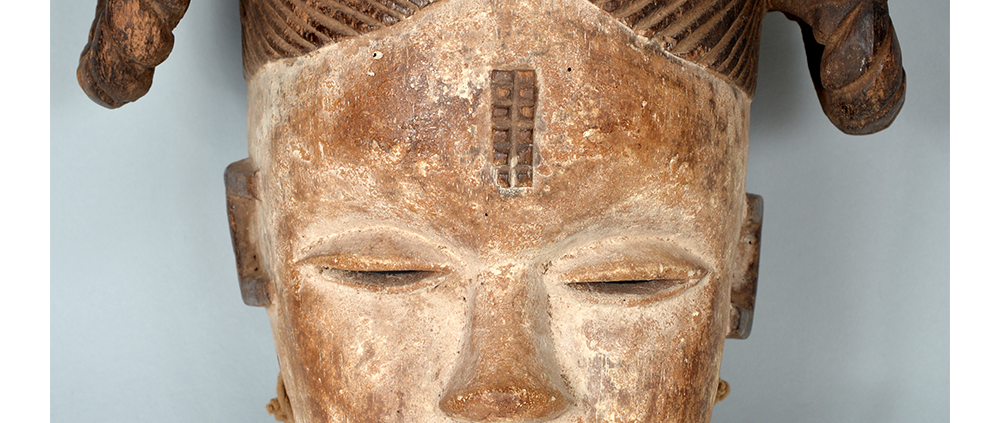
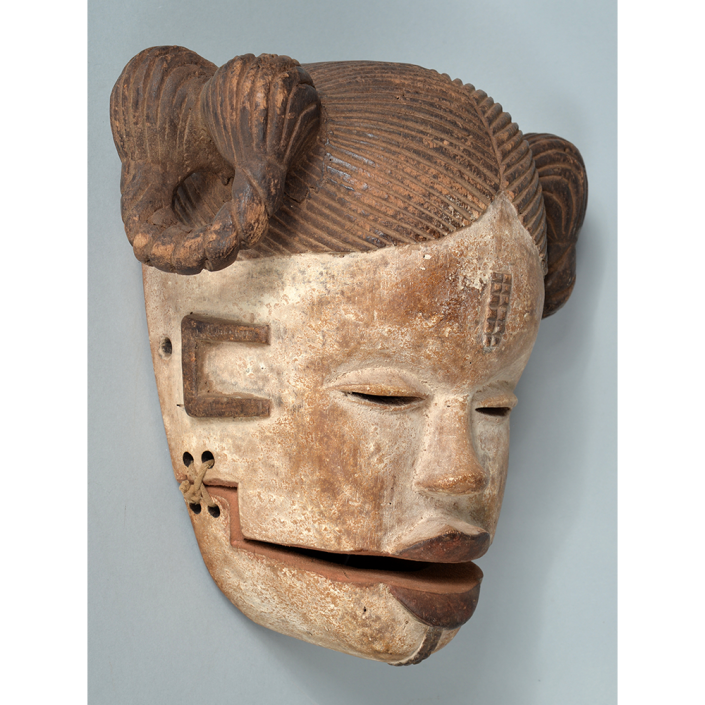
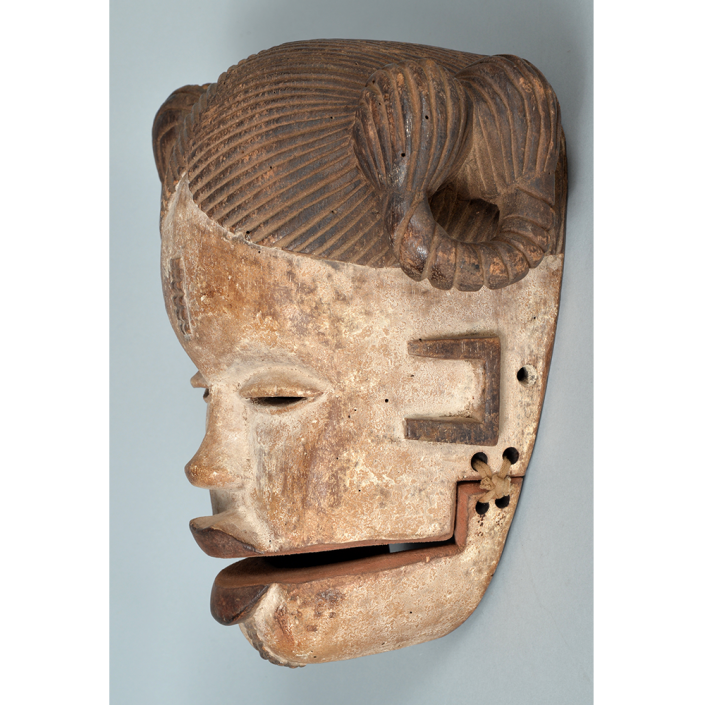
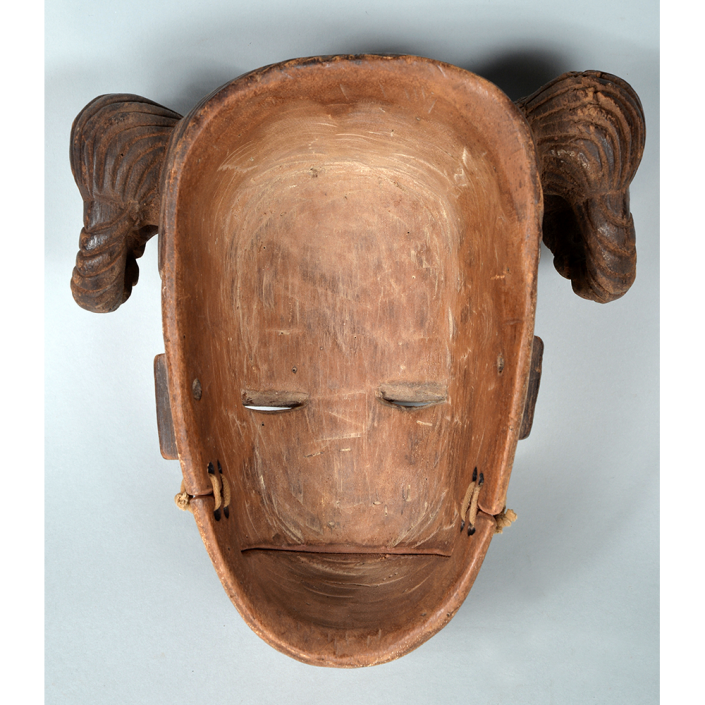
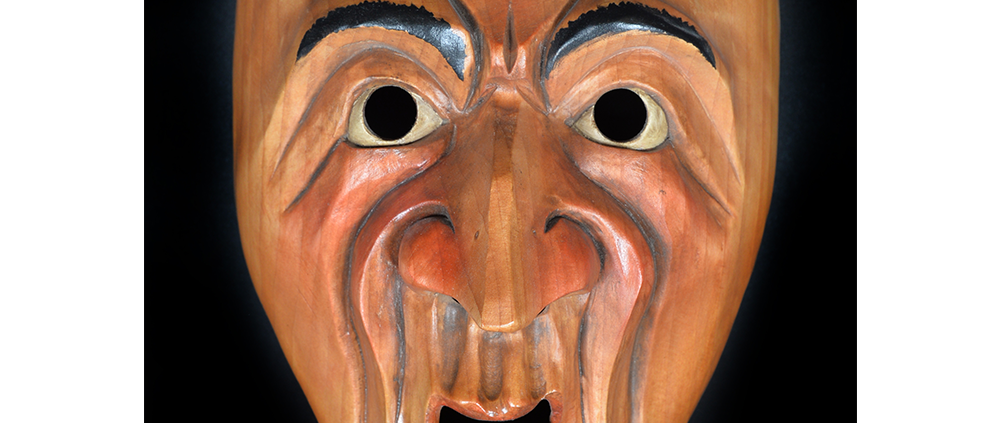
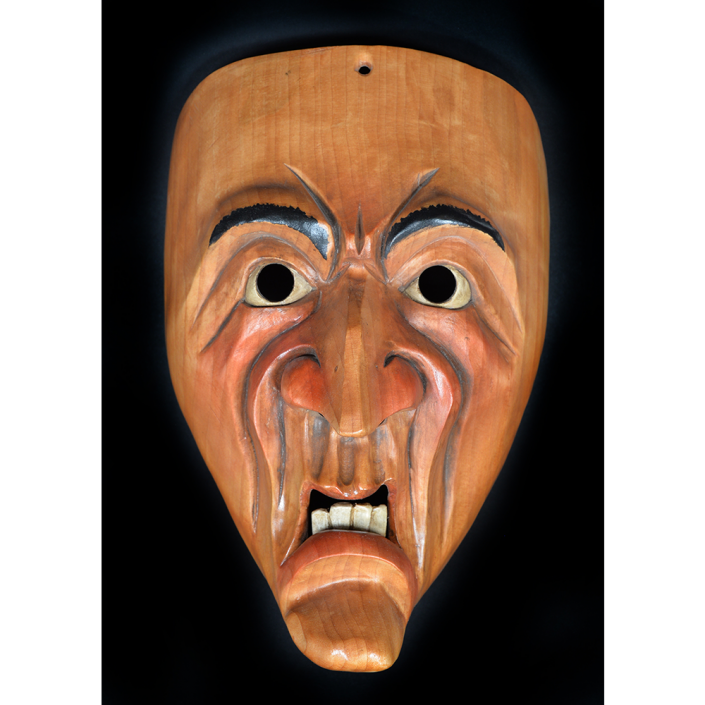
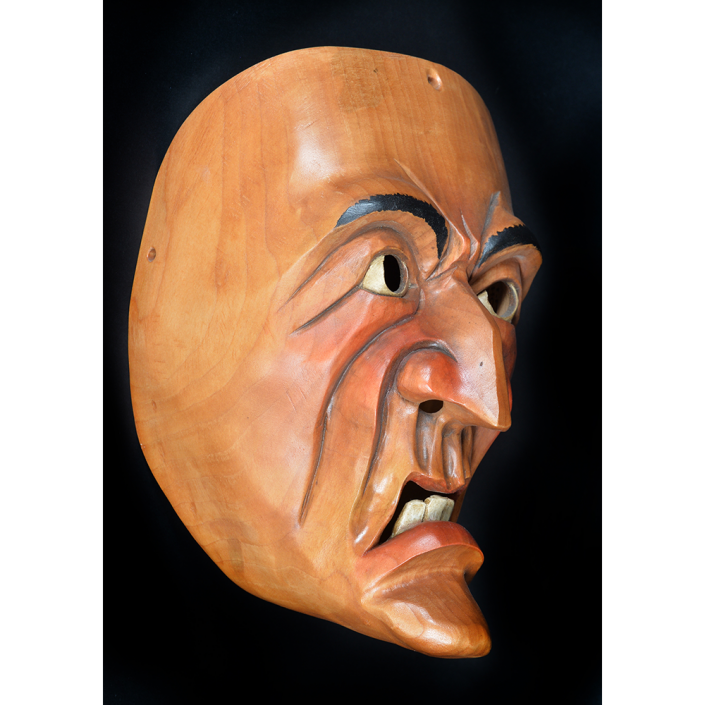
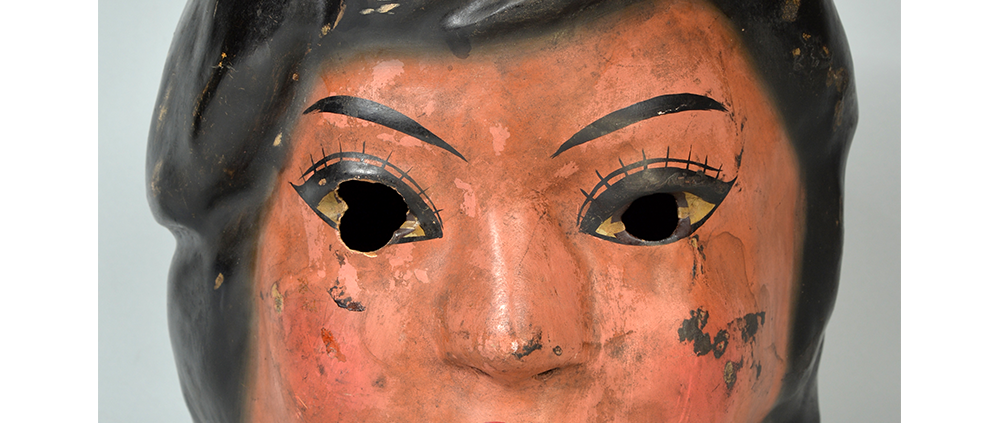
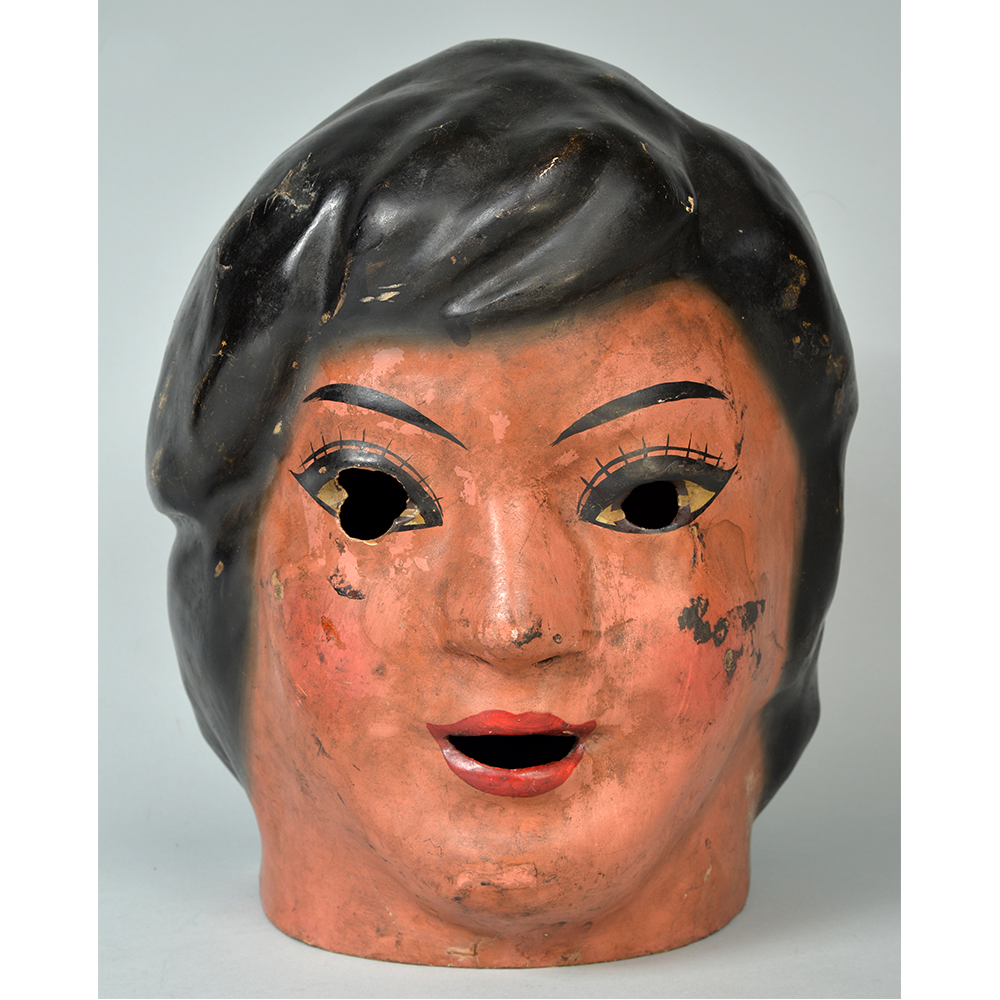
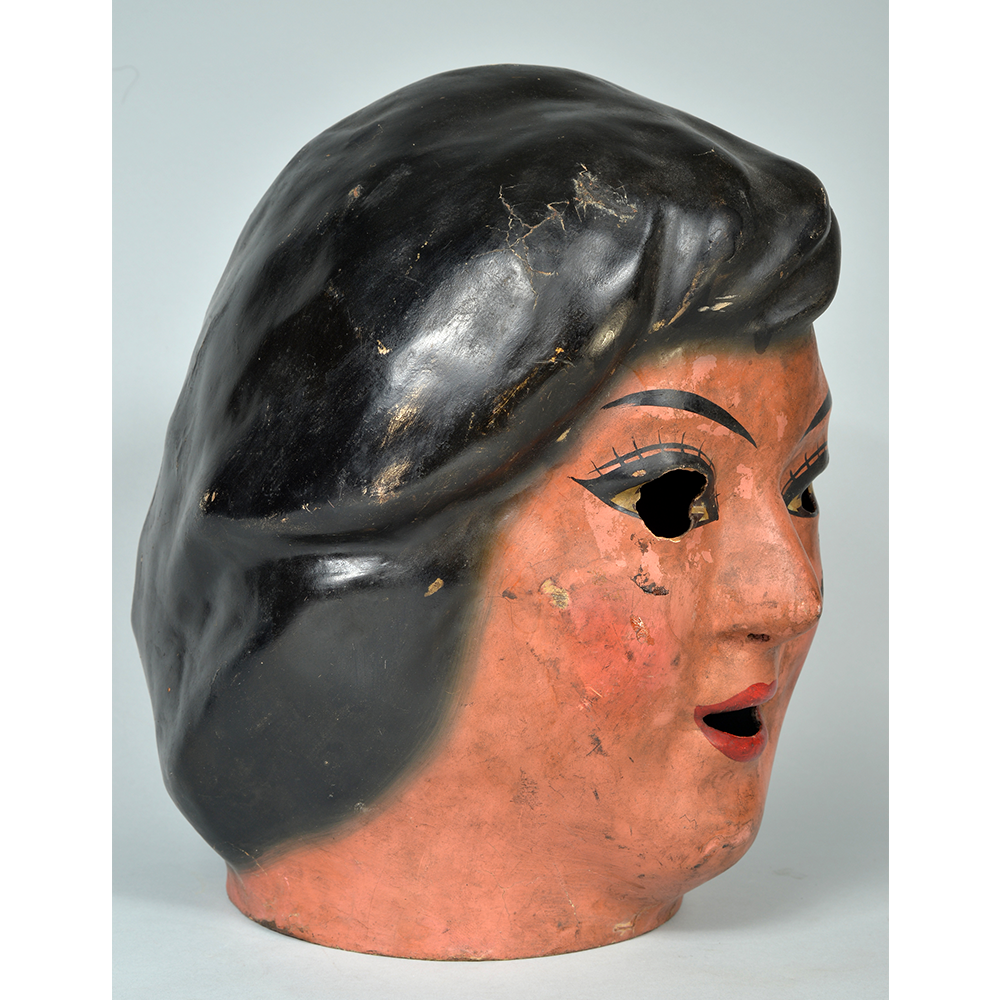
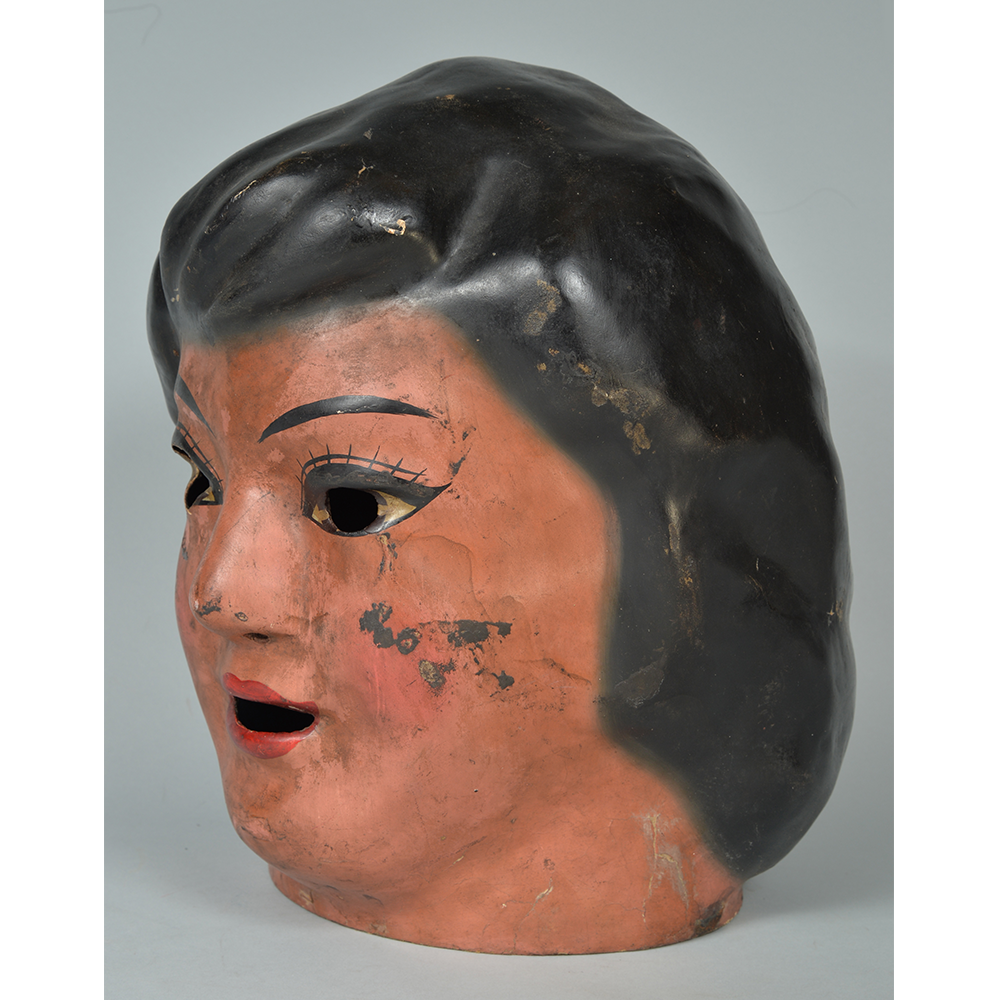
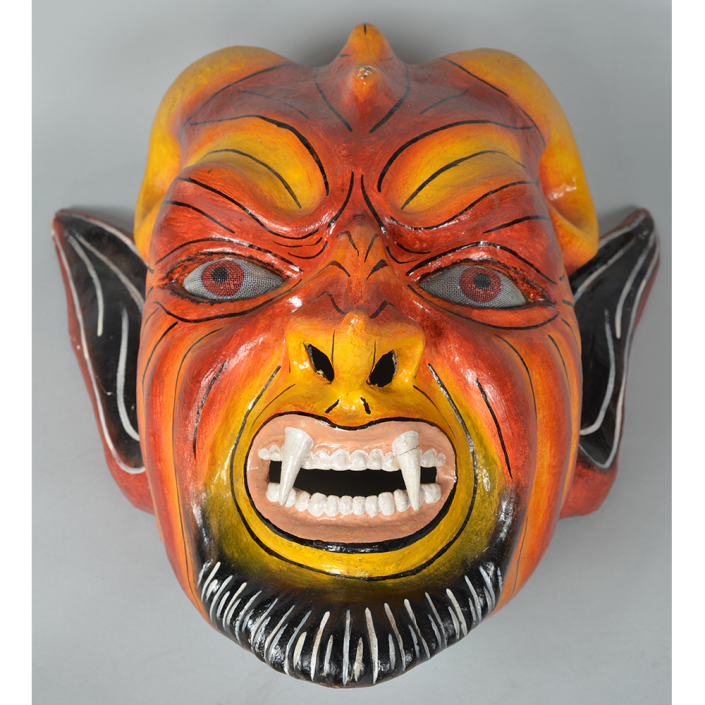
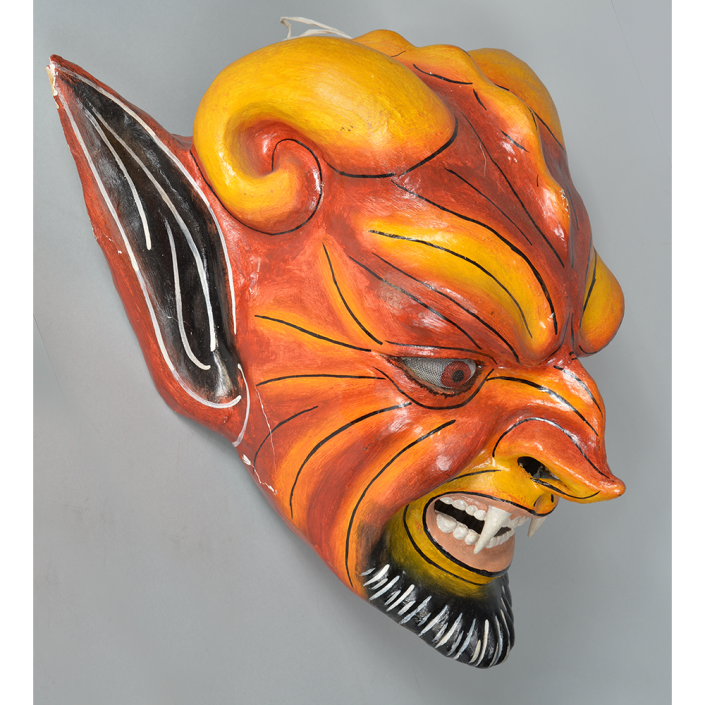
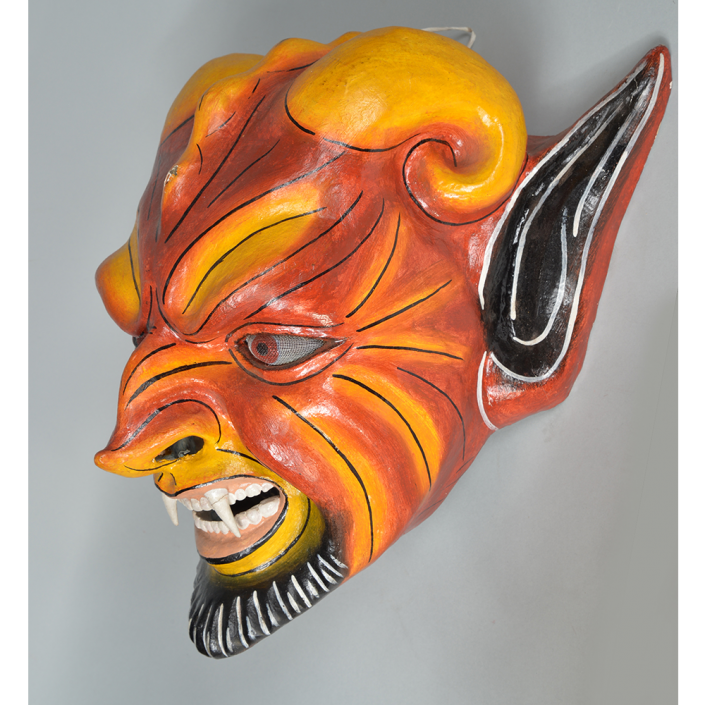
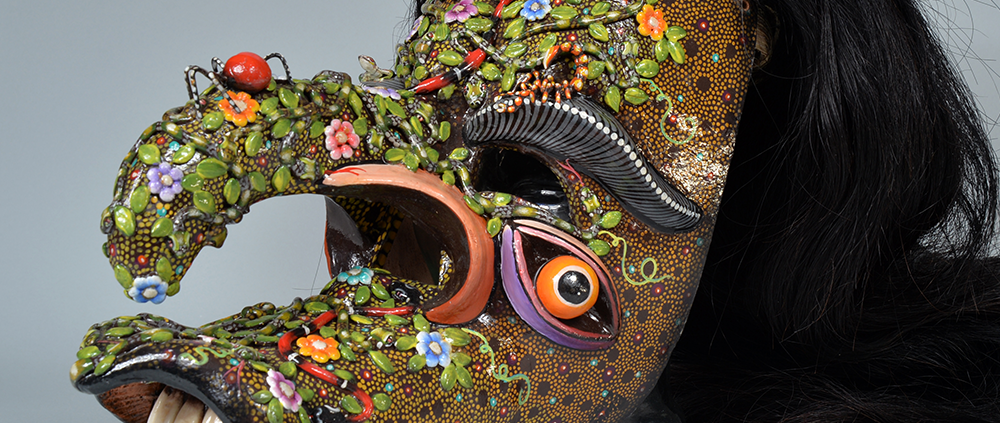
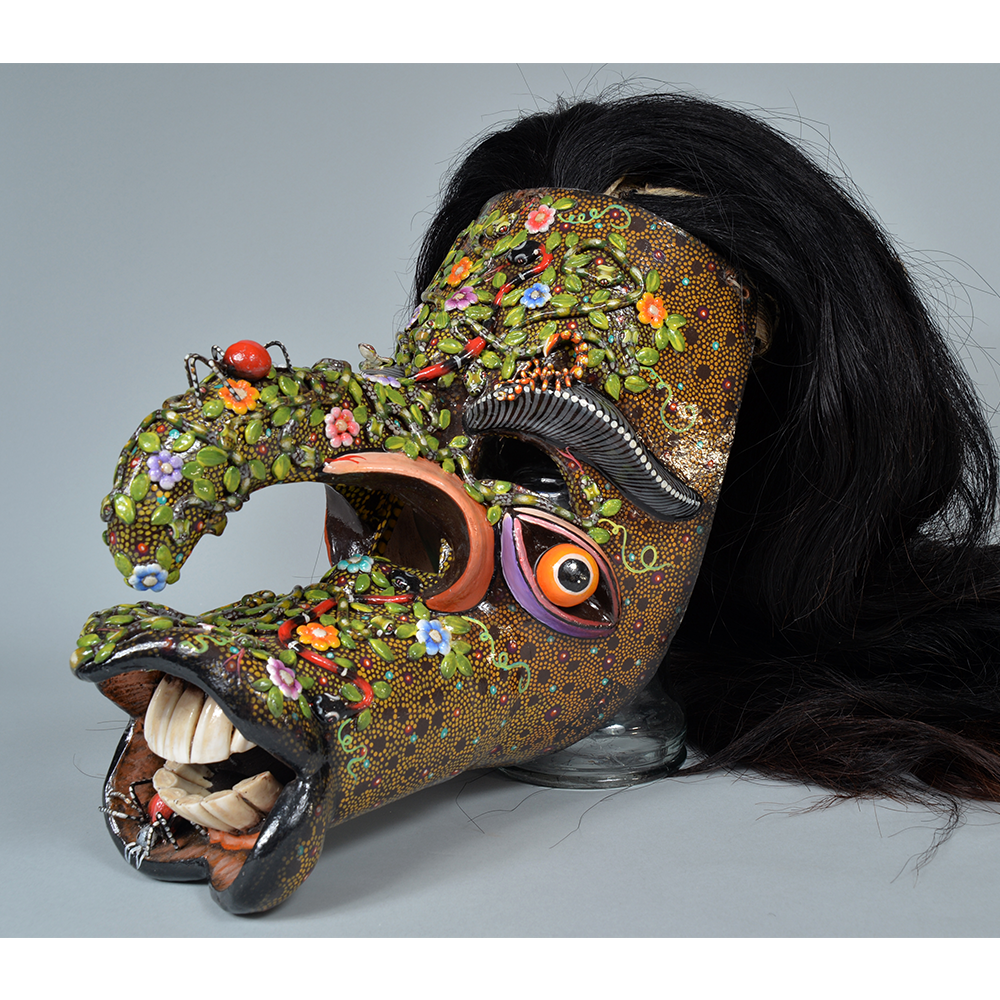
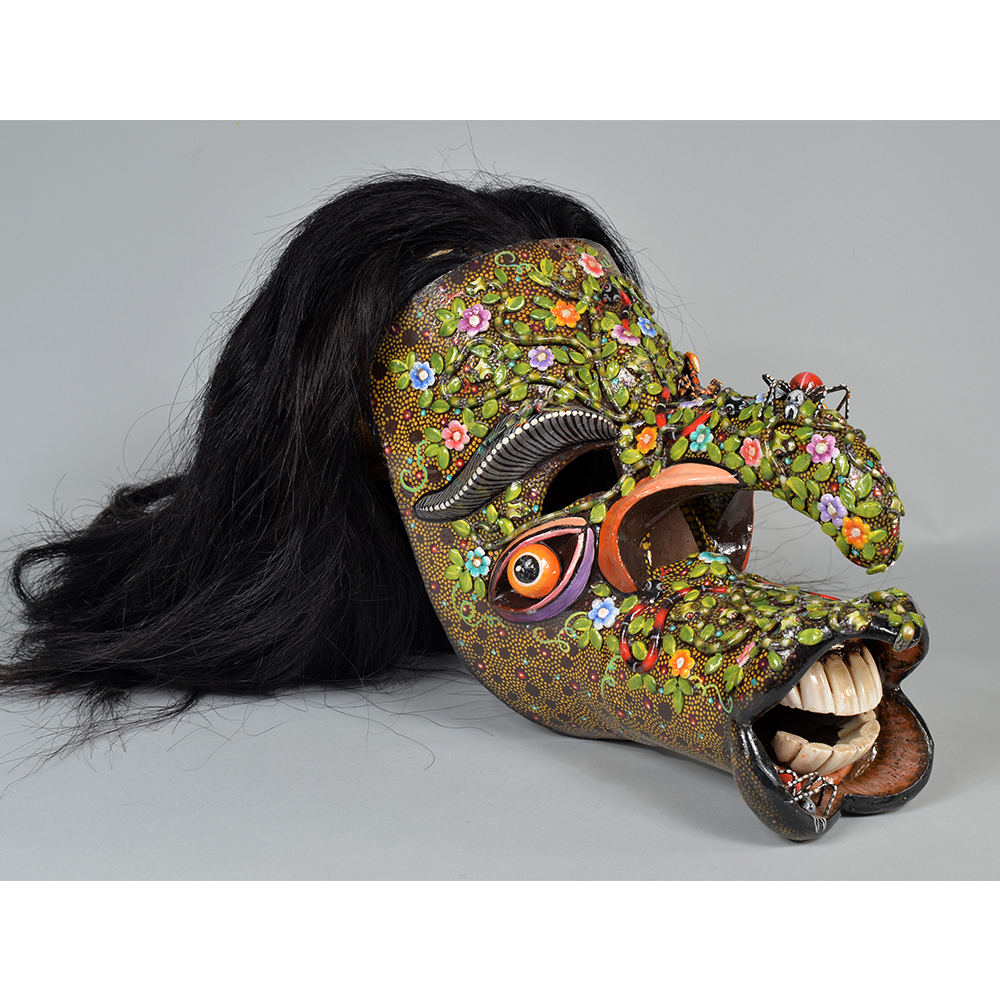
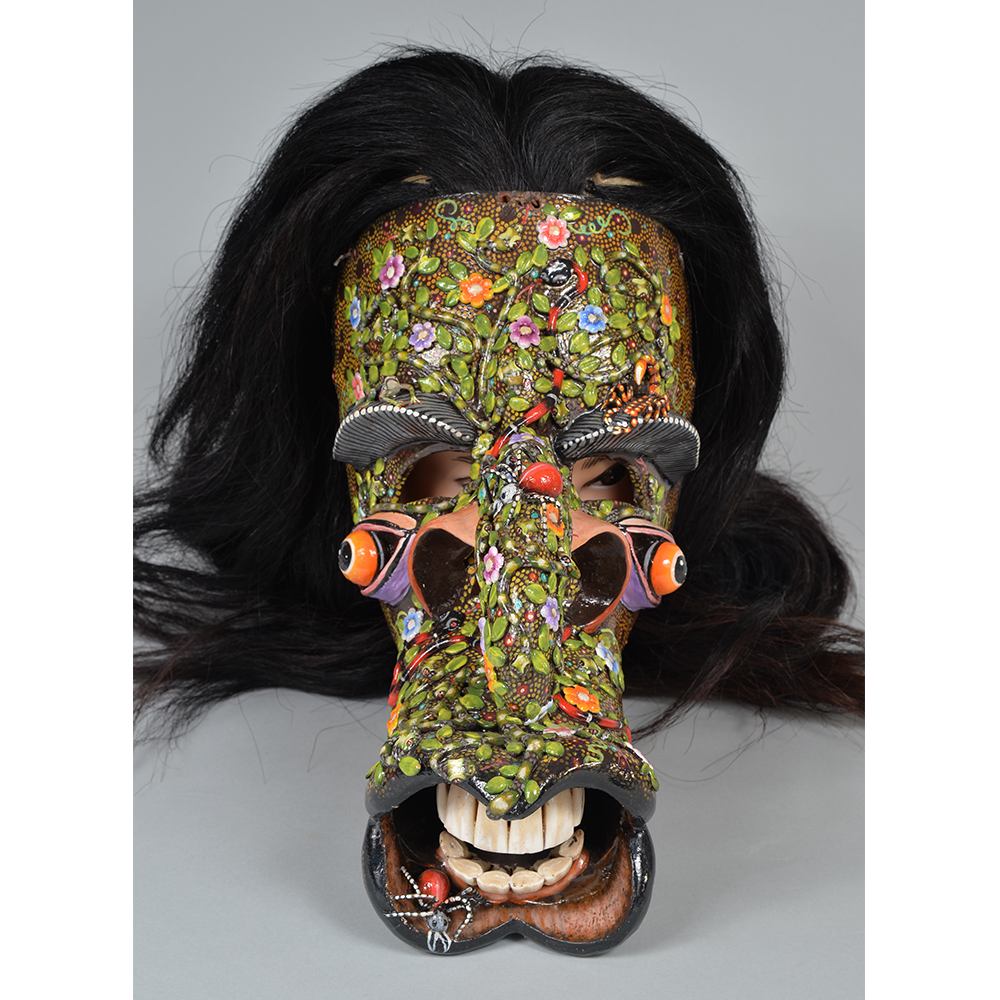
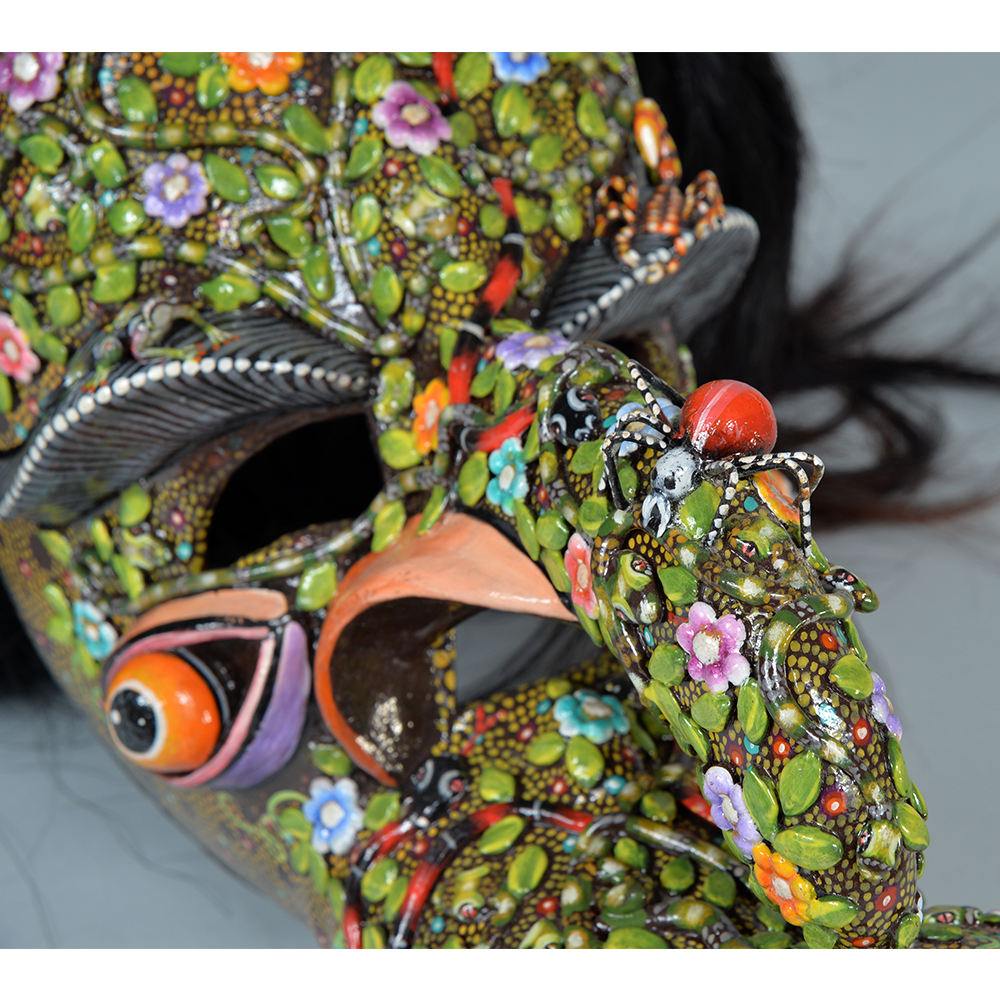
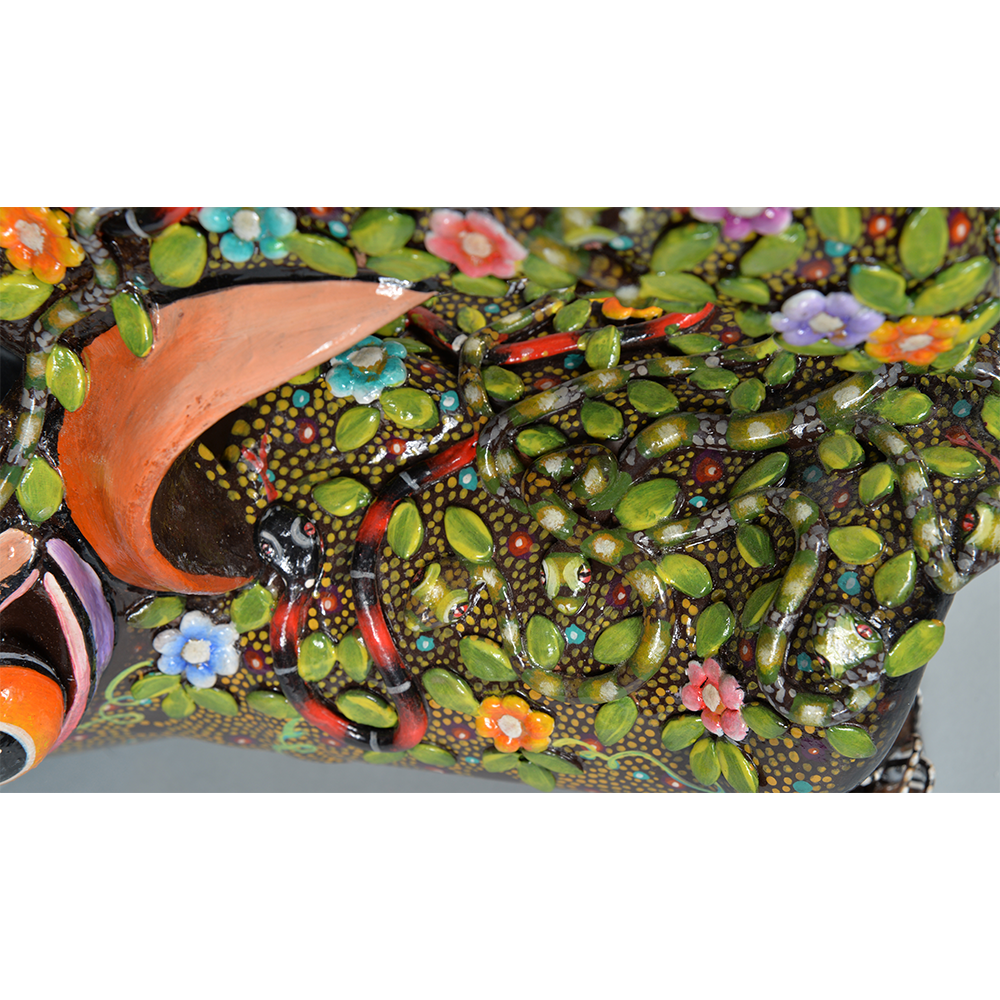
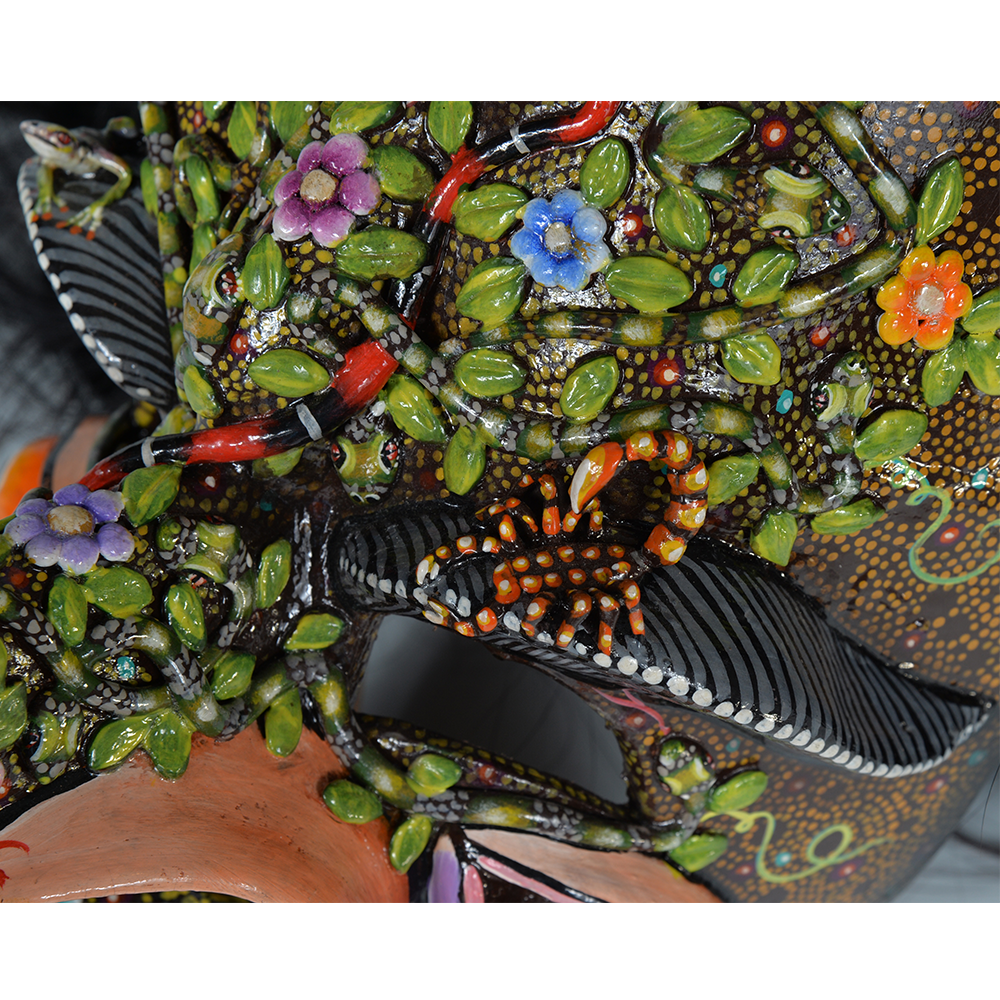
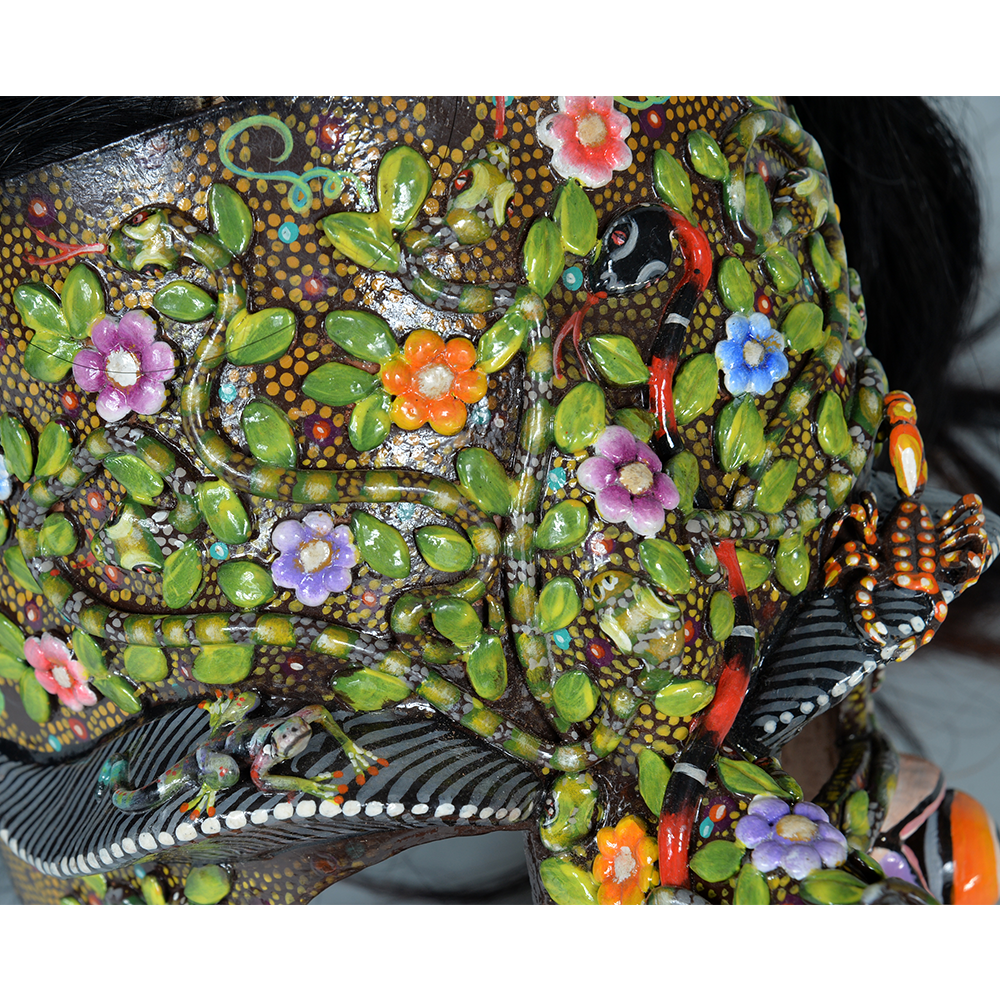
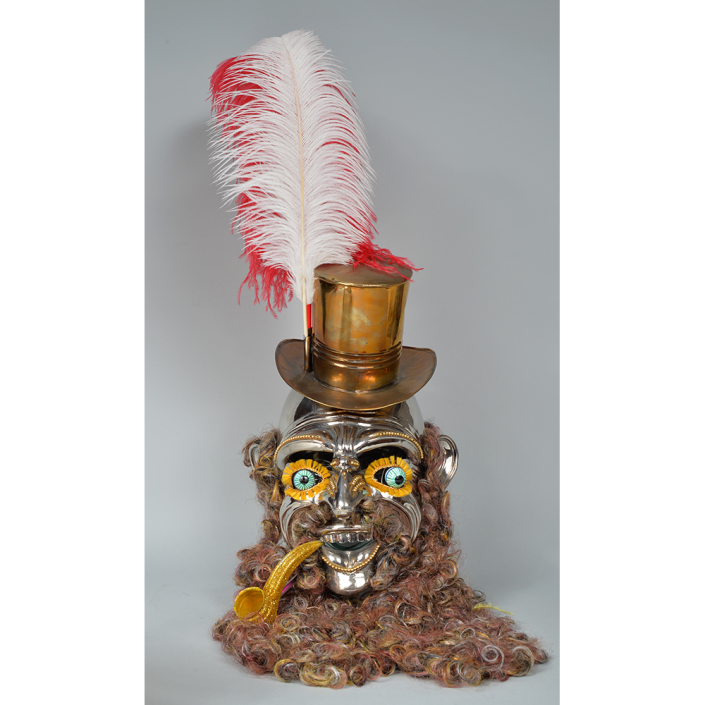
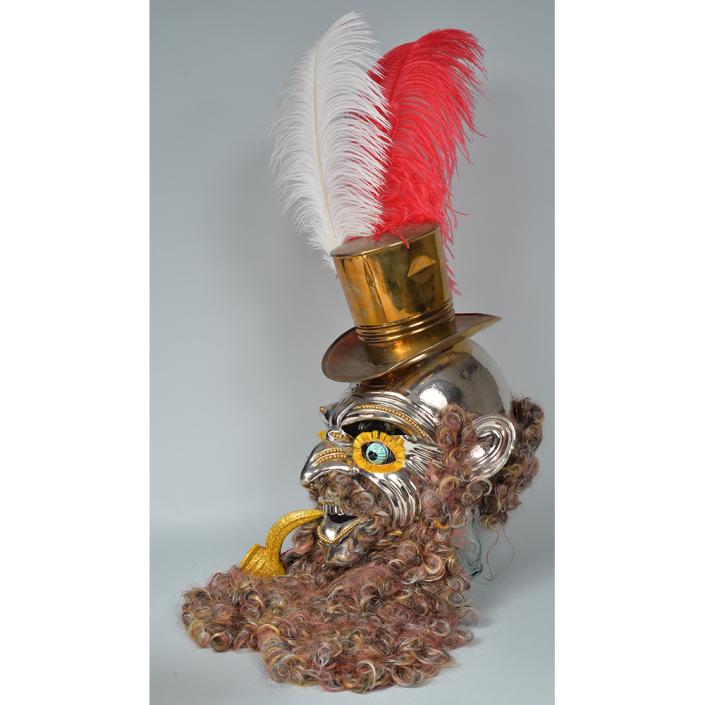
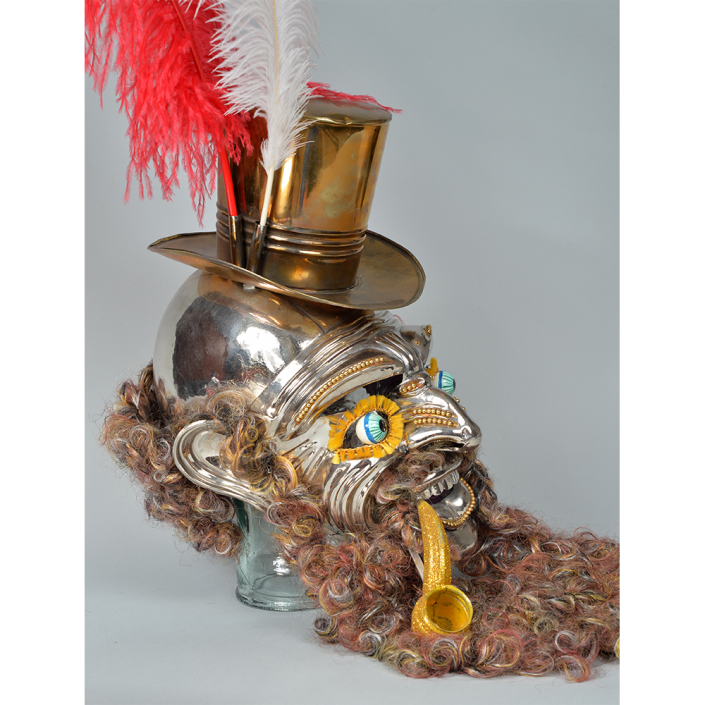
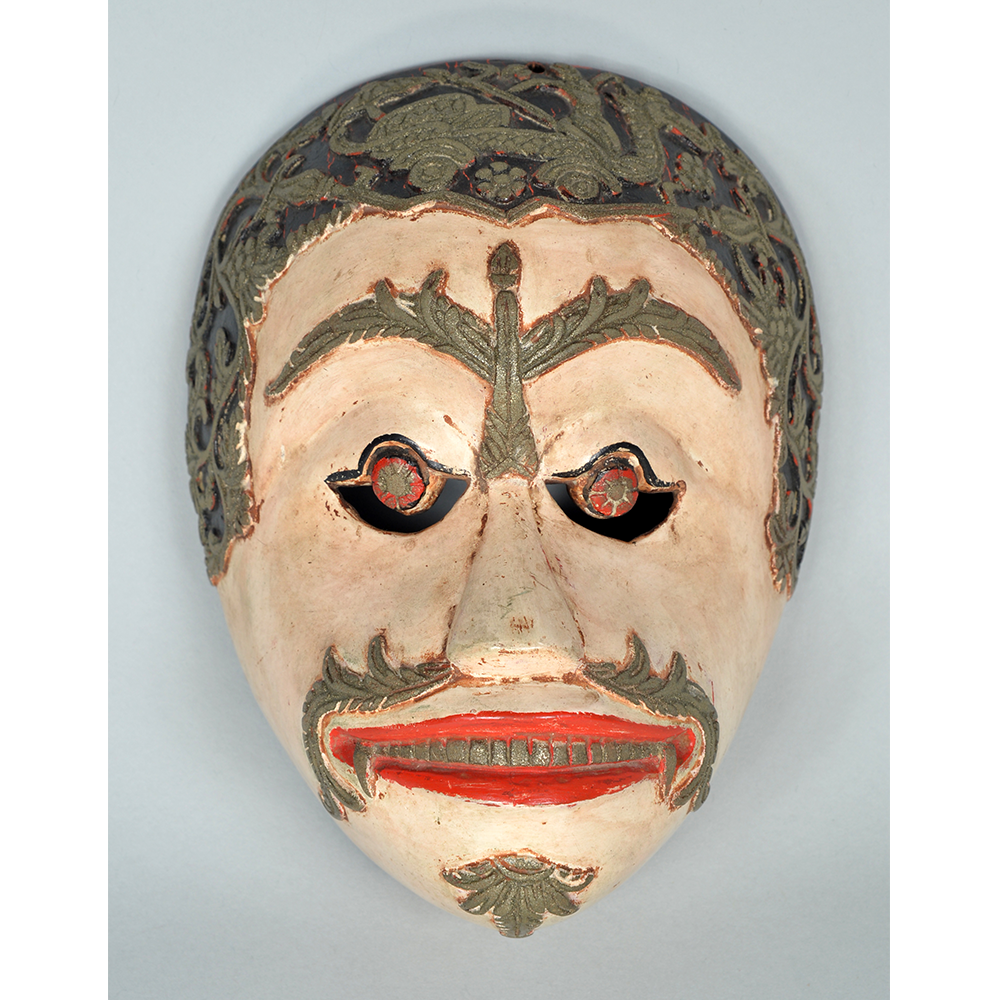
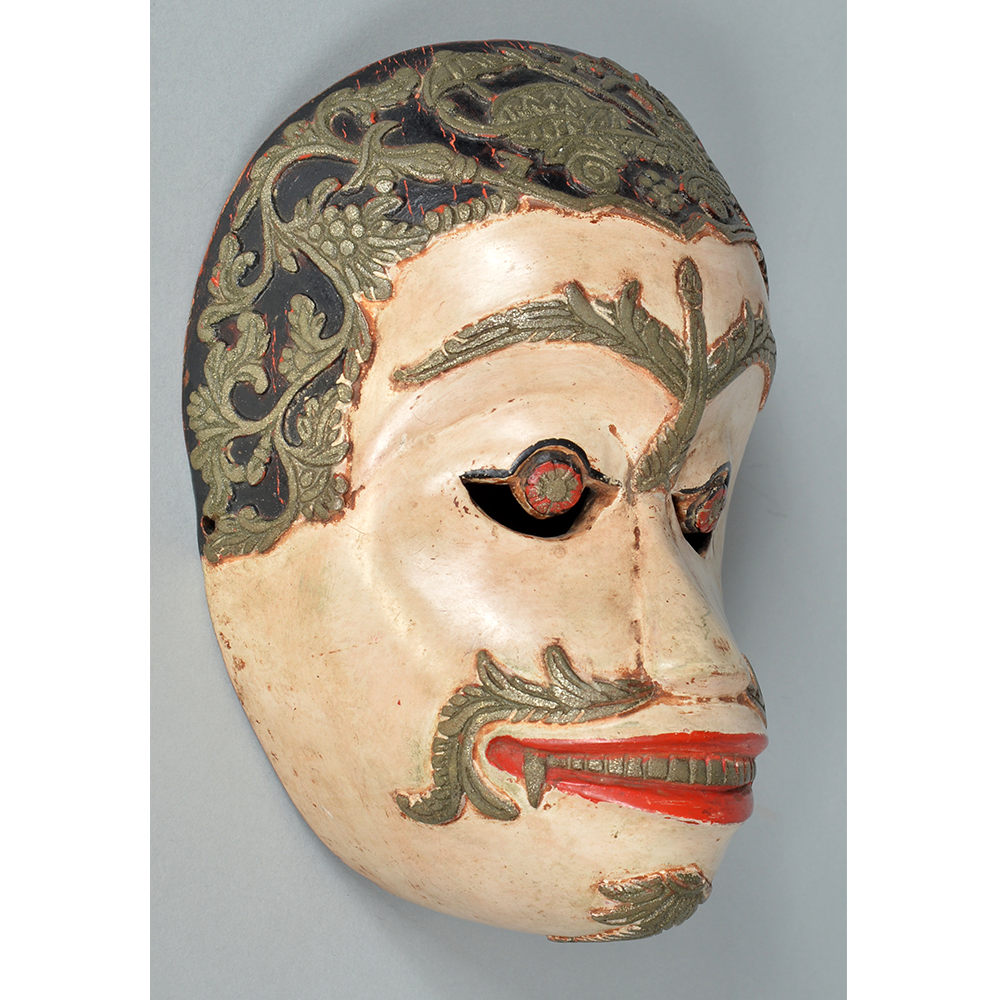
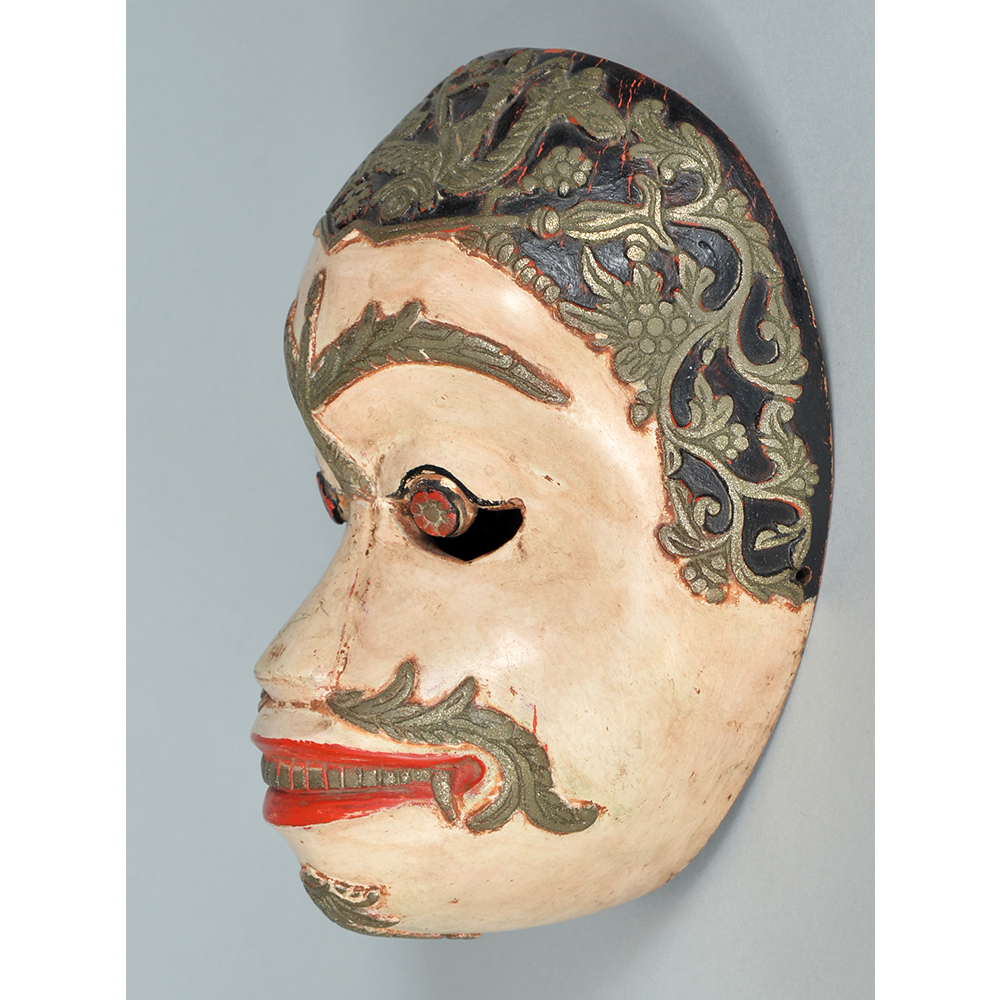
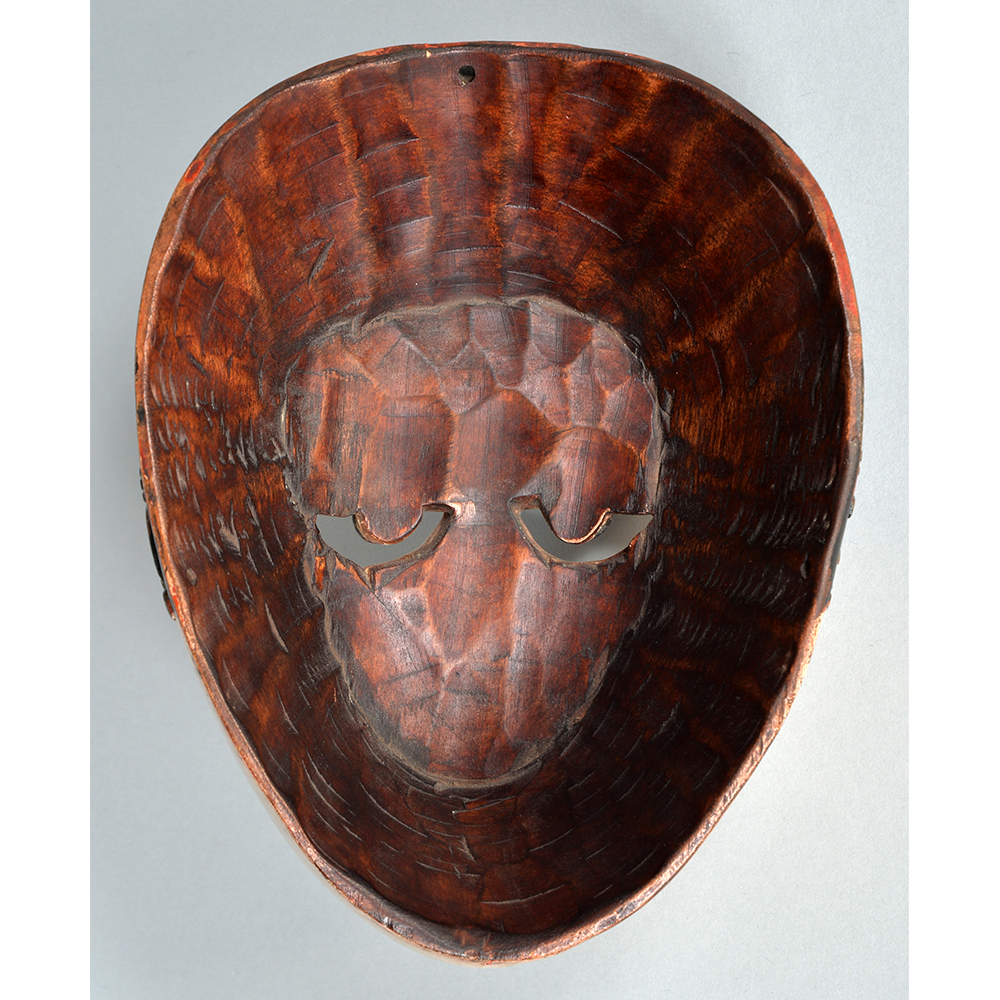
DESCRIPTION: Maximón (St. Simon) Mask
CATALOG ID: LAGT025
MAKER: Unknown
CEREMONY: Protection; Spirit Invocation
AGE: 1960s
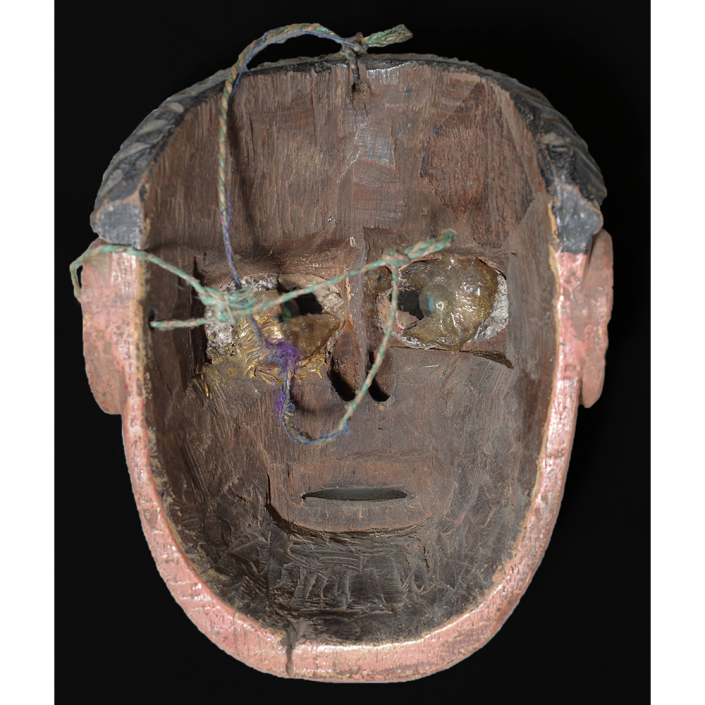
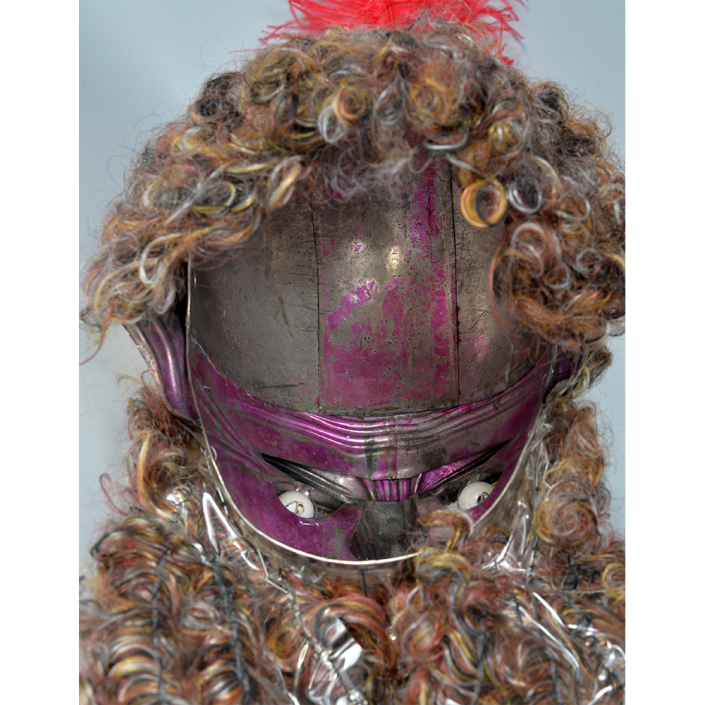
MAIN MATERIAL: wood
OTHER MATERIALS: paint; glass marbles; glue
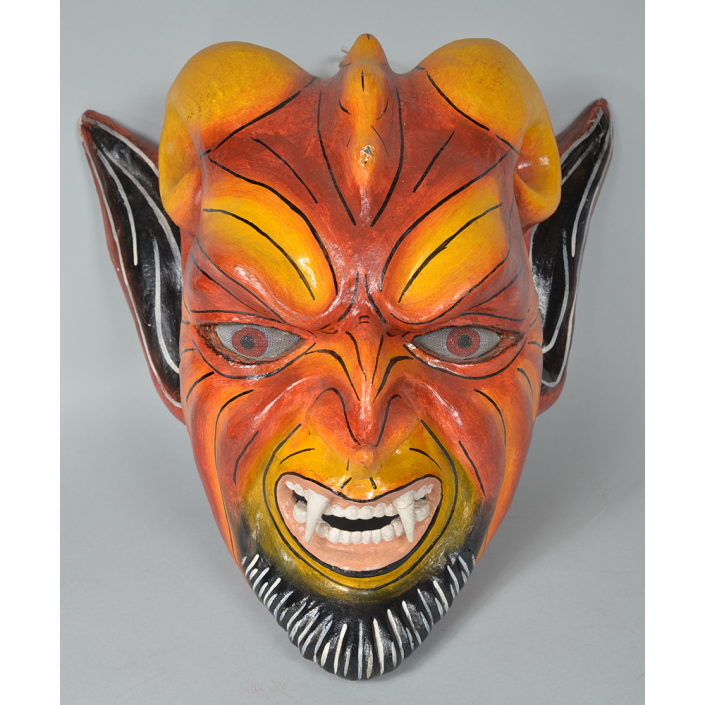
Maximón, a common Mayan pronunciation of St. Simón, is a complex and somewhat obscure figure. He seems to be the descendant of the pre-conquest Mayan god Mam, a sacred trickster whom the Catholic invaders associated with the Devil (as they did with nearly all local gods). He was worshiped in shrines as a protector of the village, but with the advent of Catholicism, the missionaries sought to convert the practice to saint worship, in this case worship of Simon the Zealot, reputedly a cousin of Jesus of Nazareth. Nonetheless, the image of Mam remains, as the Mayan descendants of Guatemala propitiate Maximón with offerings of liquor and cigarettes, along with the more traditional Catholic offerings of candles and flowers. The shrine typically moves from house to house annually in any given village, although some villages have more than one shrine.
For more on Guatemalan masks, see Jim Pieper, Guatemala’s Masks and Drama(University of New Mexico Press, 2006).